Impairment of glymphatic pathway function promotes tau pathology after traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 25471560
- PMCID: PMC4252540
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3020-14.2014
Impairment of glymphatic pathway function promotes tau pathology after traumatic brain injury
Abstract
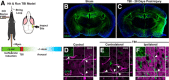
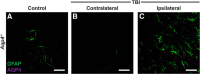
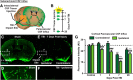
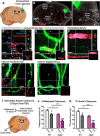
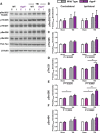
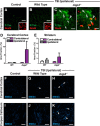
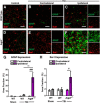
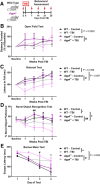
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an established risk factor for the early development of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease, and the post-traumatic brain frequently exhibits neurofibrillary tangles comprised of aggregates of the protein tau. We have recently defined a brain-wide network of paravascular channels, termed the "glymphatic" pathway, along which CSF moves into and through the brain parenchyma, facilitating the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid-β, from the brain. Here we demonstrate in mice that extracellular tau is cleared from the brain along these paravascular pathways. After TBI, glymphatic pathway function was reduced by ∼60%, with this impairment persisting for at least 1 month post injury. Genetic knock-out of the gene encoding the astroglial water channel aquaporin-4, which is importantly involved in paravascular interstitial solute clearance, exacerbated glymphatic pathway dysfunction after TBI and promoted the development of neurofibrillary pathology and neurodegeneration in the post-traumatic brain. These findings suggest that chronic impairment of glymphatic pathway function after TBI may be a key factor that renders the post-traumatic brain vulnerable to tau aggregation and the onset of neurodegeneration.
Keywords: AQP4; aquaporin-4; cerebrospinal fluid; neurodegeneration; tauopathy; traumatic brain injury.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/3416180-14$15.00/0.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Glymphatic system clears extracellular tau and protects from tau aggregation and neurodegeneration.J Exp Med. 2022 Mar 7;219(3):e20211275. doi: 10.1084/jem.20211275. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 35212707 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired glymphatic function and clearance of tau in an Alzheimer's disease model.Brain. 2020 Aug 1;143(8):2576-2593. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa179. Brain. 2020. PMID: 32705145 Free PMC article.
-
Focal Solute Trapping and Global Glymphatic Pathway Impairment in a Murine Model of Multiple Microinfarcts.J Neurosci. 2017 Mar 15;37(11):2870-2877. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2112-16.2017. Epub 2017 Feb 10. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28188218 Free PMC article.
-
A new glaucoma hypothesis: a role of glymphatic system dysfunction.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2015 Jun 29;12:16. doi: 10.1186/s12987-015-0012-z. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2015. PMID: 26118970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The glymphatic system's role in traumatic brain injury-related neurodegeneration.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Jul;28(7):2707-2715. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02070-7. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37185960 Review.
Cited by
-
The Mini-Craniotomy for cSDH Revisited: New Perspectives.Front Neurol. 2021 May 6;12:660885. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.660885. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34025564 Free PMC article.
-
Fast whole brain MR imaging of dynamic susceptibility contrast changes in the cerebrospinal fluid (cDSC MRI).Magn Reson Med. 2020 Dec;84(6):3256-3270. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28389. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Magn Reson Med. 2020. PMID: 32621291 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of glymphatic fluid transport in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2016 Sep;93:215-25. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.05.015. Epub 2016 May 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2016. PMID: 27234656 Free PMC article.
-
Polypathologies and Animal Models of Traumatic Brain Injury.Brain Sci. 2023 Dec 12;13(12):1709. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13121709. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 38137157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma Biomarker Concentrations Associated With Return to Sport Following Sport-Related Concussion in Collegiate Athletes-A Concussion Assessment, Research, and Education (CARE) Consortium Study.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Aug 3;3(8):e2013191. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13191. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 32852552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cirrito JR, Deane R, Fagan AM, Spinner ML, Parsadanian M, Finn MB, Jiang H, Prior JL, Sagare A, Bales KR, Paul SM, Zlokovic BV, Piwnica-Worms D, Holtzman DM. P-glycoprotein deficiency at the blood-brain barrier increases amyloid-beta deposition in an Alzheimer disease mouse model. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:3285–3290. doi: 10.1172/JCI25247. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
