Immune responses to human factor IX in haemophilia B mice of different genetic backgrounds are distinct and modified by TLR4
- PMID: 25417755
- PMCID: PMC4309508
- DOI: 10.1111/hae.12522
Immune responses to human factor IX in haemophilia B mice of different genetic backgrounds are distinct and modified by TLR4
Abstract
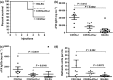
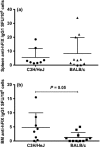
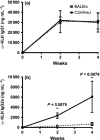
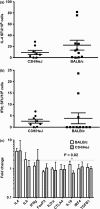
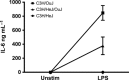
Our laboratory develops protocols to prevent or reverse ongoing anti-hFIX IgG inhibitors in haemophilia B mice with a F9 gene deletion on BALB/c and C3H/HeJ backgrounds. C3H/HeJ F9(-/Y) mice develop high titre anti-hFIX IgG1 inhibitors and anaphylaxis, whereas most BALB/c F9(-/Y) mice have mild anti-hFIX IgG1 inhibitors and no anaphylaxis. Our aim was to determine if hFIX-specific B- and T-cell responses in BALB/c and C3H/HeJ F9(-/Y) mice trigger the difference in anti-hFIX immune responses. BALB/c and C3H/HeJ F9(-/Y) mice were challenged weekly with recombinant hFIX protein. Humoral immune responses were determined by IgG1 and IgG2a anti-hFIX ELISA, Bethesda assay for inhibitors and B-cell ELISpot on bone marrow and spleen cells. T-cell studies measured the TH 1 (IFN-γ) and TH 2 (IL-4) cytokine responses in splenocytes at the mRNA and protein level in response to hFIX protein. Antibody responses were also measured in C3H/HeJ/OuJ F9(-/Y) mice with restored toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) function. BALB/c F9(-/Y) mice have a TH 2 skewed response and a reduction in anti-hFIX secreting plasma cells in the bone marrow. Independent antigen challenge revealed both strains generated equivalent IgG1 antibody titres to an intravenously delivered antigen. C3H/HeJ F9(-/Y) mice have a mixed TH 1 and TH 2 response (mainly TH 2). Importantly, TLR4 signalling has a modulatory role in the C3H background on the levels of anti-hFIX IgG1 and incidence of anaphylaxis. The background strain strongly impacts the immune response to hFIX, which can be significantly impacted by mutations in innate immune sensors.
Keywords: BALBc; C3H/HeJ; anaphylaxis; factor IX; haemophilia B murine model; immune response.
© 2014 The Authors. Haemophilia Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulating immunogenicity of factor IX by fusion to an immunoglobulin Fc domain: a study using a hemophilia B mouse model.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Apr;15(4):721-734. doi: 10.1111/jth.13649. Epub 2017 Mar 2. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28166609
-
Efficient induction of immune tolerance to coagulation factor IX following direct intramuscular gene transfer.J Thromb Haemost. 2007 Jun;5(6):1227-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02522.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2007. PMID: 17362228
-
Neonatal gene transfer with a retroviral vector results in tolerance to human factor IX in mice and dogs.Blood. 2004 Jan 1;103(1):143-51. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-06-2181. Epub 2003 Sep 11. Blood. 2004. PMID: 12969967
-
Inhibitors in young boys with haemophilia.Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2000 Sep;13(3):457-68. doi: 10.1053/beha.2000.0088. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2000. PMID: 11030045 Review.
-
Genetic mechanisms of age regulation of blood coagulation: factor IX model.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000 Apr;20(4):902-6. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.20.4.902. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000. PMID: 10764652 Review.
Cited by
-
B Cell Depletion Eliminates FVIII Memory B Cells and Enhances AAV8-coF8 Immune Tolerance Induction When Combined With Rapamycin.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 24;11:1293. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01293. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32670285 Free PMC article.
-
An avian influenza A (H7N9) virus vaccine candidate based on the fusion protein of hemagglutinin globular head and Salmonella typhimurium flagellin.BMC Biotechnol. 2015 Aug 19;15:79. doi: 10.1186/s12896-015-0195-z. BMC Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26286143 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Tolerance Induction in Hemophilia B Dogs Fed with Transplastomic Lettuce.Mol Ther. 2017 Feb 1;25(2):512-522. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.11.009. Mol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28153098 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-based oral tolerance to hemophilia therapy employs a complex immune regulatory response including LAP+CD4+ T cells.Blood. 2015 Apr 9;125(15):2418-27. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-08-597070. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Blood. 2015. PMID: 25700434 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Modulatory Cell Therapy for Hemophilia B Based on CD20-Targeted Lentiviral Gene Transfer to Primary B Cells.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2017 Mar 29;5:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2017.03.005. eCollection 2017 Jun 16. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2017. PMID: 28480307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Warrier I, Ewenstein BM, Koerper MA, et al. Factor IX inhibitors and anaphylaxis in hemophilia B. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1997;19:23–7. - PubMed
-
- Warrier I. Management of haemophilia B patients with inhibitors and anaphylaxis. Haemophilia. 1998;4:574–6. - PubMed
-
- Warrier I, Lusher JM. Development of anaphylactic shock in haemophilia B patients with inhibitors. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1998;9(Suppl 1):S125–8. - PubMed
-
- Thorland EC, Drost JB, Lusher JM, et al. Anaphylactic response to factor IX replacement therapy in haemophilia B patients: complete gene deletions confer the highest risk. Haemophilia. 1999;5:101–5. - PubMed
-
- Jadhav M, Warrier I. Anaphylaxis in patients with hemophilia. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2000;26:205–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

