Functional interplay between the 53BP1-ortholog Rad9 and the Mre11 complex regulates resection, end-tethering and repair of a double-strand break
- PMID: 25569305
- PMCID: PMC4287487
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004928
Functional interplay between the 53BP1-ortholog Rad9 and the Mre11 complex regulates resection, end-tethering and repair of a double-strand break
Abstract
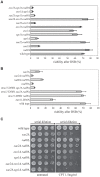
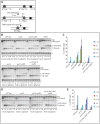
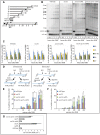
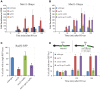
The Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2 nuclease complex, together with Sae2, initiates the 5'-to-3' resection of Double-Strand DNA Breaks (DSBs). Extended 3' single stranded DNA filaments can be exposed from a DSB through the redundant activities of the Exo1 nuclease and the Dna2 nuclease with the Sgs1 helicase. In the absence of Sae2, Mre11 binding to a DSB is prolonged, the two DNA ends cannot be kept tethered, and the DSB is not efficiently repaired. Here we show that deletion of the yeast 53BP1-ortholog RAD9 reduces Mre11 binding to a DSB, leading to Rad52 recruitment and efficient DSB end-tethering, through an Sgs1-dependent mechanism. As a consequence, deletion of RAD9 restores DSB repair either in absence of Sae2 or in presence of a nuclease defective MRX complex. We propose that, in cells lacking Sae2, Rad9/53BP1 contributes to keep Mre11 bound to a persistent DSB, protecting it from extensive DNA end resection, which may lead to potentially deleterious DNA deletions and genome rearrangements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sae2 antagonizes Rad9 accumulation at DNA double-strand breaks to attenuate checkpoint signaling and facilitate end resection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 18;115(51):E11961-E11969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816539115. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30510002 Free PMC article.
-
Processing of DNA double-stranded breaks and intermediates of recombination and repair by Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mre11 and its stimulation by Rad50, Xrs2, and Sae2 proteins.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 19;288(16):11273-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.439315. Epub 2013 Feb 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23443654 Free PMC article.
-
Release of Ku and MRN from DNA ends by Mre11 nuclease activity and Ctp1 is required for homologous recombination repair of double-strand breaks.PLoS Genet. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002271. Epub 2011 Sep 8. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21931565 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Sae2 and Rif2 in the regulation of Mre11-Rad50 activities at DNA ends.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2021 Dec;71:72-77. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2021.07.001. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2021. PMID: 34311383 Review.
-
Structure-function relationships of the Mre11 protein in the control of DNA end bridging and processing.Curr Genet. 2019 Feb;65(1):11-16. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0861-5. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 29922906 Review.
Cited by
-
Resection is responsible for loss of transcription around a double-strand break in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Elife. 2015 Jul 31;4:e08942. doi: 10.7554/eLife.08942. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26231041 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-forming CAG/CTG repeats interfere with gap repair to cause repeat expansions and chromosome breaks.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 29;14(1):2469. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37901-2. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37120647 Free PMC article.
-
Rad9/53BP1 promotes DNA repair via crossover recombination by limiting the Sgs1 and Mph1 helicases.Nat Commun. 2020 Jun 23;11(1):3181. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16997-w. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32576832 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanism of Chromatin Remodeler SMARCAD1/Fun30 in Response to DNA Damage.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 25;8:560098. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.560098. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33102471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xrs2 and Tel1 Independently Contribute to MR-Mediated DNA Tethering and Replisome Stability.Cell Rep. 2018 Nov 13;25(7):1681-1692.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.030. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30428339 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

