HITS-CLIP analysis uncovers a link between the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57 protein and host pre-mRNA metabolism
- PMID: 25710169
- PMCID: PMC4339584
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004652
HITS-CLIP analysis uncovers a link between the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57 protein and host pre-mRNA metabolism
Abstract
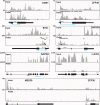
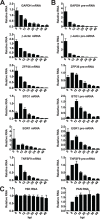
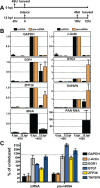
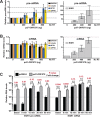
The Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is an oncogenic virus that causes Kaposi's sarcoma, primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), and some forms of multicentric Castleman's disease. The KSHV ORF57 protein is a conserved posttranscriptional regulator of gene expression that is essential for virus replication. ORF57 is multifunctional, but most of its activities are directly linked to its ability to bind RNA. We globally identified virus and host RNAs bound by ORF57 during lytic reactivation in PEL cells using high-throughput sequencing of RNA isolated by cross-linking immunoprecipitation (HITS-CLIP). As expected, ORF57-bound RNA fragments mapped throughout the KSHV genome, including the known ORF57 ligand PAN RNA. In agreement with previously published ChIP results, we observed that ORF57 bound RNAs near the oriLyt regions of the genome. Examination of the host RNA fragments revealed that a subset of the ORF57-bound RNAs was derived from transcript 5' ends. The position of these 5'-bound fragments correlated closely with the 5'-most exon-intron junction of the pre-mRNA. We selected four candidates (BTG1, EGR1, ZFP36, and TNFSF9) and analyzed their pre-mRNA and mRNA levels during lytic phase. Analysis of both steady-state and newly made RNAs revealed that these candidate ORF57-bound pre-mRNAs persisted for longer periods of time throughout infection than control RNAs, consistent with a role for ORF57 in pre-mRNA metabolism. In addition, exogenous expression of ORF57 was sufficient to increase the pre-mRNA levels and, in one case, the mRNA levels of the putative ORF57 targets. These results demonstrate that ORF57 interacts with specific host pre-mRNAs during lytic reactivation and alters their processing, likely by stabilizing pre-mRNAs. These data suggest that ORF57 is involved in modulating host gene expression in addition to KSHV gene expression during lytic reactivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein-RNA Interactome Analysis Reveals Wide Association of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus ORF57 with Host Noncoding RNAs and Polysomes.J Virol. 2022 Feb 9;96(3):e0178221. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01782-21. Epub 2021 Nov 17. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34787459 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Knockout and In Situ Inversion of the ORF57 Gene from All Copies of the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Genome in BCBL-1 Cells.J Virol. 2019 Oct 15;93(21):e00628-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00628-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31413125 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Fine-Tunes the Temporal Expression of Late Genes by Manipulating a Host RNA Quality Control Pathway.J Virol. 2020 Jul 1;94(14):e00287-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00287-20. Print 2020 Jul 1. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32376621 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV ORF57, a protein of many faces.Viruses. 2015 Feb 10;7(2):604-33. doi: 10.3390/v7020604. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25674768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The KSHV RNA regulator ORF57: target specificity and its role in the viral life cycle.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Mar-Apr;7(2):173-85. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1323. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 26769399 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective Degradation of Host RNA Polymerase II Transcripts by Influenza A Virus PA-X Host Shutoff Protein.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Feb 5;12(2):e1005427. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005427. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 26849127 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Sequencing in the Understanding of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV) Biology.Viruses. 2016 Mar 31;8(4):92. doi: 10.3390/v8040092. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27043613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Characterization of the Physiological Gene Targets of the Essential Lytic Replicative Epstein-Barr Virus SM Protein.J Virol. 2015 Nov 11;90(3):1206-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02393-15. Print 2016 Feb 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26559842 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the expression and functions of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus long noncoding PAN RNA.Virus Res. 2016 Jan 2;212:53-63. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.06.012. Epub 2015 Jun 21. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 26103097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minute Virus of Canines NP1 Protein Interacts with the Cellular Factor CPSF6 To Regulate Viral Alternative RNA Processing.J Virol. 2019 Jan 4;93(2):e01530-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01530-18. Print 2019 Jan 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30355695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Staudt MR, Dittmer DP (2003) Viral latent proteins as targets for Kaposi“s sarcoma and Kaposi”s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) induced lymphoma. Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord 3: 129–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

