Clinicopathological significance of nuclear factor (erythroid-2)-related factor 2 (Nrf2) expression in gastric cancer
- PMID: 25588809
- PMCID: PMC4302133
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1008-4
Clinicopathological significance of nuclear factor (erythroid-2)-related factor 2 (Nrf2) expression in gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: The transcription factor nuclear factor (erythroid-2)-related factor 2 (Nrf2) was originally identified as a critical regulator of intracellular anti-oxidants and of phase II detoxification enzymes through its transcriptional up-regulation of many anti-oxidant response element (ARE)-containing genes. Nrf2 protects not only normal cells but also cancer cells from cellular stress, and enhances cancer cell survival. Some studies have shown that Nrf2 expression in cancer patients has clinical significance. However, there has been no comprehensive analysis of the nuclear expression level of Nrf2 in gastrointestinal cancer cells. In this study we aimed to immunohistochemically evaluate the expression of Nrf2, and to assess its clinical significance in gastric cancer.
Methods: A total of 175 gastric cancer patients who received R0 gastrectomy with standard lymph node dissection were enrolled. We immunohistochemically evaluated Nrf2 expression in the paraffin-embedded surgically resected specimens of these 175 patients. Group differences were analyzed using the χ (2) test, Fisher's exact test, and the Mann-Whitney U test. Associations between Nrf2 expression and clinicopathological features, including clinical outcome, were assessed using univariate and multivariate analyses, and Kaplan-Meier curves with the log-rank test, respectively.
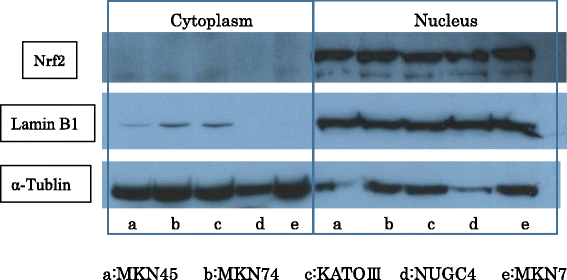
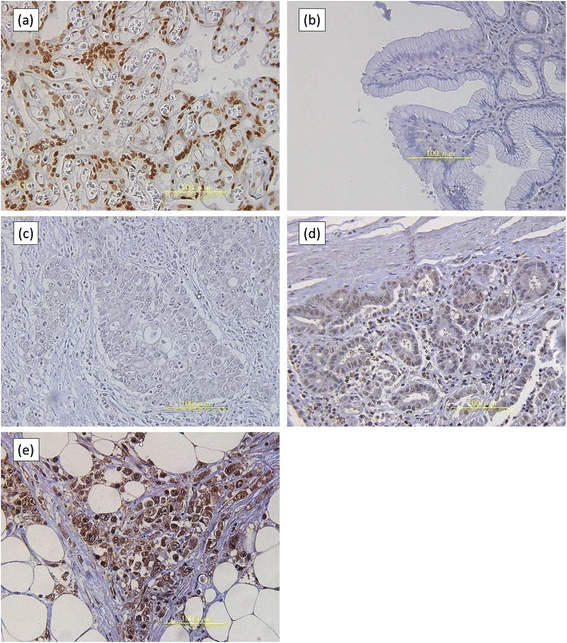
Results: Nrf2 immunoreactivity was predominantly identified in the nucleus of gastric cancer cells. Nrf2 positivity was closely associated with tumor size, tumor depth, lymph node metastases, lymphovascular invasion, histology and stage (p < 0.05 for all). A log-rank test indicated that the overall survival of the Nrf2-positive group was significantly poorer than that of the Nrf2-negative group (p < 0.01). And, positive Nrf2 expression was significantly associated with resistance to 5FU-based adjuvant chemotherapy (p = 0.024).
Conclusions: Nrf2 expression was positively associated with aggressive tumor behavior in gastric cancer. This result suggests that Nrf2 expression in gastric cancer is a potential indicator of worse prognosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Correlation Between Nuclear Factor E2-Related Factor 2 Expression and Gastric Cancer Progression.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Sep 27;21:2893-9. doi: 10.12659/MSM.894467. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26410168 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 protein expression and clinicopathological features in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb 14;21(6):1838-44. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i6.1838. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25684949 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between expression of NF-E2-related factor 2 and progression of gastric cancer.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Aug 15;8(8):13235-42. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. Retraction in: Int J Clin Exp Med. 2017 Jan 15;10(1):1733. PMID: 26550248 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Roles of Nrf2 in Gastric Cancer: Targeting for Therapeutic Strategies.Molecules. 2021 May 25;26(11):3157. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113157. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34070502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic polymorphism in the NRF2 gene as a prognosis marker for cancer chemotherapy.Front Genet. 2014 Nov 4;5:383. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00383. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25408701 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinically significant association of elevated expression of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 expression with higher glucose uptake and progression of upper urinary tract cancer.BMC Cancer. 2018 May 2;18(1):493. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4427-1. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29716554 Free PMC article.
-
Factors determining the sensitivity to proteasome inhibitors of multiple myeloma cells.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 4;15:1351565. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1351565. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38500772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NRF2-Dependent Bioactivation of Mitomycin C as a Novel Strategy To Target KEAP1-NRF2 Pathway Activation in Human Cancer.Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Jan 25;41(2):e00473-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00473-20. Print 2021 Jan 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33139492 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal phenotype of Nrf2 is associated with poor prognosis through hypoxic/VEGF-A-Rap1b/VEGFR2 pathway in gastric cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Apr 13;14(7):3293-3312. doi: 10.18632/aging.204013. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35417854 Free PMC article.
-
Novel NRF2-activated cancer treatments utilizing synthetic lethality.IUBMB Life. 2022 Dec;74(12):1209-1231. doi: 10.1002/iub.2680. Epub 2022 Oct 18. IUBMB Life. 2022. PMID: 36200139 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ni J, Mei M, Sun L. Oxidative DNA damage and repair in chronic atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012;59(115):671–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

