Integrated systems analysis reveals a molecular network underlying autism spectrum disorders
- PMID: 25549968
- PMCID: PMC4300495
- DOI: 10.15252/msb.20145487
Integrated systems analysis reveals a molecular network underlying autism spectrum disorders
Abstract
Autism is a complex disease whose etiology remains elusive. We integrated previously and newly generated data and developed a systems framework involving the interactome, gene expression and genome sequencing to identify a protein interaction module with members strongly enriched for autism candidate genes. Sequencing of 25 patients confirmed the involvement of this module in autism, which was subsequently validated using an independent cohort of over 500 patients. Expression of this module was dichotomized with a ubiquitously expressed subcomponent and another subcomponent preferentially expressed in the corpus callosum, which was significantly affected by our identified mutations in the network center. RNA-sequencing of the corpus callosum from patients with autism exhibited extensive gene mis-expression in this module, and our immunochemical analysis showed that the human corpus callosum is predominantly populated by oligodendrocyte cells. Analysis of functional genomic data further revealed a significant involvement of this module in the development of oligodendrocyte cells in mouse brain. Our analysis delineates a natural network involved in autism, helps uncover novel candidate genes for this disease and improves our understanding of its molecular pathology.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorders; corpus callosum; functional modules; oligodendrocytes; protein interaction network.
© 2014 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Figures
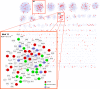
An overview of the identified loci from whole-genome and exome sequencing. Evolutionary conservation is quantified by GERP++ score, where the higher scores indicate greater selective pressure on the genomic loci. For genes with multiple significant loci, the most conserved residue is considered. Variants absent in the 1,000 Genome dataset are considered rare variants. The genes were colorized based on the fraction of deleterious mutations predicted by MutationTaster among all the identified mutations in the gene (MRI image of the corpus callosum: Allen Institute of Brain Science).
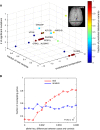
Validation using another larger patient cohort. In this dataset, variants with allele frequencies with increased absolute differences between cases and controls are more likely to affect genes that were also detected in our study (red line). The allele frequency difference is the absolute difference between cases and controls. This trend cannot be observed by 10,000 simulations (blue line for one randomized dataset).
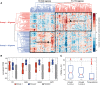
Dichotomized expression of the genes in module #13 across 295 brain sections. Relative abundance of each gene across the 295 brain sections was hierarchically clustered to reveal gene groups exhibiting similar expression patterns across tissues. Group 1 genes showed elevated expression in 175 regions (T1, e.g., corpus callosum) relative to other brain sections, and Group 2 genes showed high expression in 120 regions (T2, e.g., hippocampal regions) relative to other brain sections.
RNA-sequencing of four different brain regions from a healthy subject. The brain regions include the Brodmann areas 9 (BA9), 40 (BA40), the amygdala (AMY) and the corpus callosum (CC), which revealed the same observation as from the microarray analyses. Group 1 (red) and 2 (blue) genes were compared with 1,000 randomly sampled genes (gray) from the transcriptome in each brain region. The raw FPKM values were normalized into the cumulative density functions based on kernel density estimation. The elevation of Group 2 genes across all brain regions and the greatest increase of Group 1 genes in the corpus callosum were all statistically significant (P < 1e-5, Wilcoxon rank-sum test).
RNA-sequencing of the corpus callosum transcriptomes from six non-autistic individuals. FPKM quantifies the absolute expression of genes in each group. The two groups have similar expression in the corpus callosum (P > 0.5, Wilcoxon rank-sum test), which are all above the transcriptome background (P < 4.87e-6, Wilcoxon rank-sum test), suggesting that both sub-components are active in this tissue.
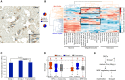
Immunohistochemistry analysis in the corpus callosum. Staining of LRP2 in the human corpus callosum reveals that the major cell population in the corpus callosum is the oligodendrocytes (the blue round nuclei), which express LRP2 stained in brown. A zoom-in view is shown in the inset.
Neural cell-type expression of the orthologous module #13 in mouse brain. Gene expression in different neural cell types was hierarchically clustered into the three major cell types in brain (neurons, oligodendrocytes and astrocytes). The clustering grouped genes in module #13 into a neuron cluster and a glial cluster, enriched for Group 1 and 2 genes, respectively. The fraction of Group 1 (red) and 2 (blue) genes in the glial and neuronal clusters were represented by the pie charts, with statistical significance determined by a chi-square test.
Overall expression of module #13 in cultured oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs). Group 1 and 2 were expressed at a similar level as the transcriptome background in OPCs. The statistical significance was determined by Wilcoxon rank-sum test, and the error bars represent one standard error.
The role of the module in oligodendrocyte (OL) development. Differentiation of OPCs into mature myelinating OLs (MOG+) led to a significant up-regulation of Group 1 genes (left, OPCs → mature OLs). On the other hand, conditional knockout (CKO) of the master myelination factor MRF from mature OLs led to a significant up-regulation of Group 2 genes (right, mature OLs → MRF CKO). The statistical significance was determined by Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
A proposed model. Up-regulation is associated with, or likely to contribute to, the differentiation of OPCs into mature myelinating OLs. The mature OLs acquire their myelination capacity by activating the MRF-mediated regulatory network, which also serves to repress expression of Group 2 genes.
Enrichment of the differentially expressed genes in module #13. RNA-sequencing of the corpus callosum of autism patients and their matched controls. Enrichment was not observed for the genes in the human synaptome or the collection of known autism genes (excluding genes in this module). Statistical significance was determined by hypergeometric test.
The mutation pattern of the genes from the innermost layers of the interaction network (K ≥ 10) to the periphery layer (K = 1). Genes in the central and periphery layers in this module are more likely to be affected, while the trend cannot be observed in 10,000 random simulations. For individual bins, significant enrichment and depletion were observed in the central layers (K ≥ 10) and the intermediate layers (3 ≤ K < 6), respectively. Statistical significance of the enrichment was determined by hypergeometric test. 10,000 random permutations were performed to determine the statistical significance of the curve.
Compositional bias of the mutated genes in central layers. The mutated genes in central layers are more biased toward the corpus callosum-specific subcomponent; this trend is not observed in background or other mutated genes with varying degree of K. Statistical significance of the enrichment was determined by hypergeometric test.
Positive correlation between network coreness and gene expression in the corpus callosum. RNA-sequencing of the corpus callosum of six non-autistic individuals revealed a positive correlation, suggesting the central layers may play critical roles in the corpus callosum. Two outlier genes, DYNLL1 and BCAS1, are separately labeled due to their extreme expression in this tissue. The correlation coefficient r and its statistical significance were computed using Spearman's correlation.
Predicted sub-complexes within this module. Genes in this module are topologically clustered to form sub-complexes, with the significantly mutated genes labeled in blue, mis-expressed genes in the corpus callosum labeled in green, and both in red. Two clusters, #6 for SHANK-DLGAP complexes and #6 for LRP2, and its binding partners, are enriched for the mis-expressed or mutated genes, respectively. Statistical significance of the enrichment was determined by hypergeometric test.
Comment in
-
Autism cornered: network analyses reveal mechanisms of autism spectrum disorders.Mol Syst Biol. 2014 Dec 30;10(12):778. doi: 10.15252/msb.20145937. Mol Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 25549969 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Integrated multifactor analysis explores core dysfunctional modules in autism spectrum disorder.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 May 22;14(8):811-818. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.24624. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29989084 Free PMC article.
-
Autism cornered: network analyses reveal mechanisms of autism spectrum disorders.Mol Syst Biol. 2014 Dec 30;10(12):778. doi: 10.15252/msb.20145937. Mol Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 25549969 Free PMC article.
-
Hierarchical cortical transcriptome disorganization in autism.Mol Autism. 2017 Jun 21;8:29. doi: 10.1186/s13229-017-0147-7. eCollection 2017. Mol Autism. 2017. PMID: 28649314 Free PMC article.
-
Functional genomics of human brain development and implications for autism spectrum disorders.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Oct 27;5(10):e665. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.153. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26506051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A common molecular signature in ASD gene expression: following Root 66 to autism.Transl Psychiatry. 2016 Jan 5;6(1):e705. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.112. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26731442 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autism spectrum disorder: prospects for treatment using gene therapy.Mol Autism. 2018 Jun 20;9:39. doi: 10.1186/s13229-018-0222-8. eCollection 2018. Mol Autism. 2018. PMID: 29951185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into Autism Spectrum Disorder Genomic Architecture and Biology from 71 Risk Loci.Neuron. 2015 Sep 23;87(6):1215-1233. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.09.016. Neuron. 2015. PMID: 26402605 Free PMC article.
-
SAPAP Scaffold Proteins: From Synaptic Function to Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Cells. 2022 Nov 28;11(23):3815. doi: 10.3390/cells11233815. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bringing machine learning to research on intellectual and developmental disabilities: taking inspiration from neurological diseases.J Neurodev Disord. 2022 May 2;14(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s11689-022-09438-w. J Neurodev Disord. 2022. PMID: 35501679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Abnormal Expression of Prion Disease Gene Pathway in Brains from Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorders.Brain Sci. 2020 Mar 29;10(4):200. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10040200. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 32235346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anney R, Klei L, Pinto D, Almeida J, Bacchelli E, Baird G, Bolshakova N, Bolte S, Bolton PF, Bourgeron T, Brennan S, Brian J, Casey J, Conroy J, Correia C, Corsello C, Crawford EL, de Jonge M, Delorme R, Duketis E. Individual common variants exert weak effects on the risk for autism spectrum disorders pi. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:4781–4792. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- SRA/SRP050187
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

