Tumor suppression by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase: mechanisms and opportunities
- PMID: 25314076
- PMCID: PMC4227608
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2014.09.013
Tumor suppression by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase: mechanisms and opportunities
Abstract
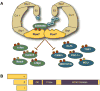
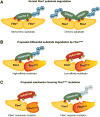
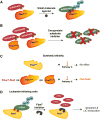
Tumor suppressors with widespread impact on carcinogenesis control broad spectra of oncogenic pathways. Protein degradation is an emerging mechanism by which tumor suppressors regulate a diversity of pathways and is exemplified by the SCF(Fbw7) ubiquitin ligase. Rapidly accumulating data indicate that SCF(Fbw7) regulates a network of crucial oncoproteins. Importantly, the FBXW7 gene, which encodes Fbw7, is one of the most frequently mutated genes in human cancers. These studies are yielding important new insights into tumorigenesis and may soon enable therapies targeting the Fbw7 pathway. Here, we focus on the mechanisms and consequences of Fbw7 deregulation in cancers and discuss possible therapeutic approaches.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor suppressor functions of FBW7 in cancer development and progression.FEBS Lett. 2012 May 21;586(10):1409-18. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.03.017. Epub 2012 Mar 21. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22673505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dependence of Human Colorectal Cells Lacking the FBW7 Tumor Suppressor on the Spindle Assembly Checkpoint.Genetics. 2015 Nov;201(3):885-95. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.180653. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 26354767 Free PMC article.
-
FBW7 ubiquitin ligase: a tumour suppressor at the crossroads of cell division, growth and differentiation.Nat Rev Cancer. 2008 Feb;8(2):83-93. doi: 10.1038/nrc2290. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18094723 Review.
-
Aberrant regulation of FBW7 in cancer.Oncotarget. 2014 Apr 30;5(8):2000-15. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1859. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24899581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Fbw7/human CDC4 tumor suppressor targets proproliferative factor KLF5 for ubiquitination and degradation through multiple phosphodegron motifs.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 11;285(24):18858-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.099440. Epub 2010 Apr 13. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20388706 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
FBW7 regulates DNA interstrand cross-link repair by modulating FAAP20 degradation.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 14;7(24):35724-35740. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9595. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27232758 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering and Targeting Oncogenic Mutations and Pathways in Breast Cancer.Oncologist. 2016 Sep;21(9):1063-78. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0369. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 27384237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the F-box Proteins FBXW2 and FBXL14 in the Initiation of Bone Regeneration in Transplants given to Nude Mice.Open Biomed Eng J. 2018 Oct 18;12:75-89. doi: 10.2174/1874120701812010075. eCollection 2018. Open Biomed Eng J. 2018. PMID: 30450135 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus and the landscape of secondary genetic alterations in oral cancers.Genome Res. 2019 Jan;29(1):1-17. doi: 10.1101/gr.241141.118. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Genome Res. 2019. PMID: 30563911 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Regulation of the p53 Family Proteins by the Ubiquitin Proteasomal Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 30;21(1):261. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010261. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31905981 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akhoondi S, Sun D, von der Lehr N, Apostolidou S, Klotz K, Maljukova A, Cepeda D, Fiegl H, Dafou D, Marth C, et al. FBXW7/hCDC4 is a general tumor suppressor in human cancer. Cancer research. 2007;67:9006–9012. - PubMed
-
- Babaei-Jadidi R, Li N, Saadeddin A, Spencer-Dene B, Jandke A, Muhammad B, Ibrahim EE, Muraleedharan R, Abuzinadah M, Davis H, et al. FBXW7 influences murine intestinal homeostasis and cancer, targeting Notch, Jun, and DEK for degradation. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2011;208:295–312. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bahram F, von der Lehr N, Cetinkaya C, Larsson LG. c-Myc hot spot mutations in lymphomas result in inefficient ubiquitination and decreased proteasome-mediated turnover. Blood. 2000;95:2104–2110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

