The autism-associated chromatin modifier CHD8 regulates other autism risk genes during human neurodevelopment
- PMID: 25752243
- PMCID: PMC4355952
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7404
The autism-associated chromatin modifier CHD8 regulates other autism risk genes during human neurodevelopment
Abstract
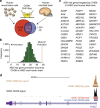
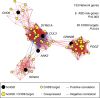
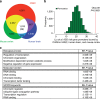
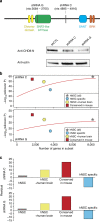
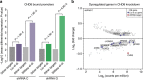
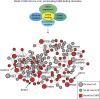
Recent studies implicate chromatin modifiers in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) through the identification of recurrent de novo loss of function mutations in affected individuals. ASD risk genes are co-expressed in human midfetal cortex, suggesting that ASD risk genes converge in specific regulatory networks during neurodevelopment. To elucidate such networks, we identify genes targeted by CHD8, a chromodomain helicase strongly associated with ASD, in human midfetal brain, human neural stem cells (hNSCs) and embryonic mouse cortex. CHD8 targets are strongly enriched for other ASD risk genes in both human and mouse neurodevelopment, and converge in ASD-associated co-expression networks in human midfetal cortex. CHD8 knockdown in hNSCs results in dysregulation of ASD risk genes directly targeted by CHD8. Integration of CHD8-binding data into ASD risk models improves detection of risk genes. These results suggest loss of CHD8 contributes to ASD by perturbing an ancient gene regulatory network during human brain development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The autism-associated gene chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 8 (CHD8) regulates noncoding RNAs and autism-related genes.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 May 19;5(5):e568. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.62. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25989142 Free PMC article.
-
CHD8 regulates neurodevelopmental pathways associated with autism spectrum disorder in neural progenitors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Oct 21;111(42):E4468-77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1405266111. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25294932 Free PMC article.
-
The complex etiology of autism spectrum disorder due to missense mutations of CHD8.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Jul;29(7):2145-2160. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02491-y. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38438524
-
Mutations and Modeling of the Chromatin Remodeler CHD8 Define an Emerging Autism Etiology.Front Neurosci. 2015 Dec 17;9:477. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00477. eCollection 2015. Front Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26733790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mechanisms of CHD8 in Neurodevelopment and Autism Spectrum Disorders.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jul 26;12(8):1133. doi: 10.3390/genes12081133. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440307 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetics and epigenetics of autism spectrum disorder-current evidence in the field.J Appl Genet. 2019 Feb;60(1):37-47. doi: 10.1007/s13353-018-00480-w. Epub 2019 Jan 10. J Appl Genet. 2019. PMID: 30627967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive literature data-mining analysis reveals a broad genetic network functionally associated with autism spectrum disorder.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Nov;42(5):2353-2362. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3845. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30226572 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling pathways in autism spectrum disorder: mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jul 11;7(1):229. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01081-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35817793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-localization between Sequence Constraint and Epigenomic Information Improves Interpretation of Whole-Genome Sequencing Data.Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Apr 2;106(4):513-524. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.03.003. Am J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 32243819 Free PMC article.
-
Damaging de novo mutations diminish motor skills in children on the autism spectrum.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 20;115(8):E1859-E1866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1715427115. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29434036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Devlin B. & Scherer S. W. Genetic architecture in autism spectrum disorder. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 22, 229–237 (2012) . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

