Epigenetic modifications of Keap1 regulate its interaction with the protective factor Nrf2 in the development of diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 25301875
- PMCID: PMC4231994
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.14-15193
Epigenetic modifications of Keap1 regulate its interaction with the protective factor Nrf2 in the development of diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
Purpose: Diabetes induces oxidative imbalance in the retina and impairs Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response, and elevates Keap1, the cytoplasmic repressor of Nrf2. The goal of this study was to understand the role of epigenetic modifications at Keap1 promoter in regulation of Nrf2 function.
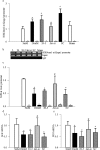
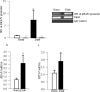
Methods: The effect of high glucose on the binding of transcriptional factor Sp1 at Keap1 promoter and histone methylation status of the promoter was investigated in retinal endothelial cells. Role of histone methylation was confirmed in cells transfected with siRNA of methyltransferase enzyme Set7/9 (SetD7). In vitro results were confirmed in the retina from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The role of epigenetic modifications of Keap1 promoter in the metabolic memory was examined in rats maintained in poor control for 3 months followed by good control for 3 months.
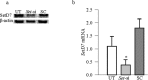
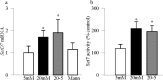
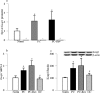
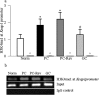
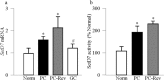
Results: Hyperglycemia increased the binding of Sp1 at Keap1 promoter, and enriched H3K4me1 and activated SetD7. SetD7-siRNA prevented increase in Sp1 binding at Keap1 promoter and Keap1 expression, and ameliorated decrease in Nrf2-regulated antioxidant genes. Cessation of hyperglycemia failed to attenuate increased binding of Sp1 at Keap1, and the promoter continued to be methylated with increased expression of Keap1 and decreased expression of Nrf2-regulated genes.
Conclusions: Epigenetic modifications at Keap1 promoter by SetD7 facilitate its binding with Sp1, increasing its expression. Keap1 restrains Nrf2 in the cytosol, impairing its transcriptional activity. Reversal of hyperglycemia fails to provide any benefit to epigenetic modifications of Keap1 promoter, suggesting their role in both the development of diabetic retinopathy and the metabolic memory phenomenon.
Keywords: Keap1; Nrf2; diabetic retinopathy; epigenetic modifications; metabolic memory.
Copyright 2014 The Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology, Inc.
Figures
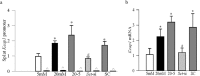
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic regulation of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):337-349. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.013. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26117320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription factor Nrf2-mediated antioxidant defense system in the development of diabetic retinopathy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Jun 6;54(6):3941-8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-11598. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23633659 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modifications of Nrf2-mediated glutamate-cysteine ligase: implications for the development of diabetic retinopathy and the metabolic memory phenomenon associated with its continued progression.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Oct;75:129-39. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.07.001. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 25016074 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 and Regulation of the Antioxidant Defense System in Diabetic Retinopathy.Diabetes. 2021 Jan;70(1):227-239. doi: 10.2337/db20-0375. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 33051272 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of redox signaling in diabetic retinopathy: Role of Nrf2.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Feb;103:155-164. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.12.030. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28012783 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DNA Methylation Profiles of PSMA6, PSMB5, KEAP1, and HIF1A Genes in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Diabetic Retinopathy.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 18;12(6):1354. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061354. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927561 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing Dimethyl Fumarate for Cardiovascular Diseases: Pharmacological Effects, Molecular Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Promise.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Apr 19;15(5):497. doi: 10.3390/ph15050497. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probucol promotes high glucose-induced proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by reducing reactive oxygen species generation in Müller cells.Int Ophthalmol. 2019 Dec;39(12):2833-2842. doi: 10.1007/s10792-019-01130-8. Epub 2019 May 29. Int Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31144240
-
NRF2-Related Epigenetic Modifications in Cardiac and Vascular Complications of Diabetes Mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jun 25;12:598005. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.598005. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34248833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):337-349. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.013. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26117320 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baynes JW, Thrope SR. Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications: a new perspective on an old paradigm. Diabetes. 1999; 48: 1–9. - PubMed
-
- Kowluru RA, Engerman RL, Kern TS. Abnormalities of retinal metabolism in diabetes or experimental galactosemia VI. Comparison of retinal and cerebral cortex metabolism, and effects of antioxidant therapy. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999; 26: 371–378. - PubMed
-
- Kowluru RA, Tang J, Kern TS. Abnormalities of retinal metabolism in diabetes and experimental galactosemia. VII. Effect of long-term administration of antioxidants on the development of retinopathy. Diabetes. 2001; 50: 1938–1942. - PubMed
-
- Kowluru RA. Diabetic retinopathy, oxidative stress and antioxidants. Curr Topics Nutraceutical Res. 2005; 3: 209–218.
-
- Kern TS, Kowluru R, Engerman RL. Abnormalities of retinal metabolism in diabetes or galactosemia. ATPases and glutathione. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994; 35: 2962–2967. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

