Exosome delivered anticancer drugs across the blood-brain barrier for brain cancer therapy in Danio rerio
- PMID: 25609010
- PMCID: PMC4520542
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-014-1593-y
Exosome delivered anticancer drugs across the blood-brain barrier for brain cancer therapy in Danio rerio
Abstract
Purpose: The blood-brain barrier (BBB) essentially restricts therapeutic drugs from entering into the brain. This study tests the hypothesis that brain endothelial cell derived exosomes can deliver anticancer drug across the BBB for the treatment of brain cancer in a zebrafish (Danio rerio) model.
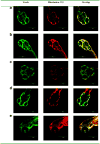
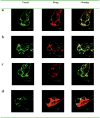
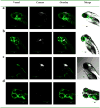
Materials and methods: Four types of exosomes were isolated from brain cell culture media and characterized by particle size, morphology, total protein, and transmembrane protein markers. Transport mechanism, cell uptake, and cytotoxicity of optimized exosome delivery system were tested. Brain distribution of exosome delivered anticancer drugs was evaluated using transgenic zebrafish TG (fli1: GFP) embryos and efficacies of optimized formations were examined in a xenotransplanted zebrafish model of brain cancer model.
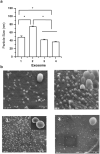
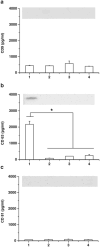
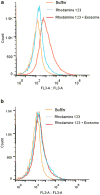
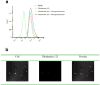
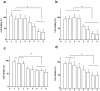
Results: Four exosomes in 30-100 diameters showed different morphologies and exosomes derived from brain endothelial cells expressed more CD63 tetraspanins transmembrane proteins. Optimized exosomes increased the uptake of fluorescent marker via receptor mediated endocytosis and cytotoxicity of anticancer drugs in cancer cells. Images of the zebrafish showed exosome delivered anticancer drugs crossed the BBB and entered into the brain. In the brain cancer model, exosome delivered anticancer drugs significantly decreased fluorescent intensity of xenotransplanted cancer cells and tumor growth marker.
Conclusions: Brain endothelial cell derived exosomes could be potentially used as a carrier for brain delivery of anticancer drug for the treatment of brain cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Delivery of Small Interfering RNA to Inhibit Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Zebrafish Using Natural Brain Endothelia Cell-Secreted Exosome Nanovesicles for the Treatment of Brain Cancer.AAPS J. 2017 Mar;19(2):475-486. doi: 10.1208/s12248-016-0015-y. Epub 2016 Nov 23. AAPS J. 2017. PMID: 27882487
-
Microvesicle- and exosome-mediated drug delivery enhances the cytotoxicity of Paclitaxel in autologous prostate cancer cells.J Control Release. 2015 Dec 28;220(Pt B):727-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.09.031. Epub 2015 Sep 24. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 26390807
-
Inhibition of Glioma Cells' Proliferation by Doxorubicin-Loaded Exosomes via Microfluidics.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Oct 28;15:8331-8343. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S263956. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33149579 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Brain Tumors with Nanomedicines: Overcoming Blood Brain Barrier Challenges.Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2018;13(2):110-119. doi: 10.2174/1574884713666180412150153. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29651960 Review.
-
Transporter-based delivery of anticancer drugs to the brain: improving brain penetration by minimizing drug efflux at the blood-brain barrier.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(10):1499-509. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990458. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 23789953 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in innovative exosome-technology for real time monitoring of viable drugs in clinical translation, prognosis and treatment response.Oncotarget. 2021 May 25;12(11):1029-1031. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27927. eCollection 2021 May 25. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 34084276 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Recent Advances in the Use of Exosomes in Sjögren's Syndrome.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 6;11:1509. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01509. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32903777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles: Emerging tools as therapeutic agent carriers.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Oct;12(10):3822-3842. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.05.002. Epub 2022 May 11. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 36213541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization and optimization of polymer-polymer aqueous two-phase systems for the isolation and purification of CaCo2 cell-derived exosomes.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 2;17(9):e0273243. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273243. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36054216 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of atorvastatin loaded exosome as an anti-glioblastoma carrier to induce apoptosis of U87 cancer cells in 3D culture model.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020 Aug 4;23:100792. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100792. eCollection 2020 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020. PMID: 32793818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lai RC, Yeo RW, Tan KH, Lim SK. Exosomes for drug delivery—a novel application for the mesenchymal stem cell. Biotechnol Adv. 2012 - PubMed
-
- van den Boorn JG, Dassler J, Coch C, Schlee M, Hartmann G. Exosomes as nucleic acid nanocarriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65:331–5. - PubMed
-
- Lakhaland S, Wood MJ. Exosome nanotechnology: an emerging paradigm shift in drug delivery: exploitation of exosome nanovesicles for systemic in vivo delivery of RNAi heralds new horizons for drug delivery across biological barriers. BioEssays News Rev Mol Cell Dev Biol. 2011;33:737–41. - PubMed
-
- Lai RC, Yeo RW, Tan KH, Lim SK. Exosomes for drug delivery—a novel application for the mesenchymal stem cell. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31:543–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

