Parathyroid hormone-related protein serves as a prognostic indicator in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25539663
- PMCID: PMC4393566
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-014-0100-y
Parathyroid hormone-related protein serves as a prognostic indicator in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: In our previous study, parathyroid hormone-like hormone (PTHLH) which encodes parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) was revealed to be up-regulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) compared with paired apparently normal surgical margins using microarray method. However, the function and prognostic indicators of PTHLH/PTHrP in OSCC remain obscure.
Methods: The mRNA levels of PTHLH and its protein levels were investigated in 9 OSCC cell lines and in 36 paired OSCC specimens by real-time PCR and western blotting. The biological function of PTHLH/PTHrP was investigated using small interfering RNA (siRNA) in 3 OSCC cell lines, and immunohistochemistry was used to estimate the prognostic value of PTHrP in 101 patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), including OSCC and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell cycle was tested by flow cytometry and cell cycle related genes were investigated by western blotting and immunocytochemistry assay.
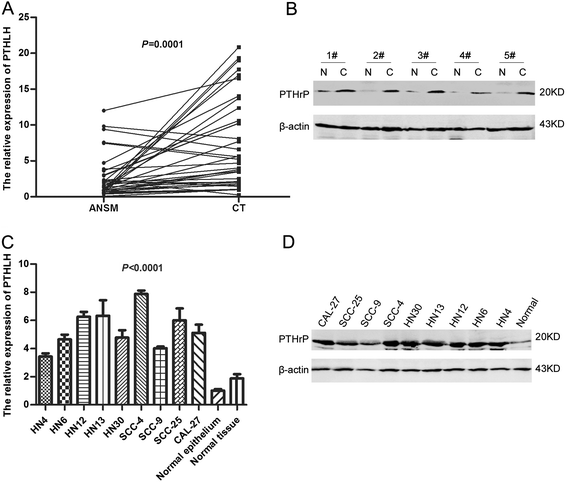
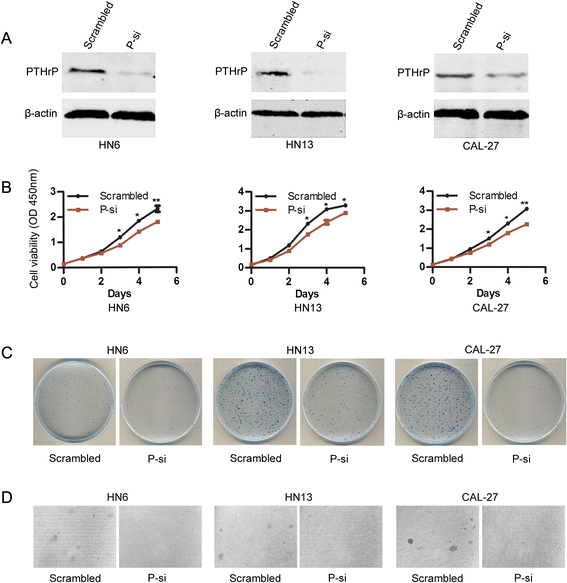
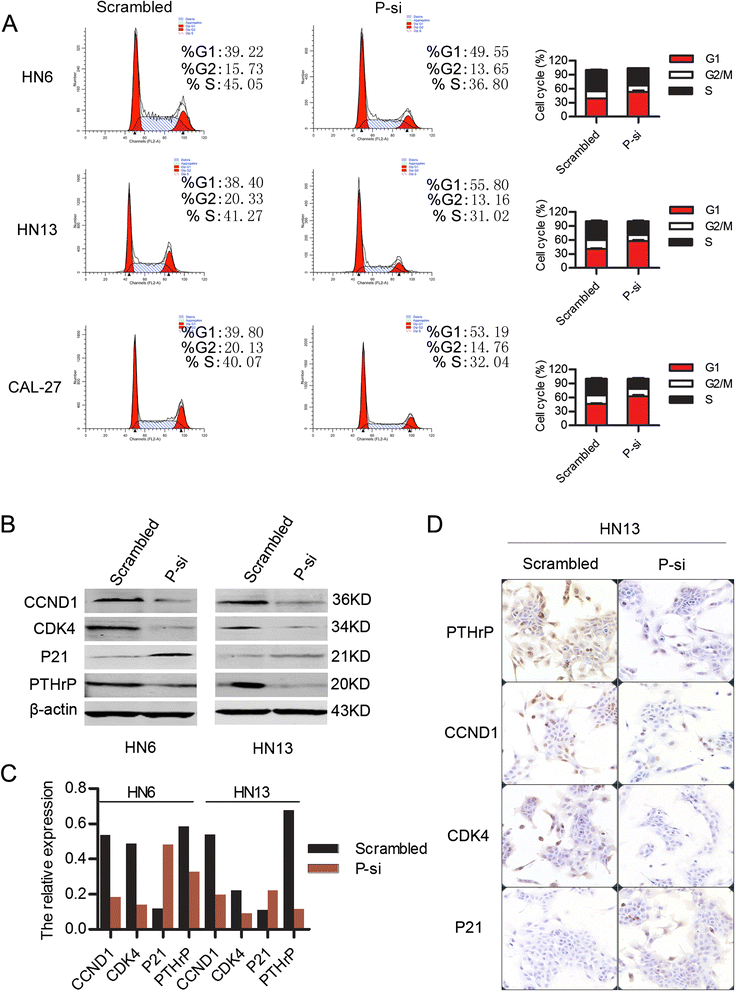
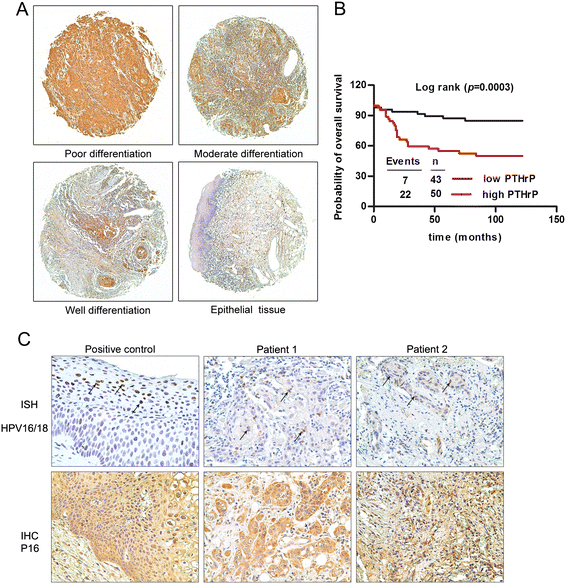
Results: This study showed that the mRNA and protein levels of PTHLH in 9 OSCC cell lines were much higher than that in normal epithelial cells (P < 0.0001). In 36 paired OSCC tissues, PTHLH mRNA expressions were found higher in 32 OSCC tissues than that of paired apparently normal surgical margins (P = 0.0001). The results revealed that the down-regulation of PTHLH/PTHrP by siRNAs could reduce cell proliferation and inhibit plate and soft agar colony formation as well as affect the cell cycle of OSCC cells. The key proteins related to the cell cycle were changed by anti-PTHLH siRNA. The results showed that cyclin D1 and CDK4 expressions were significantly reduced in the cells transfected with anti-PTHLH siRNA. On the other hand, the expression of p21 was increased. The results also showed that high PTHrP level was associated with poor pathologic differentiation (P = 0.0001) and poor prognosis (P = 0.0003) in patients with HNSCC.
Conclusions: This study suggests that PTHLH/PTHrP is up-regulated in OSCCs. Therefore, PTHLH/PTHrP could play a role in the pathogenesis of OSCC by affecting cell proliferation and cell cycle, and the protein levels of PTHrP might serve as a prognostic indicator for evaluating patients with HNSCCs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loss of RUNX3 expression inhibits bone invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 7;8(6):9079-9092. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14071. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28030842 Free PMC article.
-
The role of E-cadherin down-regulation in oral cancer: CDH1 gene expression and epigenetic blockage.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2014;14(2):115-27. doi: 10.2174/1568009613666131126115012. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 24274398
-
Up-regulation of survivin in oral squamous cell carcinoma correlates with poor prognosis and chemoresistance.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010 Oct;110(4):484-91. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2010.04.009. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010. PMID: 20868995
-
The role of novel prognostic markers PROX1 and FOXC2 in carcinogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma.J Exp Ther Oncol. 2018 May;12(3):171-184. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29790306 Review.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of p27 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Int J Biol Markers. 2013 Dec 17;28(4):e329-35. doi: 10.5301/jbm.5000035. Int J Biol Markers. 2013. PMID: 23787492 Review.
Cited by
-
PTHrP Regulates Fatty Acid Metabolism via Novel lncRNA in Breast Cancer Initiation and Progression Models.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 25;15(15):3763. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153763. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568579 Free PMC article.
-
Autocrine parathyroid hormone-like hormone promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell proliferation via increased ERK/JNK-ATF2-cyclinD1 signaling.J Transl Med. 2017 Nov 25;15(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1342-1. J Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 29178939 Free PMC article.
-
TGFβ3-mediated induction of Periostin facilitates head and neck cancer growth and is associated with metastasis.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 9;6:20587. doi: 10.1038/srep20587. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26857387 Free PMC article.
-
PTHLH Predicts the Prognosis of Patients with Oral Leukoplakia.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Oct 8;13:10013-10023. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S261124. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33116586 Free PMC article.
-
PTHrP Drives Pancreatic Cancer Growth and Metastasis and Reveals a New Therapeutic Vulnerability.Cancer Discov. 2021 Jul;11(7):1774-1791. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1098. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Cancer Discov. 2021. PMID: 33589425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaykalova DA, Mambo E, Choudhary A, Houghton J, Buddavarapu K, Sanford T, Darden W, Adai A, Hadd A, Latham G, Danilova LV, Bishop J, Li RJ, Westra WH, Hennessey P, Koch WM, Ochs MF, Califano JA, Sun W. Novel insight into mutational landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2014;9:e93102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pries R, Hogrefe L, Xie L, Frenzel H, Brocks C, Ditz C, Wollenberg B. Induction of c-Myc-dependent cell proliferation through toll-like receptor 3 in head and neck cancer. Int J Mol Med. 2008;21:209–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

