Inhibition of reactive oxygen species production ameliorates inflammation induced by influenza A viruses via upregulation of SOCS1 and SOCS3
- PMID: 25520513
- PMCID: PMC4325759
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.03529-14
Inhibition of reactive oxygen species production ameliorates inflammation induced by influenza A viruses via upregulation of SOCS1 and SOCS3
Abstract
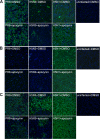
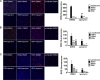
Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus infection is associated with severe mortality in both humans and poultry. The mechanisms of disease pathogenesis and immunity are poorly understood although recent evidence suggests that cytokine/chemokine dysregulation contributes to disease severity following H5N1 infection. Influenza A virus infection causes a rapid influx of inflammatory cells, resulting in increased reactive oxygen species production, cytokine expression, and acute lung injury. Proinflammatory stimuli are known to induce intracellular reactive oxygen species by activating NADPH oxidase activity. We therefore hypothesized that inhibition of this activity would restore host cytokine homeostasis following avian influenza virus infection. A panel of airway epithelial and immune cells from mammalian and avian species were infected with A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 H1N1 virus, low-pathogenicity avian influenza H5N3 virus (A/duck/Victoria/0305-2/2012), highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus (A/chicken/Vietnam/0008/2004), or low-pathogenicity avian influenza H7N9 virus (A/Anhui/1/2013). Quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase PCR showed that H5N1 and H7N9 viruses significantly stimulated cytokine (interleukin-6, beta interferon, CXCL10, and CCL5) production. Among the influenza-induced cytokines, CCL5 was identified as a potential marker for overactive immunity. Apocynin, a Nox2 inhibitor, inhibited influenza-induced cytokines and reactive oxygen species production, although viral replication was not significantly altered in vitro. Interestingly, apocynin treatment significantly increased influenza virus-induced mRNA and protein expression of SOCS1 and SOCS3, enhancing negative regulation of cytokine signaling. These findings suggest that apocynin or its derivatives (targeting host responses) could be used in combination with antiviral strategies (targeting viruses) as therapeutic agents to ameliorate disease severity in susceptible species.
Importance: Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus infection causes severe morbidity and mortality in both humans and poultry. Wide-spread antiviral resistance necessitates the need for the development of additional novel therapeutic measures to modulate overactive host immune responses after infection. Disease severity following avian influenza virus infection can be attributed in part to hyperinduction of inflammatory mediators such as cytokines, chemokines, and reactive oxygen species. Our study shows that highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus and low-pathogenicity avian influenza H7N9 virus (both associated with human fatalities) promote inactivation of FoxO3 and downregulation of the TAM receptor tyrosine kinase, Tyro3, leading to augmentation of the inflammatory cytokine response. Inhibition of influenza-induced reactive oxygen species with apocynin activated FoxO3 and stimulated SOCS1 and SOCS3 proteins, restoring cytokine homeostasis. We conclude that modulation of host immune responses with antioxidant and/or anti-inflammatory agents in combination with antiviral therapy may have important therapeutic benefits.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Production of interferon α and β, pro-inflammatory cytokines and the expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) in obese subjects infected with influenza A/H1N1.Clin Nutr. 2014 Oct;33(5):922-6. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Clin Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24182768
-
PA-X decreases the pathogenicity of highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza A virus in avian species by inhibiting virus replication and host response.J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4126-42. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02132-14. Epub 2015 Jan 28. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25631083 Free PMC article.
-
Chicken and duck myotubes are highly susceptible and permissive to influenza virus infection.J Virol. 2015 Mar;89(5):2494-506. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03421-14. Epub 2014 Dec 24. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25540384 Free PMC article.
-
[Cytokine storm in avian influenza].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2008 Apr;42(2):365-80. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2008. PMID: 18697437 Review. Turkish.
-
Non-hydrolyzed in digestive tract and blood natural L-carnosine peptide ("bioactivated Jewish penicillin") as a panacea of tomorrow for various flu ailments: signaling activity attenuating nitric oxide (NO) production, cytostasis, and NO-dependent inhibition of influenza virus replication in macrophages in the human body infected with the virulent swine influenza A (H1N1) virus.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;24(1):1-26. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2012-0037. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23425625 Review.
Cited by
-
Compounds with anti-influenza activity: present and future of strategies for the optimal treatment and management of influenza. Part II: Future compounds against influenza virus.J Prev Med Hyg. 2014 Dec;55(4):109-29. J Prev Med Hyg. 2014. PMID: 26137785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox control in the pathophysiology of influenza virus infection.BMC Microbiol. 2020 Jul 20;20(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01890-9. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32689931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct functional roles of amphibian (Xenopus laevis) colony-stimulating factor-1- and interleukin-34-derived macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 2015 Oct;98(4):641-9. doi: 10.1189/jlb.4AB0315-117RR. Epub 2015 Jul 1. J Leukoc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26136505 Free PMC article.
-
Gas6/Axl signaling attenuates alveolar inflammation in ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury by up-regulating SOCS3-mediated pathway.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 18;14(7):e0219788. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219788. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31318922 Free PMC article.
-
Apocynin attenuates angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cells osteogenic switching via suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):83588-83600. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13193. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27835878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gao R, Cao B, Hu Y, Feng Z, Wang D, Hu W, Chen J, Jie Z, Qiu H, Xu K, Xu X, Lu H, Zhu W, Gao Z, Xiang N, Shen Y, He Z, Gu Y, Zhang Z, Yang Y, Zhao X, Zhou L, Li X, Zou S, Zhang Y, Yang L, Guo J, Dong J, Li Q, Dong L, Zhu Y, Bai T, Wang S, Hao P, Yang W, Han J, Yu H, Li D, Gao GF, Wu G, Wang Y, Yuan Z, Shu Y. 2013. Human infection with a novel avian-origin influenza A (H7N9) virus. N Engl J Med 368:1888–1897. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1304459. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Imai M, Watanabe T, Hatta M, Das SC, Ozawa M, Shinya K, Zhong G, Hanson A, Katsura H, Watanabe S, Li C, Kawakami E, Yamada S, Kiso M, Suzuki Y, Maher EA, Neumann G, Kawaoka Y. 2012. Experimental adaptation of an influenza H5 HA confers respiratory droplet transmission to a reassortant H5 HA/H1N1 virus in ferrets. Nature 486:420–428. doi:10.1038/nature10831. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Herfst S, Schrauwen EJ, Linster M, Chutinimitkul S, de Wit E, Munster VJ, Sorrell EM, Bestebroer TM, Burke DF, Smith DJ, Rimmelzwaan GF, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. 2012. Airborne transmission of influenza A/H5N1 virus between ferrets. Science 336:1534–1541. doi:10.1126/science.1213362. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, Wang D, Gao R, Zhao B, Song J, Qi X, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Yang L, Zhu W, Bai T, Qin K, Lan Y, Zou S, Guo J, Dong J, Dong L, Wei H, Li X, Lu J, Liu L, Zhao X, Huang W, Wen L, Bo H, Xin L, Chen Y, Xu C, Pei Y, Yang Y, Zhang X, Wang S, Feng Z, Han J, Yang W, Gao GF, Wu G, Li D, Wang Y, Shu Y. 2013. Biological features of novel avian influenza A (H7N9) virus. Nature 499:500–503. doi:10.1038/nature12379. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

