A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of RAD51 Reduces Homologous Recombination and Sensitizes Multiple Myeloma Cells to Doxorubicin
- PMID: 25401086
- PMCID: PMC4214226
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00289
A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of RAD51 Reduces Homologous Recombination and Sensitizes Multiple Myeloma Cells to Doxorubicin
Abstract
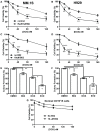
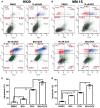
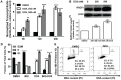
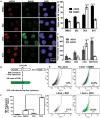
We previously reported high expression of RAD51 and increased homologous recombination (HR) rates in multiple myeloma (MM) cells, and showed that genomic instability and disease progression are commensurate with HR levels. Moreover, high RAD51 expression in vivo is associated with chemoresistance and poor patient survival. Doxorubicin (DOX) is one of the most widely used drug treatments in MM chemotherapy. DOX is cytotoxic because it induces DNA double-strand breaks, which can be repaired by RAD51-mediated HR; activation of this pathway thus contributes to resistance. To investigate the role of RAD51 in MM drug resistance, we assessed the ability of B02, a small-molecule inhibitor of RAD51, to enhance DOX sensitivity of MM cells. Combining low-toxicity doses of DOX and B02 resulted in significant synthetic lethality, observed as increased apoptosis and reduced viability compared to either agent alone, or to the product of their individual effects. In contrast, the combination did not produce significant synergy against normal human CD19(+) B cells from peripheral blood. DOX induced RAD51 at both mRNA and protein levels, while arresting cells in S and G2. DOX treatment also increased the number of RAD51 foci, a marker of HR repair, so that the fraction of cells with ≥5 foci rose fourfold, whereas γH2AX foci rose far less, implying that most new breaks are repaired. When B02 treatment preceded DOX exposure, the induction of RAD51 foci was severely blunted, whereas, γH2AX foci rose significantly relative to basal levels or either agent alone. In MM cells carrying a chromosomally integrated reporter of HR repair, DOX increased HR events while B02 inhibition of RAD51 blocked the HR response. These studies demonstrate the crucial role of RAD51 in protecting MM cells from genotoxic agents such as DOX, and suggest that specific inhibition of RAD51 may be an effective means to block DNA repair in MM cells and thus to enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy.
Keywords: B02; H2AX; RAD51; chemoresistance; doxorubicin; homologous recombination; multiple myeloma; recombinase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RAD51 Is Implicated in DNA Damage, Chemoresistance and Immune Dysregulation in Solid Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 20;14(22):5697. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225697. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428789 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of Rad51 Expression and Activity Potentiates the Cytotoxic Effect of Osimertinib in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Chemotherapy. 2025;70(1):12-25. doi: 10.1159/000540867. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Chemotherapy. 2025. PMID: 39128459
-
Prolonged Particulate Hexavalent Chromium Exposure Suppresses Homologous Recombination Repair in Human Lung Cells.Toxicol Sci. 2016 Sep;153(1):70-8. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfw103. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Toxicol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27449664 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of RAD51 at the Transcriptional and Functional Levels: What Prospects for Cancer Therapy?Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 11;13(12):2930. doi: 10.3390/cancers13122930. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34208195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting homologous recombination, new pre-clinical and clinical therapeutic combinations inhibiting RAD51.Cancer Treat Rev. 2015 Jan;41(1):35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Nov 1. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015. PMID: 25467108 Review.
Cited by
-
Valproic acid causes radiosensitivity of breast cancer cells via disrupting the DNA repair pathway.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2016 Feb 18;5(3):859-870. doi: 10.1039/c5tx00476d. eCollection 2016 May 1. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2016. PMID: 30090395 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of DNA Repair in Genomic Instability of Multiple Myeloma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 19;23(10):5688. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105688. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Development of Non-PIKKs Targeting Small Molecule Inhibitors of DNA Double-Strand Break Repair.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 6;12:850883. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.850883. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35463312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TERRA G-quadruplex stabilization as a new therapeutic strategy for multiple myeloma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Mar 27;42(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02633-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36967378 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Effect of Endogenous and Exogenous Aldehydes on Doxorubicin Toxicity in Yeast.Biomed Res Int. 2018 May 30;2018:4938189. doi: 10.1155/2018/4938189. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30003101 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

