Mouse-human experimental epigenetic analysis unmasks dietary targets and genetic liability for diabetic phenotypes
- PMID: 25565211
- PMCID: PMC4340475
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.12.014
Mouse-human experimental epigenetic analysis unmasks dietary targets and genetic liability for diabetic phenotypes
Abstract
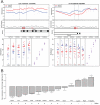
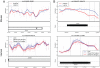
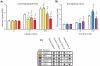
Using a functional approach to investigate the epigenetics of type 2 diabetes (T2D), we combine three lines of evidence-diet-induced epigenetic dysregulation in mouse, epigenetic conservation in humans, and T2D clinical risk evidence-to identify genes implicated in T2D pathogenesis through epigenetic mechanisms related to obesity. Beginning with dietary manipulation of genetically homogeneous mice, we identify differentially DNA-methylated genomic regions. We then replicate these results in adipose samples from lean and obese patients pre- and post-Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, identifying regions where both the location and direction of methylation change are conserved. These regions overlap with 27 genetic T2D risk loci, only one of which was deemed significant by GWAS alone. Functional analysis of genes associated with these regions revealed four genes with roles in insulin resistance, demonstrating the potential general utility of this approach for complementing conventional human genetic studies by integrating cross-species epigenomics and clinical genetic risk.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Genetics: Epigenetic mechanisms underlying type 2 diabetes mellitus.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015 May;11(5):261-2. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.31. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25752279 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic modifications of the Zfp/ZNF423 gene control murine adipogenic commitment and are dysregulated in human hypertrophic obesity.Diabetologia. 2018 Feb;61(2):369-380. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4471-4. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 29067487 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Bisulfite Sequencing of Human Pancreatic Islets Reveals Novel Differentially Methylated Regions in Type 2 Diabetes Pathogenesis.Diabetes. 2017 Apr;66(4):1074-1085. doi: 10.2337/db16-0996. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 28052964
-
Epigenetic Alterations in Human Liver From Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes in Parallel With Reduced Folate Levels.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Nov;100(11):E1491-501. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-3204. Epub 2015 Sep 29. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26418287 Free PMC article.
-
MAP4K4 and IL-6+ Th17 cells play important roles in non-obese type 2 diabetes.J Biomed Sci. 2017 Jan 7;24(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12929-016-0307-7. J Biomed Sci. 2017. PMID: 28061846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylation in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in humans.Mol Metab. 2018 Aug;14:12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.01.022. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Mol Metab. 2018. PMID: 29496428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A survey of inter-individual variation in DNA methylation identifies environmentally responsive co-regulated networks of epigenetic variation in the human genome.PLoS Genet. 2018 Oct 1;14(10):e1007707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007707. eCollection 2018 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30273333 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics of metabolic syndrome.Physiol Genomics. 2018 Nov 1;50(11):947-955. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00072.2018. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Physiol Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30240346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Learning a genome-wide score of human-mouse conservation at the functional genomics level.Nat Commun. 2021 May 3;12(1):2495. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22653-8. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33941776 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis reveals TNFAIP8L2 as an immune checkpoint regulator of inflammation and metabolism.Mol Immunol. 2018 Jul;99:154-162. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.05.007. Epub 2018 May 19. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29787979 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of Common Endocrine Disease: The Present and the Future.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Mar;101(3):787-94. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-3640. Epub 2016 Feb 23. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 26908105 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Almgren P, Lehtovirta M, Isomaa B, Sarelin L, Taskinen MR, Lyssenko V, Tuomi T, et al. Heritability and familiality of type 2 diabetes and related quantitative traits in the Botnia Study. Diabetologia. 2011;54:2811–2819. - PubMed
-
- Barres R, Kirchner H, Rasmussen M, Yan J, Kantor FR, Krook A, Naslund E, et al. Weight loss after gastric bypass surgery in human obesity remodels promoter methylation. Cell Rep. 2013;3:1020–1027. - PubMed
-
- Beale EG, Hammer RE, Antoine B, Forest C. Disregulated glyceroneogenesis: PCK1 as a candidate diabetes and obesity gene. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2004;15:129–135. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

