Double-stranded DNA translocase activity of transcription factor TFIIH and the mechanism of RNA polymerase II open complex formation
- PMID: 25775526
- PMCID: PMC4386358
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1417709112
Double-stranded DNA translocase activity of transcription factor TFIIH and the mechanism of RNA polymerase II open complex formation
Abstract
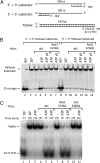
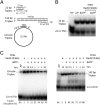
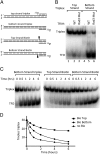
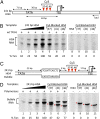
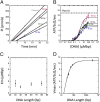
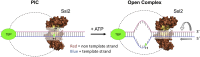
Formation of the RNA polymerase II (Pol II) open complex (OC) requires DNA unwinding mediated by the transcription factor TFIIH helicase-related subunit XPB/Ssl2. Because XPB/Ssl2 binds DNA downstream from the location of DNA unwinding, it cannot function using a conventional helicase mechanism. Here we show that yeast TFIIH contains an Ssl2-dependent double-stranded DNA translocase activity. Ssl2 tracks along one DNA strand in the 5' → 3' direction, implying it uses the nontemplate promoter strand to reel downstream DNA into the Pol II cleft, creating torsional strain and leading to DNA unwinding. Analysis of the Ssl2 and DNA-dependent ATPase activity of TFIIH suggests that Ssl2 has a processivity of approximately one DNA turn, consistent with the length of DNA unwound during transcription initiation. Our results can explain why maintaining the OC requires continuous ATP hydrolysis and the function of TFIIH in promoter escape. Our results also suggest that XPB/Ssl2 uses this translocase mechanism during DNA repair rather than physically wedging open damaged DNA.
Keywords: DNA helicase; DNA unwinding; transcription initiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of XPB/Ssl2 dsDNA Translocase Processivity in Transcription Start-site Scanning.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jul 9;433(14):166813. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166813. Epub 2021 Jan 13. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33453189 Free PMC article.
-
Ssl2/TFIIH function in transcription start site scanning by RNA polymerase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Elife. 2021 Oct 15;10:e71013. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71013. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34652274 Free PMC article.
-
TFIIH generates a six-base-pair open complex during RNAP II transcription initiation and start-site scanning.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017 Dec;24(12):1139-1145. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3500. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 29106413 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple roles of transcription/repair factor TFIIH.Trends Biochem Sci. 1996 Sep;21(9):346-50. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996. PMID: 8870499 Review.
-
Single-molecule approach for studying RNAP II transcription initiation using magnetic tweezers.Methods. 2019 Apr 15;159-160:35-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.03.010. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Methods. 2019. PMID: 30898685 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Age-related changes in Na, K-ATPase expression, subunit isoform selection and assembly in the stria vascularis lateral wall of mouse cochlea.Hear Res. 2018 Sep;367:59-73. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2018.07.006. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Hear Res. 2018. PMID: 30029086 Free PMC article.
-
XPA: DNA Repair Protein of Significant Clinical Importance.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 22;21(6):2182. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062182. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32235701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topical Treatment of Human Skin and Cultured Keratinocytes with High-Dose Spironolactone Reduces XPB Expression and Induces Toxicity.JID Innov. 2021 May 6;1(3):100023. doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2021.100023. eCollection 2021 Sep. JID Innov. 2021. PMID: 34909723 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of XPB/Ssl2 dsDNA Translocase Processivity in Transcription Start-site Scanning.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jul 9;433(14):166813. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166813. Epub 2021 Jan 13. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33453189 Free PMC article.
-
Everything at once: cryo-EM yields remarkable insights into human RNA polymerase II transcription.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021 Jul;28(7):540-543. doi: 10.1038/s41594-021-00613-6. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34131334 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sainsbury S, Niesser J, Cramer P. Structure and function of the initially transcribing RNA polymerase II-TFIIB complex. Nature. 2013;493(7432):437–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

