The Not5 subunit of the ccr4-not complex connects transcription and translation
- PMID: 25340856
- PMCID: PMC4207488
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004569
The Not5 subunit of the ccr4-not complex connects transcription and translation
Abstract
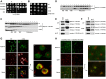
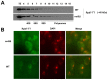
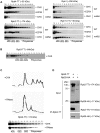
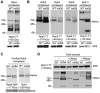
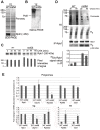
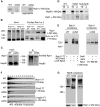
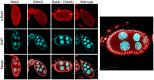
Recent studies have suggested that a sub-complex of RNA polymerase II composed of Rpb4 and Rpb7 couples the nuclear and cytoplasmic stages of gene expression by associating with newly made mRNAs in the nucleus, and contributing to their translation and degradation in the cytoplasm. Here we show by yeast two hybrid and co-immunoprecipitation experiments, followed by ribosome fractionation and fluorescent microscopy, that a subunit of the Ccr4-Not complex, Not5, is essential in the nucleus for the cytoplasmic functions of Rpb4. Not5 interacts with Rpb4; it is required for the presence of Rpb4 in polysomes, for interaction of Rpb4 with the translation initiation factor eIF3 and for association of Rpb4 with mRNAs. We find that Rpb7 presence in the cytoplasm and polysomes is much less significant than that of Rpb4, and that it does not depend upon Not5. Hence Not5-dependence unlinks the cytoplasmic functions of Rpb4 and Rpb7. We additionally determine with RNA immunoprecipitation and native gel analysis that Not5 is needed in the cytoplasm for the co-translational assembly of RNA polymerase II. This stems from the importance of Not5 for the association of the R2TP Hsp90 co-chaperone with polysomes translating RPB1 mRNA to protect newly synthesized Rpb1 from aggregation. Hence taken together our results show that Not5 interconnects translation and transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dissociation of Rpb4 from RNA polymerase II is important for yeast functionality.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 25;13(10):e0206161. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206161. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30359412 Free PMC article.
-
Rpb4 subunit functions mainly in mRNA synthesis by RNA polymerase II.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 20;289(25):17446-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.568014. Epub 2014 May 5. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24802753 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II subunits link transcription and mRNA decay to translation.Cell. 2010 Nov 12;143(4):552-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.10.033. Cell. 2010. PMID: 21074047
-
RNA polymerase II phosphorylation and gene looping: new roles for the Rpb4/7 heterodimer in regulating gene expression.Curr Genet. 2020 Oct;66(5):927-937. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01084-w. Epub 2020 Jun 7. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32508001 Review.
-
Rpb4 and Rpb7: subunits of RNA polymerase II and beyond.Trends Biochem Sci. 2004 Dec;29(12):674-81. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.10.007. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004. PMID: 15544954 Review.
Cited by
-
The Ccr4-Not complex regulates TORC1 signaling and mitochondrial metabolism by promoting vacuole V-ATPase activity.PLoS Genet. 2020 Oct 16;16(10):e1009046. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009046. eCollection 2020 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 33064727 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome dynamics and mRNA turnover, a complex relationship under constant cellular scrutiny.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021 Nov;12(6):e1658. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1658. Epub 2021 May 5. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021. PMID: 33949788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenesis of RNA Polymerases in Yeast.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 28;8:669300. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.669300. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34026841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissociation of Rpb4 from RNA polymerase II is important for yeast functionality.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 25;13(10):e0206161. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206161. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30359412 Free PMC article.
-
The FgNot3 Subunit of the Ccr4-Not Complex Regulates Vegetative Growth, Sporulation, and Virulence in Fusarium graminearum.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 22;11(1):e0147481. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147481. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26799401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilera A (2005) Cotranscriptional mRNP assembly: from the DNA to the nuclear pore. Current opinion in cell biology 17: 242–250. - PubMed
-
- de Almeida SF, Carmo-Fonseca M (2008) The CTD role in cotranscriptional RNA processing and surveillance. FEBS letters 582: 1971–1976. - PubMed
-
- Harel-Sharvit L, Eldad N, Haimovich G, Barkai O, Duek L, et al. (2010) RNA polymerase II subunits link transcription and mRNA decay to translation. Cell 143: 552–563. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

