Chromobacterium Csp_P reduces malaria and dengue infection in vector mosquitoes and has entomopathogenic and in vitro anti-pathogen activities
- PMID: 25340821
- PMCID: PMC4207801
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004398
Chromobacterium Csp_P reduces malaria and dengue infection in vector mosquitoes and has entomopathogenic and in vitro anti-pathogen activities
Abstract
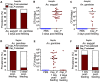
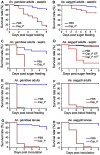
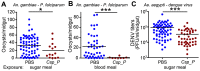
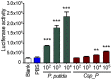
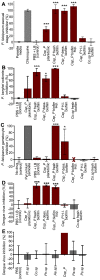
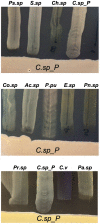
Plasmodium and dengue virus, the causative agents of the two most devastating vector-borne diseases, malaria and dengue, are transmitted by the two most important mosquito vectors, Anopheles gambiae and Aedes aegypti, respectively. Insect-bacteria associations have been shown to influence vector competence for human pathogens through multi-faceted actions that include the elicitation of the insect immune system, pathogen sequestration by microbes, and bacteria-produced anti-pathogenic factors. These influences make the mosquito microbiota highly interesting from a disease control perspective. Here we present a bacterium of the genus Chromobacterium (Csp_P), which was isolated from the midgut of field-caught Aedes aegypti. Csp_P can effectively colonize the mosquito midgut when introduced through an artificial nectar meal, and it also inhibits the growth of other members of the midgut microbiota. Csp_P colonization of the midgut tissue activates mosquito immune responses, and Csp_P exposure dramatically reduces the survival of both the larval and adult stages. Ingestion of Csp_P by the mosquito significantly reduces its susceptibility to Plasmodium falciparum and dengue virus infection, thereby compromising the mosquito's vector competence. This bacterium also exerts in vitro anti-Plasmodium and anti-dengue activities, which appear to be mediated through Csp_P -produced stable bioactive factors with transmission-blocking and therapeutic potential. The anti-pathogen and entomopathogenic properties of Csp_P render it a potential candidate for the development of malaria and dengue control strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Infection of highly insecticide-resistant malaria vector Anopheles coluzzii with entomopathogenic bacteria Chromobacterium violaceum reduces its survival, blood feeding propensity and fecundity.Malar J. 2020 Oct 2;19(1):352. doi: 10.1186/s12936-020-03420-4. Malar J. 2020. PMID: 33008454 Free PMC article.
-
A Nonlive Preparation of Chromobacterium sp. Panama (Csp_P) Is a Highly Effective Larval Mosquito Biopesticide.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 May 19;86(11):e00240-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00240-20. Print 2020 May 19. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32220845 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal tripartite interactions between the Aedes aegypti midgut microbiota, innate immune system and dengue virus influences vector competence.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(3):e1561. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001561. Epub 2012 Mar 6. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012. PMID: 22413032 Free PMC article.
-
Can Wolbachia be used to control malaria?Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2011 Aug;106 Suppl 1:212-7. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762011000900026. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2011. PMID: 21881776 Review.
-
Pathogen-insect interaction candidate molecules for transmission-blocking control strategies of vector borne diseases.Salud Publica Mex. 2018 Jan-Feb;60(1):77-85. doi: 10.21149/8140. Salud Publica Mex. 2018. PMID: 29689660 Review.
Cited by
-
An obligate microsporidian parasite modulates defense against opportunistic bacterial infection in the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti.mSphere. 2024 Feb 28;9(2):e0067823. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00678-23. Epub 2024 Feb 7. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38323845 Free PMC article.
-
Chromobacterium Csp_P biopesticide is toxic to larvae of three Diabrotica species including strains resistant to Bacillus thuringiensis.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 25;12(1):17858. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22229-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36284199 Free PMC article.
-
Complexity of virus-vector interactions.Curr Opin Virol. 2016 Dec;21:81-86. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2016.08.008. Epub 2016 Aug 28. Curr Opin Virol. 2016. PMID: 27580489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mosquito Trilogy: Microbiota, Immunity and Pathogens, and Their Implications for the Control of Disease Transmission.Front Microbiol. 2021 Apr 6;12:630438. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.630438. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33889137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zika virus outbreak in the Pacific: Vector competence of regional vectors.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Jul 17;12(7):e0006637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006637. eCollection 2018 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 30016372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gonzalez-Ceron L, Santillan F, Rodriguez MH, Mendez D, Hernandez-Avila JE (2003) Bacteria in Midguts of Field-Collected Anopheles albimanus Block Plasmodium vivax Sporogonic Development. J Med Entomol 40: 371–374. - PubMed
-
- Ramirez JL, Souza-Neto J, Torres Cosme R, Rovira J, Ortiz A, et al. (2012) Reciprocal tripartite interactions between the Aedes aegypti midgut microbiota, innate immune system and dengue virus influences vector competence. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6: e1561 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001561 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

