Utility of kynurenic acid for non-invasive detection of metastatic spread to lymph nodes in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 25589891
- PMCID: PMC4293180
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.7541
Utility of kynurenic acid for non-invasive detection of metastatic spread to lymph nodes in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Kynurenic acid (KYNA) is a side-stream product of the kynurenine metabolic pathway that plays a controversial role in malignancies either enabling escape of malignant cells from immune surveillance or exerting antiproliferative effect on cancer cells, and is associated with differences in invasiveness related to metastatic spread to lymph nodes in lung cancer. Nodal involvement is a significant negative prognostic factor usually considered a contraindication for primary surgical resection.
Objective: To assess potential value of circulating KYNA for non-invasive identification of patients with metastatic lymph nodes (N+) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: KYNA level in venous blood serum was determined with use of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) in 312 subjects including 230 patients with NSCLC and 32 healthy controls.
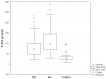
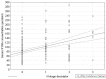
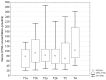
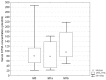
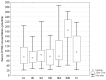
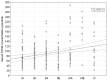
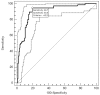
Results: Circulating KYNA level in NSCLC patients was higher than in controls (93.6±61.9 pmol/ml vs. 31.4±16.6 pmol/ml; p=2.2•10(-15)) and positively correlated with N (R=0.326; p=2•(10-6)) but not with T or M stage (p>0.05). In N+ patients it was higher than in N0 patients (137.7±51.8 pmol/ml vs. 71.9±41.7 pmol/ml; p=4.8•10(-16)). KYNA effectively discriminated N+ from N0 patients at a cut-off value 82.3 pmol/ml with sensitivity 94.7% (95%CI 87.1-98.5%), specificity 80.5% (95%CI 73.4-86.5%), negative predictive value NPV=96.8%, PPV=70.5% and area under the ROC curve AUC=0.900 (95%CI 0.854-0.935; p=0.0001).
Discussion and conclusion: Circulating KYNA level measurement offers reliable non-invasive discrimination between N0 and N+ patients in NSCLC. Robust discriminatory characteristics of KYNA assay predestines it for clinical use as an adjunct facilitating selection of candidates for primary surgical resection.
Keywords: diagnosis; immunology; kynurenine; marker.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum kynurenic acid: possible association with invasiveness of non-small cell lung cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(9):4241-4. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2012.13.9.4741. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012. PMID: 23167321
-
Determination of kynurenic acid in human serum and its correlation with the concentration of certain amino acids.Clin Chim Acta. 2007 Feb;377(1-2):174-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2006.09.019. Epub 2006 Sep 30. Clin Chim Acta. 2007. PMID: 17112493
-
Age-related increase of kynurenic acid in human cerebrospinal fluid - IgG and beta2-microglobulin changes.Neurosignals. 2005;14(3):126-35. doi: 10.1159/000086295. Neurosignals. 2005. PMID: 16088227
-
Accuracy of diffusion-weighted (DW) MRI with background signal suppression (MR-DWIBS) in diagnosis of mediastinal lymph node metastasis of nonsmall-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014 Jul;40(1):200-5. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24343. Epub 2013 Oct 29. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24923480
-
Preoperative intrathoracic lymph node staging in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: accuracy of integrated positron emission tomography and computed tomography.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009 Sep;36(3):440-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2009.04.003. Epub 2009 May 22. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009. PMID: 19464906 Review.
Cited by
-
Defining the AHR-regulated transcriptome in NK cells reveals gene expression programs relevant to development and function.Blood Adv. 2021 Nov 23;5(22):4605-4618. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004533. Blood Adv. 2021. PMID: 34559190 Free PMC article.
-
Specific urinary metabolites in canine mammary gland tumors.J Vet Sci. 2020 Mar;21(2):e23. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2020.21.e23. J Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32233131 Free PMC article.
-
Kynurenic acid and cancer: facts and controversies.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Apr;77(8):1531-1550. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03332-w. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31659416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomics of Non-muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Biomarkers for Early Detection of Bladder Cancer.Front Oncol. 2018 Nov 2;8:494. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00494. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30450336 Free PMC article.
-
Kynurenic Acid: The Janus-Faced Role of an Immunomodulatory Tryptophan Metabolite and Its Link to Pathological Conditions.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 10;8:1957. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01957. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29379504 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mellor AL, Keskin DB, Johnson T. et al. Cells expressing indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibit T cell responses. J Immunol. 2002;168:3771–3776. - PubMed
-
- Dubinett S, Sharma S. Towards effective immunotherapy for lung cancer: simultaneous targeting of tumor-initiating cells and immune pathways in the tumor microenvironment. Immunotherapy. 2009;1:721–725. - PubMed
-
- Halak BK, Maguire HC Jr, Lattime EC. Tumor-induced interleukin-10 inhibits type 1 immune responses directed at a tumor antigen as well as a non-tumor antigen present at the tumor site. Cancer Res. 1999;59:911–917. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

