PRSice: Polygenic Risk Score software
- PMID: 25550326
- PMCID: PMC4410663
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu848
PRSice: Polygenic Risk Score software
Abstract
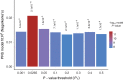
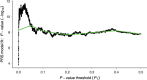
Summary: A polygenic risk score (PRS) is a sum of trait-associated alleles across many genetic loci, typically weighted by effect sizes estimated from a genome-wide association study. The application of PRS has grown in recent years as their utility for detecting shared genetic aetiology among traits has become appreciated; PRS can also be used to establish the presence of a genetic signal in underpowered studies, to infer the genetic architecture of a trait, for screening in clinical trials, and can act as a biomarker for a phenotype. Here we present the first dedicated PRS software, PRSice ('precise'), for calculating, applying, evaluating and plotting the results of PRS. PRSice can calculate PRS at a large number of thresholds ("high resolution") to provide the best-fit PRS, as well as provide results calculated at broad P-value thresholds, can thin Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) according to linkage disequilibrium and P-value or use all SNPs, handles genotyped and imputed data, can calculate and incorporate ancestry-informative variables, and can apply PRS across multiple traits in a single run. We exemplify the use of PRSice via application to data on schizophrenia, major depressive disorder and smoking, illustrate the importance of identifying the best-fit PRS and estimate a P-value significance threshold for high-resolution PRS studies.
Availability and implementation: PRSice is written in R, including wrappers for bash data management scripts and PLINK-1.9 to minimize computational time. PRSice runs as a command-line program with a variety of user-options, and is freely available for download from http://PRSice.info
Contact: jack.euesden@kcl.ac.uk or paul.oreilly@kcl.ac.uk
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PRSice-2: Polygenic Risk Score software for biobank-scale data.Gigascience. 2019 Jul 1;8(7):giz082. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giz082. Gigascience. 2019. PMID: 31307061 Free PMC article.
-
PRS-on-Spark (PRSoS): a novel, efficient and flexible approach for generating polygenic risk scores.BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Aug 8;19(1):295. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2289-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 30089455 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic risk score in postmortem diagnosed sporadic early-onset Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Aging. 2018 Feb;62:244.e1-244.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.09.035. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Neurobiol Aging. 2018. PMID: 29103623 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic Risk Scores in Alzheimer's Disease: Current Applications and Future Directions.Front Digit Health. 2020 Aug 11;2:14. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2020.00014. eCollection 2020. Front Digit Health. 2020. PMID: 34713027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards clinical utility of polygenic risk scores.Hum Mol Genet. 2019 Nov 21;28(R2):R133-R142. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddz187. Hum Mol Genet. 2019. PMID: 31363735 Review.
Cited by
-
Peripheral biomarkers of treatment-resistant schizophrenia: Genetic, inflammation and stress perspectives.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 12;13:1005702. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1005702. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36313375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging both individual-level genetic data and GWAS summary statistics increases polygenic prediction.Am J Hum Genet. 2021 Jun 3;108(6):1001-1011. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.04.014. Epub 2021 May 7. Am J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33964208 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of 42 genome-wide significant loci associated with dyslexia.Nat Genet. 2022 Nov;54(11):1621-1629. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01192-y. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Nat Genet. 2022. PMID: 36266505 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide study of tardive dyskinesia in schizophrenia.Transl Psychiatry. 2021 Jun 8;11(1):351. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01471-y. Transl Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34103471 Free PMC article.
-
DNAm scores for serum GDF15 and NT-proBNP levels associate with a range of traits affecting the body and brain.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Sep 10;16(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01734-7. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 39256775 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

