Epigenetic upregulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 in the spinal cord attenuates oestrogen-induced visceral hypersensitivity
- PMID: 25378524
- PMCID: PMC4562903
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307748
Epigenetic upregulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 in the spinal cord attenuates oestrogen-induced visceral hypersensitivity
Abstract
Objective: Epigenetic mechanisms are potential targets to relieve somatic pain. However, little is known whether epigenetic regulation interferes with visceral pain. Previous studies show that oestrogen facilitates visceral pain. This study aimed to determine whether histone hyperacetylation in the spinal cord could attenuate oestrogen-facilitated visceral pain.
Design: The effect of the histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) on the magnitude of the visceromotor response (VMR) to colorectal distention was examined in ovariectomised rats with/without oestrogen replacement. An additional interaction with the metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3 (mGluR2/3) antagonist LY341495 was tested. The levels of acetylated histone and mGluR2 mRNA and protein were analysed. The binding of acetylated H3 and oestrogen receptor α (ERα) to the GRM2 promoter was measured by chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with qPCR.
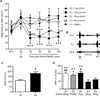
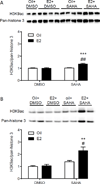
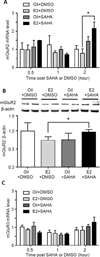
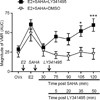
Results: In ovariectomised rats, 17β-estradiol (E2), but not safflower oil, increased the magnitude of the VMR to colorectal distention. SAHA attenuated the E2-facilitated VMR, but had no effect in safflower oil-treated rats. Subsequent spinal administration of LY341495 reversed the antinociceptive effect of SAHA in E2 rats. In addition, SAHA increased mGluR2 mRNA and protein in the spinal dorsal horn following E2, but not vehicle, treatment. In contrast, neither E2 nor SAHA alone altered mGluR2 mRNA. SAHA increased binding of H3K9ac and ERα to the same regions of the GRM2 promoter in E2-SAHA-treated animals.
Conclusions: Histone hyperacetylation in the spinal cord attenuates the pronociceptive effects of oestrogen on visceral sensitivity, suggesting that epigenetic regulation may be a potential approach to relieve visceral pain.
Keywords: IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME; NEUROPHARMACOLOGY; SEX STEROIDS; VISCERAL HYPERSENSITIVITY; VISCERAL NOCICEPTION.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
EXPRESS: Histone hyperacetylation modulates spinal type II metabotropic glutamate receptor alleviating stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity in female rats.Mol Pain. 2016 Jul 5;12:1744806916660722. doi: 10.1177/1744806916660722. Print 2016. Mol Pain. 2016. PMID: 27385724 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol modulates visceral hyperalgesia by increasing thoracolumbar spinal GluN2B subunit activity in female rats.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015 Jun;27(6):775-86. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12549. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015. PMID: 25810326 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modulation of mGlu2 receptors by histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of inflammatory pain.Mol Pharmacol. 2009 May;75(5):1014-20. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.054346. Epub 2009 Mar 2. Mol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19255242
-
Spinal microglia: A potential target in the treatment of chronic visceral pain.J Chin Med Assoc. 2014 Jan;77(1):3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Oct 1. J Chin Med Assoc. 2014. PMID: 24090601 Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of persistent pain.Transl Res. 2015 Jan;165(1):177-99. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2014.05.012. Epub 2014 May 29. Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 24948399 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Estrogens Play a Critical Role in Stress-Related Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in a Spontaneous Model of Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction.Cells. 2022 Apr 4;11(7):1214. doi: 10.3390/cells11071214. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406778 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Modulation of Pain by the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors.Cells. 2022 Aug 21;11(16):2608. doi: 10.3390/cells11162608. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36010684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress-induced visceral pain in female rats is associated with epigenetic remodeling in the central nucleus of the amygdala.Neurobiol Stress. 2021 Sep 20;15:100386. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100386. eCollection 2021 Nov. Neurobiol Stress. 2021. PMID: 34584907 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal CCK1 Receptors Contribute to Somatic Pain Hypersensitivity Induced by Malocclusion via a Reciprocal Neuron-Glial Signaling Cascade.J Pain. 2022 Oct;23(10):1629-1645. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2022.05.009. Epub 2022 Jun 10. J Pain. 2022. PMID: 35691467 Free PMC article.
-
Role of estrogen and stress on the brain-gut axis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):G203-G209. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00144.2019. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31241977 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
