Evasion of anti-growth signaling: A key step in tumorigenesis and potential target for treatment and prophylaxis by natural compounds
- PMID: 25749195
- PMCID: PMC4561219
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.02.005
Evasion of anti-growth signaling: A key step in tumorigenesis and potential target for treatment and prophylaxis by natural compounds
Abstract
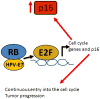
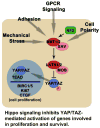
The evasion of anti-growth signaling is an important characteristic of cancer cells. In order to continue to proliferate, cancer cells must somehow uncouple themselves from the many signals that exist to slow down cell growth. Here, we define the anti-growth signaling process, and review several important pathways involved in growth signaling: p53, phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), retinoblastoma protein (Rb), Hippo, growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15), AT-rich interactive domain 1A (ARID1A), Notch, insulin-like growth factor (IGF), and Krüppel-like factor 5 (KLF5) pathways. Aberrations in these processes in cancer cells involve mutations and thus the suppression of genes that prevent growth, as well as mutation and activation of genes involved in driving cell growth. Using these pathways as examples, we prioritize molecular targets that might be leveraged to promote anti-growth signaling in cancer cells. Interestingly, naturally occurring phytochemicals found in human diets (either singly or as mixtures) may promote anti-growth signaling, and do so without the potentially adverse effects associated with synthetic chemicals. We review examples of naturally occurring phytochemicals that may be applied to prevent cancer by antagonizing growth signaling, and propose one phytochemical for each pathway. These are: epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) for the Rb pathway, luteolin for p53, curcumin for PTEN, porphyrins for Hippo, genistein for GDF15, resveratrol for ARID1A, withaferin A for Notch and diguelin for the IGF1-receptor pathway. The coordination of anti-growth signaling and natural compound studies will provide insight into the future application of these compounds in the clinical setting.
Keywords: Anti-growth signaling; Cancer prevention; Hallmark of cancer; Reversible and irreversible evasion; Tumor suppressor.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gene methylation in gastric cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23669186 Review.
-
Klf5 deletion promotes Pten deletion-initiated luminal-type mouse prostate tumors through multiple oncogenic signaling pathways.Neoplasia. 2014 Nov 20;16(11):883-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.09.006. eCollection 2014 Nov. Neoplasia. 2014. PMID: 25425963 Free PMC article.
-
Growth differentiation factor-15: a p53- and demethylation-upregulating gene represses cell proliferation, invasion, and tumorigenesis in bladder carcinoma cells.Sci Rep. 2015 Aug 7;5:12870. doi: 10.1038/srep12870. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26249737 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating tumor suppressor genes: post-translational modifications.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Jun 10;5(1):90. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0196-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32532965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in malignant transformation and drug resistance.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2006;46:249-79. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2006.01.004. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2006. PMID: 16854453
Cited by
-
Ursolic Acid's Alluring Journey: One Triterpenoid vs. Cancer Hallmarks.Molecules. 2023 Dec 1;28(23):7897. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237897. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38067626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of the IGF Axis.Cells. 2019 Aug 14;8(8):895. doi: 10.3390/cells8080895. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31416218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vernonia amygdalina Delile Induces Apoptotic Effects of PC3 Cells: Implication in the Prevention of Prostate Cancer.J Biomed Res Environ Sci. 2022 Oct;3(9):1118-1124. doi: 10.37871/jbres1564. Epub 2022 Sep 30. J Biomed Res Environ Sci. 2022. PMID: 36578651 Free PMC article.
-
Biological and toxicological evaluation of Rhus trilobata Nutt. (Anacardiaceae) used traditionally in mexico against cancer.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Jul 1;19(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2566-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31262287 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Compounds as Modulators of Cell Cycle Arrest: Application for Anticancer Chemotherapies.Curr Genomics. 2017 Apr;18(2):106-131. doi: 10.2174/1389202917666160808125645. Curr Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28367072 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Haddad RI, Shin DM. Recent advances in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(11):1143–54. - PubMed
-
- Hahn WC, Weinberg RA. Rules for making human tumor cells. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(20):1593–603. - PubMed
-
- Lundberg AS, Randell SH, Stewart SA, Elenbaas B, et al. Immortalization and transformation of primary human airway epithelial cells by gene transfer. Oncogene. 2002;21(29):4577–86. - PubMed
-
- Kohno T, Yokota J. How many tumor suppressor genes are involved in human lung carcinogenesis? Carcinogenesis. 1999;20(8):1403–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

