Accelerated pericyte degeneration and blood-brain barrier breakdown in apolipoprotein E4 carriers with Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 25757756
- PMCID: PMC4758554
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.44
Accelerated pericyte degeneration and blood-brain barrier breakdown in apolipoprotein E4 carriers with Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
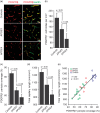
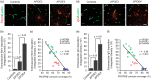
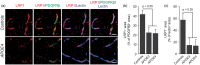
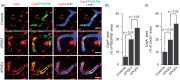
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) limits the entry of neurotoxic blood-derived products and cells into the brain that is required for normal neuronal functioning and information processing. Pericytes maintain the integrity of the BBB and degenerate in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The BBB is damaged in AD, particularly in individuals carrying apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4) gene, which is a major genetic risk factor for late-onset AD. The mechanisms underlying the BBB breakdown in AD remain, however, elusive. Here, we show accelerated pericyte degeneration in AD APOE4 carriers >AD APOE3 carriers >non-AD controls, which correlates with the magnitude of BBB breakdown to immunoglobulin G and fibrin. We also show accumulation of the proinflammatory cytokine cyclophilin A (CypA) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in pericytes and endothelial cells in AD (APOE4 >APOE3), previously shown to lead to BBB breakdown in transgenic APOE4 mice. The levels of the apoE lipoprotein receptor, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1), were similarly reduced in AD APOE4 and APOE3 carriers. Our data suggest that APOE4 leads to accelerated pericyte loss and enhanced activation of LRP1-dependent CypA–MMP-9 BBB-degrading pathway in pericytes and endothelial cells, which can mediate a greater BBB damage in AD APOE4 compared with AD APOE3 carriers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
APOE4 leads to blood-brain barrier dysfunction predicting cognitive decline.Nature. 2020 May;581(7806):71-76. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2247-3. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32376954 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E regulates the integrity of tight junctions in an isoform-dependent manner in an in vitro blood-brain barrier model.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 20;286(20):17536-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.225532. Epub 2011 Apr 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21471207 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E controls cerebrovascular integrity via cyclophilin A.Nature. 2012 May 16;485(7399):512-6. doi: 10.1038/nature11087. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22622580 Free PMC article.
-
ApoE4-mediated blood-brain barrier damage in Alzheimer's disease: Progress and prospects.Brain Res Bull. 2023 Jul;199:110670. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2023.110670. Epub 2023 May 22. Brain Res Bull. 2023. PMID: 37224887 Review.
-
APOE genotype-dependent pharmacogenetic responses to rapamycin for preventing Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Jun;139:104834. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104834. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32173556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Blood-brain barrier dysfunction as a potential therapeutic target for neurodegenerative disorders.Arch Pharm Res. 2021 May;44(5):487-498. doi: 10.1007/s12272-021-01332-8. Epub 2021 May 24. Arch Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 34028650 Review.
-
Physiological and Pathological Factors Affecting Drug Delivery to the Brain by Nanoparticles.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Jun;8(11):e2002085. doi: 10.1002/advs.202002085. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34105297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased Type I interferon signaling and brain endothelial barrier dysfunction in an experimental model of Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 1;12(1):16488. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20889-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36182964 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the brain mural cell transcriptome.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 11;6:35108. doi: 10.1038/srep35108. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27725773 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-vascular interactions drive myeloperoxidase accumulation in the brain in Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022 Mar 24;10(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01347-2. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022. PMID: 35331340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zlokovic BV. The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 2008; 57: 178–201. - PubMed
-
- Zlokovic B. Cerebrovascular permeability to peptides: manipulations of transport systems at the blood-brain barrier. Pharm Res 1995; 12: 1395–1406. - PubMed
-
- Zlokovic BV, Lipovac MN, Begley DJ, Davson H, Rakic L. Transport of leucine-enkephalin across the blood-brain barrier in the perfused guinea pig brain. J Neurochem 1987; 49: 310–315. - PubMed
-
- Zlokovic BV, Begley DJ, Chain-Eliash DG. Blood-brain barrier permeability to leucine-enkephalin,d-Alanine2-d-leucine5-enkephalin and their N-terminal amino acid (tyrosine). Brain Res 1985; 336: 125–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

