The blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 25561720
- PMCID: PMC4292164
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a020412
The blood-brain barrier
Abstract
Blood vessels are critical to deliver oxygen and nutrients to all of the tissues and organs throughout the body. The blood vessels that vascularize the central nervous system (CNS) possess unique properties, termed the blood-brain barrier, which allow these vessels to tightly regulate the movement of ions, molecules, and cells between the blood and the brain. This precise control of CNS homeostasis allows for proper neuronal function and also protects the neural tissue from toxins and pathogens, and alterations of these barrier properties are an important component of pathology and progression of different neurological diseases. The physiological barrier is coordinated by a series of physical, transport, and metabolic properties possessed by the endothelial cells (ECs) that form the walls of the blood vessels, and these properties are regulated by interactions with different vascular, immune, and neural cells. Understanding how these different cell populations interact to regulate the barrier properties is essential for understanding how the brain functions during health and disease.
Copyright © 2015 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
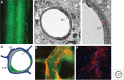
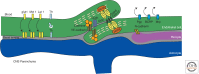
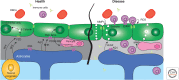
Similar articles
-
The Blood-Brain Barrier: Composition, Properties, and Roles in Brain Health.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2024 Jul 1:a041422. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041422. Online ahead of print. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2024. PMID: 38951020
-
Formation and maintenance of the BBB.Mech Dev. 2015 Nov;138 Pt 1:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2015.07.007. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Mech Dev. 2015. PMID: 26215350 Review.
-
Recent progress and new challenges in modeling of human pluripotent stem cell-derived blood-brain barrier.Theranostics. 2021 Nov 2;11(20):10148-10170. doi: 10.7150/thno.63195. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34815809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1135:415-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0320-7_34. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24510883
-
The dynamic blood-brain barrier.FEBS J. 2015 Nov;282(21):4067-79. doi: 10.1111/febs.13412. Epub 2015 Sep 8. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 26277326 Review.
Cited by
-
The psychoactive drug of abuse mephedrone differentially disrupts blood-brain barrier properties.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Mar 1;18(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02116-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 33648543 Free PMC article.
-
MCAM+ brain endothelial cells contribute to neuroinflammation by recruiting pathogenic CD4+ T lymphocytes.Brain. 2023 Apr 19;146(4):1483-1495. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac389. Brain. 2023. PMID: 36319587 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral BDNF Response to Physical and Cognitive Exercise and Its Association With Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Healthy Older Adults.Front Physiol. 2020 Aug 25;11:1080. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.01080. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32982796 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling mysteries at the perivascular space: a new rationale for cerebral malaria pathogenesis.Trends Parasitol. 2024 Jan;40(1):28-44. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2023.11.005. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Trends Parasitol. 2024. PMID: 38065791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocytes propel neurovascular dysfunction during cerebral cavernous malformation lesion formation.J Clin Invest. 2021 Jul 1;131(13):e139570. doi: 10.1172/JCI139570. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 34043589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Khan EU, Rollinson CM, Reichel A, Janigro D, Dombrowski SM, Dobbie MS, Begley DJ 2002. Drug resistance in epilepsy: The role of the blood–brain barrier. Novartis Found Symp 243: 38–47; discussion 47–53, 180–185. - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E 2006. Astrocyte–endothelial interactions at the blood–brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci 7: 41–53. - PubMed
-
- Aird WC 2007a. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds. Circ Res 100: 174–190. - PubMed
-
- Aird WC 2007b. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res 100: 158–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
