Lipid clustering correlates with membrane curvature as revealed by molecular simulations of complex lipid bilayers
- PMID: 25340788
- PMCID: PMC4207469
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003911
Lipid clustering correlates with membrane curvature as revealed by molecular simulations of complex lipid bilayers
Abstract
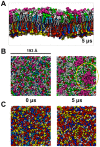
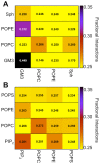
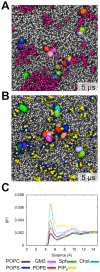
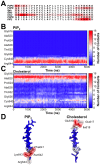
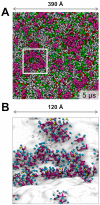
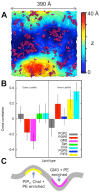
Cell membranes are complex multicomponent systems, which are highly heterogeneous in the lipid distribution and composition. To date, most molecular simulations have focussed on relatively simple lipid compositions, helping to inform our understanding of in vitro experimental studies. Here we describe on simulations of complex asymmetric plasma membrane model, which contains seven different lipids species including the glycolipid GM3 in the outer leaflet and the anionic lipid, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphophate (PIP2), in the inner leaflet. Plasma membrane models consisting of 1500 lipids and resembling the in vivo composition were constructed and simulations were run for 5 µs. In these simulations the most striking feature was the formation of nano-clusters of GM3 within the outer leaflet. In simulations of protein interactions within a plasma membrane model, GM3, PIP2, and cholesterol all formed favorable interactions with the model α-helical protein. A larger scale simulation of a model plasma membrane containing 6000 lipid molecules revealed correlations between curvature of the bilayer surface and clustering of lipid molecules. In particular, the concave (when viewed from the extracellular side) regions of the bilayer surface were locally enriched in GM3. In summary, these simulations explore the nanoscale dynamics of model bilayers which mimic the in vivo lipid composition of mammalian plasma membranes, revealing emergent nanoscale membrane organization which may be coupled both to fluctuations in local membrane geometry and to interactions with proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Domain coupling in asymmetric lipid bilayers.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jan;1788(1):64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.09.003. Epub 2008 Sep 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 18848518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The importance of membrane defects-lessons from simulations.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Aug 19;47(8):2244-51. doi: 10.1021/ar4002729. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24892900
-
Computer simulations of lipid membrane domains.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Aug;1828(8):1765-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.03.004. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23500617 Review.
-
Interactions of the EGFR juxtamembrane domain with PIP2-containing lipid bilayers: Insights from multiscale molecular dynamics simulations.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1850(5):1017-1025. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.09.006. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25219456 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Structure-Function Insights from Asymmetric Lipid Vesicles.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Aug 20;52(8):2382-2391. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00300. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31386337 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nanoporous Membranes of Densely Packed Carbon Nanotubes Formed by Lipid-Mediated Self-Assembly.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 Feb 19;7(2):528-534. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.2c00585. Epub 2022 Sep 7. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 36070609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural organization and dynamics of FCHo2 docking on membranes.Elife. 2022 Jan 19;11:e73156. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73156. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35044298 Free PMC article.
-
K-Ras G-domain binding with signaling lipid phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-phosphate (PIP2): membrane association, protein orientation, and function.J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 26;294(17):7068-7084. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004021. Epub 2019 Feb 21. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30792310 Free PMC article.
-
Formation and Properties of a Self-Assembled Nanoparticle-Supported Lipid Bilayer Probed through Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Langmuir. 2020 May 26;36(20):5524-5533. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c00593. Epub 2020 May 12. Langmuir. 2020. PMID: 32362127 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid regulation of the glucagon receptor family.J Endocrinol. 2024 May 6;261(3):e230335. doi: 10.1530/JOE-23-0335. Print 2024 Jun 1. J Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38614123 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Quinn PJ (2012) Lipid-lipid interactions in bilayer membranes: Married couples and casual liaisons. Progress Lipid Res 51: 179–198. - PubMed
-
- Lingwood D, Simons K (2010) Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science 327: 46–50. - PubMed
-
- Lee AG (2004) How lipids affect the activities of integral membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1666: 62–87. - PubMed
-
- Niggli V (2005) Regulation of protein activities by phosphoinositide phosphates. Ann Rev Cell Develop Biol 21: 57–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

