γδ T cells confer protection against murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV)
- PMID: 25747674
- PMCID: PMC4352080
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004702
γδ T cells confer protection against murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV)
Abstract
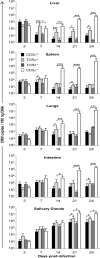
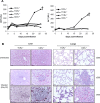
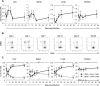
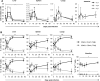
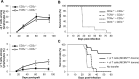
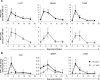
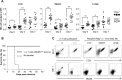
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a leading infectious cause of morbidity in immune-compromised patients. γδ T cells have been involved in the response to CMV but their role in protection has not been firmly established and their dependency on other lymphocytes has not been addressed. Using C57BL/6 αβ and/or γδ T cell-deficient mice, we here show that γδ T cells are as competent as αβ T cells to protect mice from CMV-induced death. γδ T cell-mediated protection involved control of viral load and prevented organ damage. γδ T cell recovery by bone marrow transplant or adoptive transfer experiments rescued CD3ε-/- mice from CMV-induced death confirming the protective antiviral role of γδ T cells. As observed in humans, different γδ T cell subsets were induced upon CMV challenge, which differentiated into effector memory cells. This response was observed in the liver and lungs and implicated both CD27+ and CD27- γδ T cells. NK cells were the largely preponderant producers of IFNγ and cytotoxic granules throughout the infection, suggesting that the protective role of γδ T cells did not principally rely on either of these two functions. Finally, γδ T cells were strikingly sufficient to fully protect Rag-/-γc-/- mice from death, demonstrating that they can act in the absence of B and NK cells. Altogether our results uncover an autonomous protective antiviral function of γδ T cells, and open new perspectives for the characterization of a non classical mode of action which should foster the design of new γδ T cell based therapies, especially useful in αβ T cell compromised patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long-lived central memory γδ T cells confer protection against murine cytomegalovirus reinfection.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jul 8;20(7):e1010785. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010785. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38976755 Free PMC article.
-
Control of murine cytomegalovirus infection by γδ T cells.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Feb 6;11(2):e1004481. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004481. eCollection 2015 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25658831 Free PMC article.
-
Vgamma1+ gammadelta T cells play protective roles at an early phase of murine cytomegalovirus infection through production of interferon-gamma.Immunology. 2000 Feb;99(2):187-94. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00938.x. Immunology. 2000. PMID: 10692035 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the Role of γδ T Cells in Anti-CMV Immune Response after Transplantation.Viruses. 2021 May 29;13(6):1031. doi: 10.3390/v13061031. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34072610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
At the Bench: Preclinical rationale for exploiting NK cells and γδ T lymphocytes for the treatment of high-risk leukemias.J Leukoc Biol. 2013 Dec;94(6):1123-39. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0613312. Epub 2013 Oct 9. J Leukoc Biol. 2013. PMID: 24108703 Review.
Cited by
-
Increase in liver γδ T cells with concurrent augmentation of IFN-β production during the early stages of a mouse model of acute experimental hepatitis B virus infection.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Jan;19(1):67-78. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8197. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 31853274 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Model of Cytomegalovirus Disease and Immunotherapy in the Immunocompromised Host: Predictions for Medical Translation that Survived the "Test of Time".Viruses. 2018 Dec 6;10(12):693. doi: 10.3390/v10120693. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30563202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The T-cell Response to Epstein-Barr Virus-New Tricks From an Old Dog.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 18;10:2193. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02193. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31620125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue-Resident Innate and Innate-Like Lymphocyte Responses to Viral Infection.Viruses. 2019 Mar 19;11(3):272. doi: 10.3390/v11030272. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30893756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct phenotype and function of circulating Vδ1+ and Vδ2+ γδT-cells in acute and chronic hepatitis B.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Apr 18;15(4):e1007715. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007715. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30998783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Broers AE, van Der Holt R, van Esser JW, Gratama JW, Henzen-Logmans S, et al. (2000) Increased transplant-related morbidity and mortality in CMV-seropositive patients despite highly effective prevention of CMV disease after allogeneic T-cell-depleted stem cell transplantation. Blood 95: 2240–2245. - PubMed
-
- Craddock C, Szydlo RM, Dazzi F, Olavarria E, Cwynarski K, et al. (2001) Cytomegalovirus seropositivity adversely influences outcome after T-depleted unrelated donor transplant in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia: the case for tailored graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis. Br J Haematol 112: 228–236. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt-Hieber M, Labopin M, Beelen D, Volin L, Ehninger G, et al. (2013) CMV serostatus has still an important prognostic impact in de novo acute leukemia patients after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a report from the acute leukemia working party of EBMT. Blood 122: 3359–3364. 10.1182/blood-2013-05-499830 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

