Methylation analysis of the DAPK1 gene in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia patients
- PMID: 25435999
- PMCID: PMC4246661
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.2677
Methylation analysis of the DAPK1 gene in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia patients
Abstract
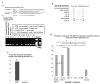
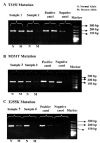
Death-associated protein kinase-1 (DAPK1) is a pro-apoptotic gene that induces cellular apoptosis in response to internal and external apoptotic stimulants. The silencing of DAPK1 can result in uncontrolled cell proliferation, indicating that it may have a role in tumor suppression. DAPK1 activity can be inhibited by the cytosine methylation that occurs in its promoter region. These methylation changes in the promoter region of DAPK1 have been reported in a range of solid and hematological malignancies. In the present study, DAPK1 methylation was investigated in chronic myeloid leukemia patients (n=43) using bisulfite conversion followed by methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction. The present study included a number of patients who were identified to be resistant to the common chemotherapeutic agent imatinib (STI571, Gleevec®, Glivec®), exhibiting at least one mutation in the breakpoint cluster region-Abelson murine leukemia (BCR-ABL) gene. Thus, the patients in the present study were divided into two groups according to their response to imatinib therapy: Non-resistant (n=26) and resistant (n=17) to imatinib. Resistant patients were characterized by the presence of single or multiple mutations of the BCR-ABL gene: i) T315I, ii) M351T, iii) E255K, iv) T315I and M351T or v) T315I, M351T and E255K. The present study identified that: i) The incidence of DAPK1 methylation was significantly higher in the resistant patients compared with the non-resistant patients; ii) the extent of resistance varied between mutation types; and iii) there was no DAPK1 methylation in any of the healthy controls. These findings indicate that DAPK1 methylation may be associated with a signaling pathway for imatinib resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia.
Keywords: DAPK1; DNA methylation; chronic myeloid leukemia; imatinib resistance; methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silencing of suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 due to methylation results in phosphorylation of STAT3 in imatinib resistant BCR-ABL positive chronic myeloid leukemia cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(11):4555-61. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.11.4555. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 24969884
-
PHA-680626 exhibits anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic activity on Imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cell lines and primary CD34+ cells by inhibition of both Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase and Aurora kinases.Leuk Res. 2008 Dec;32(12):1857-65. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2008.04.012. Epub 2008 Jun 2. Leuk Res. 2008. PMID: 18514829
-
HS-438, a new inhibitor of imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL T315I mutation in chronic myeloid leukemia.Cancer Lett. 2014 Jun 28;348(1-2):50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.03.012. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 24657654
-
Mutations in the ABL kinase domain pre-exist the onset of imatinib treatment.Semin Hematol. 2003 Apr;40(2 Suppl 2):80-2. doi: 10.1053/shem.2003.50046. Semin Hematol. 2003. PMID: 12783380 Review.
-
Resistance of Philadelphia-chromosome positive leukemia towards the kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571, Glivec): a targeted oncoprotein strikes back.Leukemia. 2003 May;17(5):829-38. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402889. Leukemia. 2003. PMID: 12750693 Review.
Cited by
-
Death Associated Protein Kinase 1 (DAPK1): A Regulator of Apoptosis and Autophagy.Front Mol Neurosci. 2016 Jun 23;9:46. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00046. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27445685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant DNA Methylation Status and mRNA Expression Level of SMG1 Gene in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Case-Control Study.Cell J. 2022 Dec 1;24(12):757-763. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2022.8526. Cell J. 2022. PMID: 36527348 Free PMC article.
-
Low DAPK1 expression correlates with poor prognosis and sunitinib resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Nov 16;13(2):1842-1858. doi: 10.18632/aging.103638. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33201837 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Microenvironment: A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 27;15(23):5600. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235600. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cationic liposomes induce cytotoxicity in HepG2 via regulation of lipid metabolism based on whole-transcriptome sequencing analysis.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Jul 11;19(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s40360-018-0230-5. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29996945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tang X, Wu W, Sun SY, et al. Hypermethylation of the death-associated protein kinase promoter attenuates the sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2004;2:685–691. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
