EZH2 inhibition sensitizes BRG1 and EGFR mutant lung tumours to TopoII inhibitors
- PMID: 25629630
- PMCID: PMC4393352
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14122
EZH2 inhibition sensitizes BRG1 and EGFR mutant lung tumours to TopoII inhibitors
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: EZH2 inhibition sensitizes BRG1 and EGFR mutant lung tumours to TopoII inhibitors.Nature. 2018 Nov;563(7732):E27. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0580-6. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30250255
Abstract
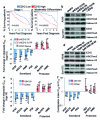
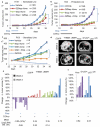
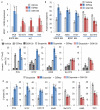
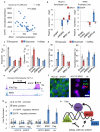
Non-small-cell lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Chemotherapies such as the topoisomerase II (TopoII) inhibitor etoposide effectively reduce disease in a minority of patients with this cancer; therefore, alternative drug targets, including epigenetic enzymes, are under consideration for therapeutic intervention. A promising potential epigenetic target is the methyltransferase EZH2, which in the context of the polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) is well known to tri-methylate histone H3 at lysine 27 (H3K27me3) and elicit gene silencing. Here we demonstrate that EZH2 inhibition has differential effects on the TopoII inhibitor response of non-small-cell lung cancers in vitro and in vivo. EGFR and BRG1 mutations are genetic biomarkers that predict enhanced sensitivity to TopoII inhibitor in response to EZH2 inhibition. BRG1 loss-of-function mutant tumours respond to EZH2 inhibition with increased S phase, anaphase bridging, apoptosis and TopoII inhibitor sensitivity. Conversely, EGFR and BRG1 wild-type tumours upregulate BRG1 in response to EZH2 inhibition and ultimately become more resistant to TopoII inhibitor. EGFR gain-of-function mutant tumours are also sensitive to dual EZH2 inhibition and TopoII inhibitor, because of genetic antagonism between EGFR and BRG1. These findings suggest an opportunity for precision medicine in the genetically complex disease of non-small-cell lung cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined inhibition of EZH2 and histone deacetylases as a potential epigenetic therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer cells.Cancer Sci. 2016 Jul;107(7):955-62. doi: 10.1111/cas.12957. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27116120 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2 inhibitors reverse resistance to gefitinib in primary EGFR wild-type lung cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2020 Dec 4;20(1):1189. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07667-7. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33276757 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic therapy with 3-deazaneplanocin A, an inhibitor of the histone methyltransferase EZH2, inhibits growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells.Lung Cancer. 2012 Nov;78(2):138-43. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Aug 25. Lung Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22925699 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting EZH2 and PRC2 dependence as novel anticancer therapy.Exp Hematol. 2015 Aug;43(8):698-712. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 May 28. Exp Hematol. 2015. PMID: 26027790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EZH2 as a potential target in cancer therapy.Epigenomics. 2014 Jun;6(3):341-51. doi: 10.2217/epi.14.23. Epigenomics. 2014. PMID: 25111487 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) in Transcriptional Regulation and Cancer.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016 Sep 1;6(9):a026575. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a026575. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016. PMID: 27449971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycomb Group (PcG) Proteins and Human Cancers: Multifaceted Functions and Therapeutic Implications.Med Res Rev. 2015 Nov;35(6):1220-67. doi: 10.1002/med.21358. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Med Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 26227500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Finding an easy way to harmonize: a review of advances in clinical research and combination strategies of EZH2 inhibitors.Clin Epigenetics. 2021 Mar 24;13(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01045-1. Clin Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 33761979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Many Roles of BAF (mSWI/SNF) and PBAF Complexes in Cancer.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016 Aug 1;6(8):a026930. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a026930. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016. PMID: 27413115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EZH2 endorses cell plasticity to non-small cell lung cancer cells facilitating mesenchymal to epithelial transition and tumour colonization.Oncogene. 2022 Jul;41(28):3611-3624. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02375-x. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35680984
References
-
- Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2011;61:69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107. - PubMed
-
- Zornosa C, et al. First-Line Systemic Therapy Practice Patterns and Concordance With NCCN Guidelines for Patients Diagnosed With Metastatic NSCLC Treated at NCCN Institutions. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. 2012;10:847–856. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, et al. Randomized phase II study of concurrent cisplatin/etoposide or paclitaxel/carboplatin and thoracic radiotherapy in patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2012;77:89–96. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.02.011. - PubMed
-
- Simon JA, Lange CA. Roles of the EZH2 histone methyltransferase in cancer epigenetics. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis. 2008;647:21–29. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.07.010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA166480/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA163677/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL125821/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA166480/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA122794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA154303/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL100402/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA163896/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA154303/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA163896/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA140594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090136/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

