Accurate transcriptome-wide prediction of microRNA targets and small interfering RNA off-targets with MIRZA-G
- PMID: 25628353
- PMCID: PMC4330396
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv050
Accurate transcriptome-wide prediction of microRNA targets and small interfering RNA off-targets with MIRZA-G
Erratum in
-
Accurate transcriptome-wide prediction of microRNA targets and small interfering RNA off-targets with MIRZA-G.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 15;43(18):9095. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv924. Epub 2015 Sep 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26365243 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
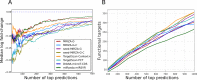
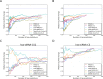
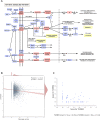
Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated knock-down is a widely used experimental approach to characterizing gene function. Although siRNAs are designed to guide the cleavage of perfectly complementary mRNA targets, acting similarly to microRNAs (miRNAs), siRNAs down-regulate the expression of hundreds of genes to which they have only partial complementarity. Prediction of these siRNA 'off-targets' remains difficult, due to the incomplete understanding of siRNA/miRNA-target interactions. Combining a biophysical model of miRNA-target interaction with structure and sequence features of putative target sites we developed a suite of algorithms, MIRZA-G, for the prediction of miRNA targets and siRNA off-targets on a genome-wide scale. The MIRZA-G variant that uses evolutionary conservation performs better than currently available methods in predicting canonical miRNA target sites and in addition, it predicts non-canonical miRNA target sites with similarly high accuracy. Furthermore, MIRZA-G variants predict siRNA off-target sites with an accuracy unmatched by currently available programs. Thus, MIRZA-G may prove instrumental in the analysis of data resulting from large-scale siRNA screens.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of putative miRNA binding sites and mRNA 3' ends as targets for siRNA-mediated gene knockdown.Oligonucleotides. 2009 Mar;19(1):41-52. doi: 10.1089/oli.2008.0154. Oligonucleotides. 2009. PMID: 19196098
-
MicroRNAs--targeting and target prediction.N Biotechnol. 2010 Jul 31;27(3):243-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2010.02.016. Epub 2010 Feb 26. N Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20219708 Review.
-
Identification and validation of miRNA target sites within nontraditional miRNA targets.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1206:53-67. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1369-5_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25240886
-
Analyses of a Glycine max degradome library identify microRNA targets and microRNAs that trigger secondary siRNA biogenesis.J Integr Plant Biol. 2013 Feb;55(2):160-76. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12002. J Integr Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23131131
-
Prediction of human microRNA targets.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;342:101-13. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-123-1:101. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16957370 Review.
Cited by
-
Population variation in miRNAs and isomiRs and their impact on human immunity to infection.Genome Biol. 2020 Jul 30;21(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02098-w. Genome Biol. 2020. PMID: 32731901 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA target prediction using thermodynamic and sequence curves.BMC Genomics. 2015 Nov 25;16:999. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1933-2. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26608597 Free PMC article.
-
Improving microRNA target prediction by modeling with unambiguously identified microRNA-target pairs from CLIP-ligation studies.Bioinformatics. 2016 May 1;32(9):1316-22. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw002. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 26743510 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of Functional MicroRNA Targeting.Mol Cells. 2023 Jan 31;46(1):21-32. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2023.2157. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Mol Cells. 2023. PMID: 36697234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Learning to Predict miRNA-mRNA Interactions from AGO CLIP Sequencing and CLASH Data.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Jul 20;12(7):e1005026. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005026. eCollection 2016 Jul. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27438777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huntzinger E., Izaurralde E. Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011;12:99–110. - PubMed
-
- Calin G.A., Croce C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2006;6:857–866. - PubMed
-
- Rajewsky N., Socci N.D. Computational identification of microRNA targets. Dev. Biol. 2004;267:529–535. - PubMed
-
- Lewis B.P., Burge C.B., Bartel D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

