Intrinsically disordered proteins in cellular signalling and regulation
- PMID: 25531225
- PMCID: PMC4405151
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3920
Intrinsically disordered proteins in cellular signalling and regulation
Abstract
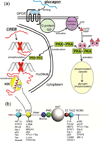
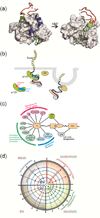
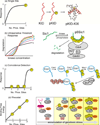
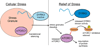
Intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) are important components of the cellular signalling machinery, allowing the same polypeptide to undertake different interactions with different consequences. IDPs are subject to combinatorial post-translational modifications and alternative splicing, adding complexity to regulatory networks and providing a mechanism for tissue-specific signalling. These proteins participate in the assembly of signalling complexes and in the dynamic self-assembly of membrane-less nuclear and cytoplasmic organelles. Experimental, computational and bioinformatic analyses combine to identify and characterize disordered regions of proteins, leading to a greater appreciation of their widespread roles in biological processes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functions of short lifetime biological structures at large: the case of intrinsically disordered proteins.Brief Funct Genomics. 2020 Jan 22;19(1):60-68. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/ely023. Brief Funct Genomics. 2020. PMID: 29982297 Review.
-
Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Link Alternative Splicing and Post-translational Modifications to Complex Cell Signaling and Regulation.J Mol Biol. 2018 Aug 3;430(16):2342-2359. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.03.028. Epub 2018 Apr 4. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29626537
-
Introduction to the Thematic Minireview Series on Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.J Biol Chem. 2016 Mar 25;291(13):6679-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R116.719930. Epub 2016 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26851284 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Protein Interaction Networks and New Structural Paradigms in Signaling.Chem Rev. 2016 Jun 8;116(11):6424-62. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00548. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Chem Rev. 2016. PMID: 26922996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrinsically disordered proteins and multicellular organisms.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Jan;37:44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.09.025. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25307499 Review.
Cited by
-
Translational Diffusion and Self-Association of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein κ-Casein Using NMR with Ultra-High Pulsed-Field Gradient and Time-Resolved FRET.J Phys Chem B. 2024 Aug 15;128(32):7781-7791. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.4c03625. Epub 2024 Aug 6. J Phys Chem B. 2024. PMID: 39106061 Free PMC article.
-
Determining Binding Kinetics of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins by NMR Spectroscopy.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2141:663-681. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0524-0_34. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32696383 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathogenesis of spinal bulbar muscular atrophy (Kennedy's disease) and avenues for treatment.Curr Opin Neurol. 2020 Oct;33(5):629-634. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000856. Curr Opin Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32773451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanical cell - the role of force dependencies in synchronising protein interaction networks.J Cell Sci. 2022 Nov 15;135(22):jcs259769. doi: 10.1242/jcs.259769. Epub 2022 Nov 18. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 36398718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrinsically Disordered Membrane Anchors of Rheb, RhoA, and DiRas3 Small GTPases: Molecular Dynamics, Membrane Organization, and Interactions.J Phys Chem B. 2024 Jul 11;128(27):6518-6528. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.4c01876. Epub 2024 Jun 28. J Phys Chem B. 2024. PMID: 38942776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wright PE, Dyson HJ. Intrinsically unstructured proteins: Re-assessing the protein structure-function paradigm. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1999;293:321–331. - PubMed
-
- Dunker AK, Brown CJ, Lawson JD, Iakoucheva LM, Obradovic Z. Intrinsic disorder and protein function. Biochemistry. 2002;41:6573–6582. - PubMed
-
- Dyson HJ, Wright PE. Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2005;6:197–208. - PubMed
-
- Dunker AK, Cortese MS, Romero P, Iakoucheva LM, Uversky VN. Flexible nets. The roles of intrinsic disorder in protein interaction networks. FEBSJournal. 2005;272:5129–5148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

