MBSTAR: multiple instance learning for predicting specific functional binding sites in microRNA targets
- PMID: 25614300
- PMCID: PMC4648438
- DOI: 10.1038/srep08004
MBSTAR: multiple instance learning for predicting specific functional binding sites in microRNA targets
Abstract
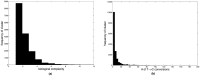
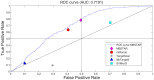
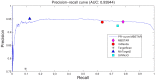
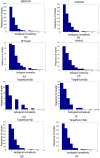
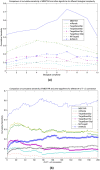
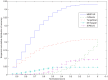
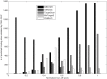
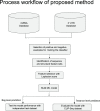
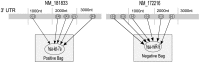
MicroRNA (miRNA) regulates gene expression by binding to specific sites in the 3'untranslated regions of its target genes. Machine learning based miRNA target prediction algorithms first extract a set of features from potential binding sites (PBSs) in the mRNA and then train a classifier to distinguish targets from non-targets. However, they do not consider whether the PBSs are functional or not, and consequently result in high false positive rates. This substantially affects the follow up functional validation by experiments. We present a novel machine learning based approach, MBSTAR (Multiple instance learning of Binding Sites of miRNA TARgets), for accurate prediction of true or functional miRNA binding sites. Multiple instance learning framework is adopted to handle the lack of information about the actual binding sites in the target mRNAs. Biologically validated 9531 interacting and 973 non-interacting miRNA-mRNA pairs are identified from Tarbase 6.0 and confirmed with PAR-CLIP dataset. It is found that MBSTAR achieves the highest number of binding sites overlapping with PAR-CLIP with maximum F-Score of 0.337. Compared to the other methods, MBSTAR also predicts target mRNAs with highest accuracy. The tool and genome wide predictions are available at http://www.isical.ac.in/~bioinfo_miu/MBStar30.htm.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TargetMiner: microRNA target prediction with systematic identification of tissue-specific negative examples.Bioinformatics. 2009 Oct 15;25(20):2625-31. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp503. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19692556
-
The Limitations of Existing Approaches in Improving MicroRNA Target Prediction Accuracy.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1617:133-158. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7046-9_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28540682
-
STarMir Tools for Prediction of microRNA Binding Sites.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1490:73-82. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6433-8_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27665594 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA target finding by comparative genomics.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1097:457-76. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-709-9_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24639172 Review.
-
Prediction of human microRNA targets.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;342:101-13. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-123-1:101. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16957370 Review.
Cited by
-
4acCPred: Weakly supervised prediction of N 4-acetyldeoxycytosine DNA modification from sequences.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 Oct 14;30:337-345. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.10.004. eCollection 2022 Dec 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 36381577 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Detection of MicroRNA Targets.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2257:187-209. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1170-8_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34432280
-
In silico methods for predicting functional synonymous variants.Genome Biol. 2023 May 22;24(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-02966-1. Genome Biol. 2023. PMID: 37217943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling DTA by Combining Multiple-Instance Learning with a Private-Public Mechanism.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 22;23(19):11136. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911136. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232434 Free PMC article.
-
miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 18;13(10):e0206239. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206239. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30335862 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

