DSTYK kinase domain ablation impaired the mice capabilities of learning and memory in water maze test
- PMID: 25400726
- PMCID: PMC4230056
DSTYK kinase domain ablation impaired the mice capabilities of learning and memory in water maze test
Abstract
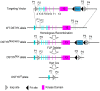
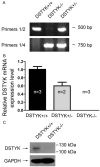
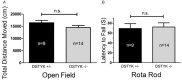
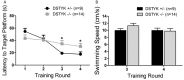
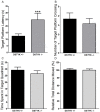
DSTYK (Dual serine/threonine and tyrosine protein kinase) is a putative dual Ser/Thr and Tyr protein kinase with unique structural features. It is proposed that DSTYK may play important roles in brain because of its high expression in most brain areas. In the present study, a DSTYK knockout (KO) mouse line with the ablation of C-terminal of DSTYK including the kinase domain was generated to study the physiological function of DSTYK. The DSTYK KO mice are fertile and have no significant morphological defects revealed by Nissl staining compared with wildtype mice. Open field test and rotarod test showed there is no obvious difference in basic motor and balance capacity between the DSTYK homozygous KO mice and DSTYK heterozygous KO mice. In water maze test, however, the DSTYK homozygous KO mice show impaired capabilities of learning and memory compared with the DSTYK heterozygous KO mice.
Keywords: DSTYK; brain development; knockout mice; learning and memory.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Episodic-like and procedural memory impairments in histamine H1 Receptor knockout mice coincide with changes in acetylcholine esterase activity in the hippocampus and dopamine turnover in the cerebellum.Neuroscience. 2008 Dec 2;157(3):532-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.09.025. Epub 2008 Sep 25. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18926883
-
Male and female Fmr1 knockout mice on C57 albino background exhibit spatial learning and memory impairments.Genes Brain Behav. 2010 Aug;9(6):562-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2010.00585.x. Epub 2010 Apr 6. Genes Brain Behav. 2010. PMID: 20398059
-
Behavioural phenotyping of knockout mice for the sigma-1 (σ₁) chaperone protein revealed gender-related anxiety, depressive-like and memory alterations.J Psychopharmacol. 2011 Jul;25(7):960-75. doi: 10.1177/0269881111400648. Epub 2011 May 9. J Psychopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21555330
-
Behavioral performance of tfm mice supports the beneficial role of androgen receptors in spatial learning and memory.Brain Res. 2005 Feb 9;1034(1-2):132-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.12.002. Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15713264
-
Hyperactivity, neuromotor defects, and impaired learning and memory in a mouse model for metachromatic leukodystrophy.Brain Res. 2001 Jul 13;907(1-2):35-43. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)02374-5. Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11430883
Cited by
-
DSTYK Promotes Metastasis and Chemoresistance via EMT in Colorectal Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 2;11:1250. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01250. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32982725 Free PMC article.
-
DSTYK inhibition increases the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to T cell-mediated cytotoxicity.J Exp Med. 2022 Dec 5;219(12):e20220726. doi: 10.1084/jem.20220726. Epub 2022 Sep 28. J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 36169652 Free PMC article.
-
Dstyk mutation leads to congenital scoliosis-like vertebral malformations in zebrafish via dysregulated mTORC1/TFEB pathway.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 24;11(1):479. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14169-z. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 31980602 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Insight into Paraptosis-Related Classification and Signature in Lower-Grade Gliomas.Int J Genomics. 2022 Nov 14;2022:6465760. doi: 10.1155/2022/6465760. eCollection 2022. Int J Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36419652 Free PMC article.
-
Large Intragenic Deletion in DSTYK Underlies Autosomal-Recessive Complicated Spastic Paraparesis, SPG23.Am J Hum Genet. 2017 Feb 2;100(2):364-370. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.01.014. Am J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28157540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zha J, Zhou Q, Xu LG, Chen D, Li L, Zhai Z, Shu HB. RIP5 is a RIP-homologous inducer of cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;319:298–303. - PubMed
-
- Hu ZL, Huang Y, Tao XR, Qi ZH, Chen JY, Ding YQ. Inducible Prrxl1-CreER(T2) recombination activity in the somatosensory afferent pathway. Genesis. 2012;50:552–560. - PubMed
-
- Sanna-Cherchi S, Sampogna RV, Papeta N, Burgess KE, Nees SN, Perry BJ, Choi M, Bodria M, Liu Y, Weng PL, Lozanovski VJ, Verbitsky M, Lugani F, Sterken R, Paragas N, Caridi G, Carrea A, Dagnino M, Materna-Kiryluk A, Santamaria G, Murtas C, Ristoska-Bojkovska N, Izzi C, Kacak N, Bianco B, Giberti S, Gigante M, Piaggio G, Gesualdo L, Kosuljandic Vukic D, Vukojevic K, Saraga-Babic M, Saraga M, Gucev Z, Allegri L, Latos-Bielenska A, Casu D, State M, Scolari F, Ravazzolo R, Kiryluk K, Al-Awqati Q, D’Agati VD, Drummond IA, Tasic V, Lifton RP, Ghiggeri GM, Gharavi AG. Mutations in DSTYK and dominant urinary tract malformations. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:621–629. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
