PDK1 orchestrates early NK cell development through induction of E4BP4 expression and maintenance of IL-15 responsiveness
- PMID: 25624444
- PMCID: PMC4322053
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20141703
PDK1 orchestrates early NK cell development through induction of E4BP4 expression and maintenance of IL-15 responsiveness
Abstract
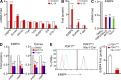
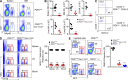
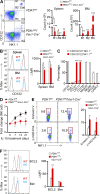
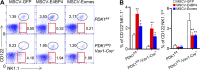
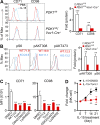
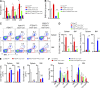
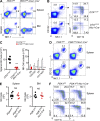
E4BP4, a circadian protein, is indispensable for NK cell development. It remains largely unknown which signal is required to induce E4BP4 expression and what effects it has during NK cell differentiation. Here, we reveal that PDK1, a kinase upstream of mTOR, connects IL-15 signaling to E4BP4. Early deletion of PDK1 caused a severe loss of NK cells and compromised antitumor activity in vivo. PDK1-deficient NK cells displayed much weaker IL-15-induced mTOR activation and E4BP4 induction, as well as remarkable reduction in CD122, a receptor subunit specifying NK cell responsiveness to IL-15. The phenotypes were partially reversible by ectopic expression of E4BP4 or bypassed activation of mTOR. We also determined that PDK1-mediated metabolic signaling was dispensable for NK cell terminal maturation and survival. Thus, we identify a role for PDK1 signaling as a key mediator in regulating E4BP4 expression during early NK cell development. Our findings underscore the importance of IL-15 self-responsiveness through a positive feedback loop that involves PDK1-mTOR-E4BP4-CD122 signaling.
© 2015 Yang et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Full Activation of Kinase Protein Kinase B by Phosphoinositide-Dependent Protein Kinase-1 and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 2 Is Required for Early Natural Killer Cell Development and Survival.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 9;11:617404. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.617404. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33633735 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor E4BP4 is not required for extramedullary pathways of NK cell development.J Immunol. 2014 Mar 15;192(6):2677-88. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302765. Epub 2014 Feb 17. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24534532 Free PMC article.
-
Stage-specific requirement of kinase PDK1 for NK cells development and activation.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Oct;26(10):1918-1928. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0263-8. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30622306 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Natural Killer Cell Homeostasis.Front Immunol. 2020 May 12;11:812. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00812. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32477340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of basic leucine zipper transcription factor E4BP4 in cancer: a review and update.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jan 9;51(1):91. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09079-9. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38193973 Review.
Cited by
-
Context-dependent T-BOX transcription factor family: from biology to targeted therapy.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jul 4;22(1):350. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01719-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38965548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional control of natural killer cell differentiation.Immunology. 2019 Feb;156(2):111-119. doi: 10.1111/imm.13017. Epub 2018 Nov 18. Immunology. 2019. PMID: 30450565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamical Analysis of the Regulatory Network Controlling Natural Killer Cells Differentiation.Front Physiol. 2018 Aug 2;9:1029. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01029. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30116200 Free PMC article.
-
Shared Transcriptional Control of Innate Lymphoid Cell and Dendritic Cell Development.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Oct 6;35:381-406. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100818-125403. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31283378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and maturation of natural killer cells.Curr Opin Immunol. 2016 Apr;39:82-9. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.01.007. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26845614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

