LIMK1 regulates long-term memory and synaptic plasticity via the transcriptional factor CREB
- PMID: 25645926
- PMCID: PMC4372699
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01263-14
LIMK1 regulates long-term memory and synaptic plasticity via the transcriptional factor CREB
Abstract
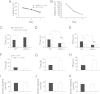
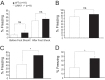
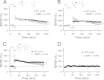
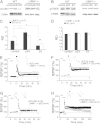
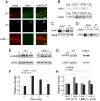
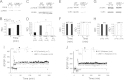
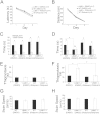
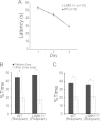
Deletion of the LIMK1 gene is associated with Williams syndrome, a unique neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by severe defects in visuospatial cognition and long-term memory (LTM). However, whether LIMK1 contributes to these deficits remains elusive. Here, we show that LIMK1-knockout (LIMK1(-/-)) mice are drastically impaired in LTM but not short-term memory (STM). In addition, LIMK1(-/-) mice are selectively defective in late-phase long-term potentiation (L-LTP), a form of long-lasting synaptic plasticity specifically required for the formation of LTM. Furthermore, we show that LIMK1 interacts and regulates the activity of cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB), an extensively studied transcriptional factor critical for LTM. Importantly, both L-LTP and LTM deficits in LIMK1(-/-) mice are rescued by increasing the activity of CREB. These results provide strong evidence that LIMK1 deletion is sufficient to lead to an LTM deficit and that this deficit is attributable to CREB hypofunction. Our study has identified a direct gene-phenotype link in mice and provides a potential strategy to restore LTM in patients with Williams syndrome through the enhancement of CREB activity in the adult brain.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
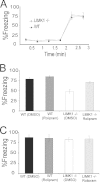
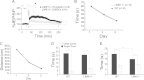
Similar articles
-
The p75 Neurotrophin Receptor Is an Essential Mediator of Impairments in Hippocampal-Dependent Associative Plasticity and Memory Induced by Sleep Deprivation.J Neurosci. 2019 Jul 10;39(28):5452-5465. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2876-18.2019. Epub 2019 May 13. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31085607 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of CREB-mediated transcription enhances both short- and long-term memory.J Neurosci. 2011 Jun 15;31(24):8786-802. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3257-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21677163 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of LIMK1 in hippocampal excitatory neurons improves synaptic plasticity and social recognition memory in APP/PS1 mice.Mol Brain. 2021 Jul 27;14(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s13041-021-00833-3. Mol Brain. 2021. PMID: 34315506 Free PMC article.
-
LIM-Kinases in Synaptic Plasticity, Memory, and Brain Diseases.Cells. 2021 Aug 13;10(8):2079. doi: 10.3390/cells10082079. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF-induced local protein synthesis and synaptic plasticity.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:639-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23602987 Review.
Cited by
-
Rho-associated kinases contribute to the regulation of tau phosphorylation and amyloid metabolism during neuronal plasticity.Pharmacol Rep. 2021 Oct;73(5):1303-1314. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00279-3. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Pharmacol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34060063
-
LIM Kinases, LIMK1 and LIMK2, Are Crucial Node Actors of the Cell Fate: Molecular to Pathological Features.Cells. 2023 Mar 4;12(5):805. doi: 10.3390/cells12050805. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Aspects of LIMK Regulation and Pharmacology.Cells. 2022 Jan 2;11(1):142. doi: 10.3390/cells11010142. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35011704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Up-regulation of miR-106a targets LIMK1 and contributes to cognitive impairment induced by isoflurane anesthesia in mice.Genes Genomics. 2020 Apr;42(4):405-412. doi: 10.1007/s13258-019-00913-8. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Genes Genomics. 2020. PMID: 31933141
-
LIM kinases: cofilin and beyond.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 20;8(25):41749-41763. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16978. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28445157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
