Fatty acid elongase 7 catalyzes lipidome remodeling essential for human cytomegalovirus replication
- PMID: 25732827
- PMCID: PMC4354725
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.02.003
Fatty acid elongase 7 catalyzes lipidome remodeling essential for human cytomegalovirus replication
Abstract
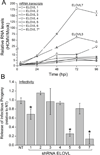
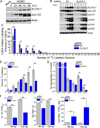
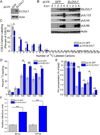
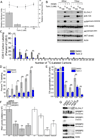
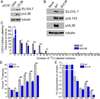
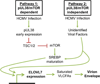
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection rewires host-cell metabolism, upregulating flux from glucose into acetyl-CoA to feed fatty acid metabolism, with saturated very-long-chain fatty acids (VLFCAs) required for production of infectious virion progeny. The human genome encodes seven elongase enzymes (ELOVL) that extend long-chain fatty acids into VLCFA. Here, we identify ELOVL7 as pivotal for HCMV infection. HCMV induces ELOVL7 by more than 150-fold. This induction is dependent on mTOR and SREBP-1. ELOVL7 knockdown or mTOR inhibition impairs HCMV-induced fatty acid elongation, HCMV particle release, and infectivity per particle. ELOVL7 overexpression enhances HCMV replication. During HCMV infection, mTOR activity is maintained by the viral protein pUL38. Expression of pUL38 is sufficient to induce ELOVL7, and pUL38-deficient virus is partially defective in ELOVL7 induction and fatty acid elongation. Thus, through its ability to modulate mTOR and SREBP-1, HCMV induces ELOVL7 to synthesize the saturated VLCFA required for efficient virus replication.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Uses a Host Stress Response To Balance the Elongation of Saturated/Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acids.mBio. 2021 May 4;12(3):e00167-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00167-21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33947752 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus pUL37x1 Is Important for Remodeling of Host Lipid Metabolism.J Virol. 2019 Oct 15;93(21):e00843-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00843-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31391267 Free PMC article.
-
Novel lipogenic enzyme ELOVL7 is involved in prostate cancer growth through saturated long-chain fatty acid metabolism.Cancer Res. 2009 Oct 15;69(20):8133-40. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0775. Epub 2009 Oct 13. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19826053
-
[Interrelationship between human cytomegalovirus infection and chemokine].Nihon Rinsho. 1998 Jan;56(1):69-74. Nihon Rinsho. 1998. PMID: 9465667 Review. Japanese.
-
Modulation of host cell stress responses by human cytomegalovirus.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;325:263-79. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-77349-8_15. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18637511 Review.
Cited by
-
LipidSig: a web-based tool for lipidomic data analysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jul 2;49(W1):W336-W345. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab419. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34048582 Free PMC article.
-
Four-dimensional analyses show that replication compartments are clonal factories in which Epstein-Barr viral DNA amplification is coordinated.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Dec 3;116(49):24630-24638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1913992116. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31744871 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Molecular Mechanisms and Remdesivir Treatment for Acute Respiratory Syndrome Corona Virus 2 Infection/COVID 19 Through RNA Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2021 Dec 23;15:11779322211067365. doi: 10.1177/11779322211067365. eCollection 2021. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2021. PMID: 34992355 Free PMC article.
-
Disturbance in Plasma Metabolic Profile in Different Types of Human Cytomegalovirus-Induced Liver Injury in Infants.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 16;7(1):15696. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16051-8. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29146975 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in CMV tropism, latency, and diagnosis during aging.Geroscience. 2017 Jun;39(3):251-259. doi: 10.1007/s11357-017-9985-7. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Geroscience. 2017. PMID: 28681110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alwine JC. Modulation of host cell stress responses by human cytomegalovirus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;325:263–279. - PubMed
-
- Bissinger AL, Sinzger C, Kaiserling E, Jahn G. Human cytomegalovirus as a direct pathogen: correlation of multiorgan involvement and cell distribution with clinical and pathological findings in a case of congenital inclusion disease. Journal of medical virology. 2002;67:200–206. - PubMed
-
- Britt W. Manifestations of human cytomegalovirus infection: proposed mechanisms of acute and chronic disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;325:417–470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

