EFR3s are palmitoylated plasma membrane proteins that control responsiveness to G-protein-coupled receptors
- PMID: 25380825
- PMCID: PMC4282049
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.157495
EFR3s are palmitoylated plasma membrane proteins that control responsiveness to G-protein-coupled receptors
Abstract
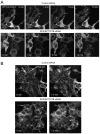
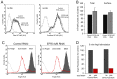
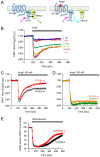
The yeast Efr3p protein is a main regulator of the Stt4p phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase at contact sites between the endoplasmic reticulum and the plasma membrane. A mutation in its fly homologue Rbo, leads to diminished light responses in the eye attributed to progressively impaired PLC signaling. Here, we find that Efr3s plays a role in maintaining responsiveness to the type-I angiotensin II (AngII) receptors. siRNA-mediated depletion of EFR3A and EFR3B impaired the sustained phase of cytosolic Ca(2+) response to high concentration of AngII in HEK293 cells that express wild type but not truncated AGTR1 (AT1a receptor), missing the phosphorylation sites. Efr3 depletion had minimal effect on the recovery of plasma membrane phosphoinositides during stimulation, and AT1 receptors still underwent ligand-induced internalization. A higher level of basal receptor phosphorylation and a larger response was observed after stimulation. Moreover, Gq activation more rapidly desensitized after AngII stimulation in Efr3 downregulated cells. A similar but less pronounced effect of EFR3 depletion was observed on the desensitization of the cAMP response after stimulation with isoproterenol. These data suggest that mammalian Efr3s contribute to the control of the phosphorylation state and, hence, desensitization of AT1a receptors, and could affect responsiveness of G-protein-coupled receptors in higher eukaryotes.
Keywords: Angiotensin II; EFR3; GPCR; PI 4-kinase; Phosphoinositide; Receptor desensitization.
© 2015. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Altered patterns of agonist-stimulated cAMP accumulation in cells expressing mutant beta 2-adrenergic receptors lacking phosphorylation sites.Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;36(4):641-6. Mol Pharmacol. 1989. PMID: 2554115
-
Phosphorylation of the angiotensin II (AT1A) receptor carboxyl terminus: a role in receptor endocytosis.Mol Endocrinol. 1998 Oct;12(10):1513-24. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.10.0179. Mol Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9773975
-
Clathrin-dependent internalization of the angiotensin II AT₁A receptor links receptor internalization to COX-2 protein expression in rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Feb 5;748:143-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.12.018. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25542758
-
Uncoupling of the beta-adrenergic receptor as a mechanism of in vitro neutrophil desensitization.J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Feb;103(2):322-32. J Lab Clin Med. 1984. PMID: 6319518
-
Molecular mechanisms of angiotensin II receptor internalization.J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999 Jan;10 Suppl 11:S47-56. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999. PMID: 9892140 Review.
Cited by
-
Joint genotype and ancestry analysis identify novel loci associated with atopic dermatitis in African American population.HGG Adv. 2024 Oct 10;5(4):100350. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2024.100350. Epub 2024 Sep 7. HGG Adv. 2024. PMID: 39245941 Free PMC article.
-
A novel cross-talk between CXCR4 and PI4KIIIα in prostate cancer cells.Oncogene. 2019 Jan;38(3):332-344. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0448-0. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 30111818 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid β oligomers suppress excitatory transmitter release via presynaptic depletion of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate.Nat Commun. 2019 Mar 13;10(1):1193. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09114-z. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30867420 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptor proteins mediate CXCR4 and PI4KA crosstalk in prostate cancer cells and the significance of PI4KA in bone tumor growth.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 23;13(1):20634. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47633-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37996444 Free PMC article.
-
The human olfactory transcriptome.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 11;17(1):619. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2960-3. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27515280 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balla A., Tuymetova G., Tsiomenko A., Várnai P., Balla T. (2005). A plasma membrane pool of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate is generated by phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type-III alpha: studies with the PH domains of the oxysterol binding protein and FAPP1. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 1282–1295 10.1091/mbc.E04-07-0578 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

