Hedgehog signaling restrains bladder cancer progression by eliciting stromal production of urothelial differentiation factors
- PMID: 25314078
- PMCID: PMC4326077
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2014.09.001
Hedgehog signaling restrains bladder cancer progression by eliciting stromal production of urothelial differentiation factors
Abstract
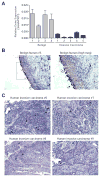
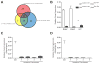
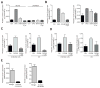
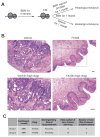
Hedgehog (Hh) pathway inhibitors are clinically effective in treatment of basal cell carcinoma and medulloblastoma, but fail therapeutically or accelerate progression in treatment of endodermally derived colon and pancreatic cancers. In bladder, another organ of endodermal origin, we find that despite its initial presence in the cancer cell of origin Sonic hedgehog (Shh) expression is invariably lost during progression to invasive urothelial carcinoma. Genetic blockade of stromal response to Shh furthermore dramatically accelerates progression and decreases survival time. This cancer-restraining effect of Hh pathway activity is associated with stromal expression of BMP signals, which stimulate urothelial differentiation. Progression is dramatically reduced by pharmacological activation of BMP pathway activity with low-dose FK506, suggesting an approach to management of human bladder cancer.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Re: Hedgehog Signaling Restrains Bladder Cancer Progression by Eliciting Stromal Production of Urothelial Differentiation Factors.J Urol. 2015 Jul;194(1):261. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.04.038. Epub 2015 Apr 16. J Urol. 2015. PMID: 26088255 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Re: Hedgehog Signaling Restrains Bladder Cancer Progression by Eliciting Stromal Production of Urothelial Differentiation Factors.J Urol. 2015 Jul;194(1):261. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.04.038. Epub 2015 Apr 16. J Urol. 2015. PMID: 26088255 No abstract available.
-
Epigenetic regulation of mammalian Hedgehog signaling to the stroma determines the molecular subtype of bladder cancer.Elife. 2019 Apr 30;8:e43024. doi: 10.7554/eLife.43024. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31036156 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of hedgehog pathway components is associated with bladder cancer progression and clinical outcome.Pathol Oncol Res. 2012 Apr;18(2):349-55. doi: 10.1007/s12253-011-9451-2. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Pathol Oncol Res. 2012. PMID: 21861243
-
Role of Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) Signaling in Bladder Cancer Stemness and Tumorigenesis.Curr Urol Rep. 2016 Feb;17(2):11. doi: 10.1007/s11934-015-0568-9. Curr Urol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26757905 Review.
-
Hedgehog Signaling in Colorectal Cancer: All in the Stroma?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 20;22(3):1025. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031025. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33498528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin Affects Gastric Cancer Cell Migration, Invasion and Cytoskeletal Remodeling Through Gli1-β-Catenin.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 May 21;12:3795-3806. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S244384. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32547215 Free PMC article.
-
The Hedgehog pathway: role in cell differentiation, polarity and proliferation.Arch Toxicol. 2015 Feb;89(2):179-91. doi: 10.1007/s00204-014-1433-1. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Arch Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25559776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of TFCP2L1 by CDK1 is required for stem cell pluripotency and bladder carcinogenesis.EMBO Mol Med. 2020 Jan 9;12(1):e10880. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201910880. Epub 2019 Nov 11. EMBO Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31709755 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting stromal remodeling and cancer stem cell plasticity overcomes chemoresistance in triple negative breast cancer.Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 24;9(1):2897. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05220-6. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30042390 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Possible correlation of sonic hedgehog signaling with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in muscle-invasive bladder cancer progression.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 Sep;145(9):2261-2271. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02987-z. Epub 2019 Jul 31. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31367836
References
-
- Ahn S, Joyner AL. In vivo analysis of quiescent adult neural stem cells responding to Sonic hedgehog. Nature. 2005;437:894–897. - PubMed
-
- Bragdon B, Moseychuk O, Saldanha S, King D, Julian J, Nohe A. Bone morphogenetic proteins: a critical review. Cell Signal. 2011;23:609–620. - PubMed
-
- Bryan GT. The pathogenesis of experimental bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 1977;37:2813–2816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

