MiR-181b-5p downregulates NOVA1 to suppress proliferation, migration and invasion and promote apoptosis in astrocytoma
- PMID: 25299073
- PMCID: PMC4192361
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109124
MiR-181b-5p downregulates NOVA1 to suppress proliferation, migration and invasion and promote apoptosis in astrocytoma
Erratum in
-
Correction: MiR-181b-5p Downregulates NOVA1 to Suppress Proliferation, Migration and Invasion and Promote Apoptosis in Astrocytoma.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 1;19(7):e0306667. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306667. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38950023 Free PMC article.
Abstract
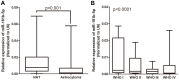
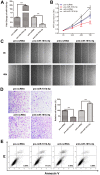
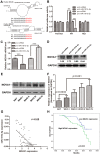
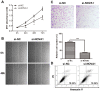
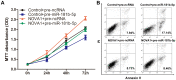
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, short noncoding RNAs that modulate the expression of numerous genes by targeting their mRNA. Numerous abnormal miRNA expression patterns are observed in various human malignancies, and certain miRNAs can act as oncogenes or tumor suppressors. Astrocytoma, the most common neuroepithelial cancer, represents the majority of malignant brain tumors in humans. In our previous studies, we found that the downregulation of miR-181b-5p in astrocytomas is associated with a poor prognosis. The aim of the present study was to investigate the functional role of miR-181b-5p and its possible target genes. miR-181b-5p was significantly downregulated in astrocytoma specimens, and the reduced expression of miR-181b-5p was inversely correlated with the clinical stage. The ectopic expression of miR-181b-5p inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion and induced apoptosis in astrocytoma cancer cells in vitro. The NOVA1 (neuro-oncological ventral antigen 1) gene was further identified as a novel direct target of miR-181b-5p. Specifically, miR-181b-5p bound directly to the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of NOVA1 and suppressed its expression. In clinical specimens, NOVA1 was overexpressed, and its protein levels were inversely correlated with miR-181b-5p expression. Furthermore, the changing level of NOVA1 was significantly associated with a poor survival outcome. Similar to restoring miR-181b-5p expression, downregulating NOVA1 inhibited cell growth, migration and invasion. Overexpression of NOVA1 reversed the inhibitory effects of miR-181b-5p. Our results indicate that miR-181b-5p is a tumor suppressor in astrocytoma that inhibits tumor progression by targeting NOVA1. These findings suggest that miR-181b-5p may serve as a novel therapeutic target for astrocytoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-193a-5p exerts a tumor suppressor role in glioblastoma via modulating NOVA1.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;120(4):6188-6197. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27906. Epub 2018 Oct 10. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30304561
-
miR-137 acts as a tumor suppressor in astrocytoma by targeting RASGRF1.Tumour Biol. 2016 Mar;37(3):3331-40. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4110-y. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26440052
-
miR-106a-5p inhibits the proliferation and migration of astrocytoma cells and promotes apoptosis by targeting FASTK.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 27;8(8):e72390. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072390. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24013584 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miRNA‑122 in cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Sep;65(3):83. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5671. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39027994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Biomarkers in Astrocytoma: Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Potential.World Neurosurg. 2024 Sep;189:339-350.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2024.06.009. Epub 2024 Jun 8. World Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 38857866 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-124-3p regulates cell proliferation, invasion, apoptosis, and bioenergetics by targeting PIM1 in astrocytoma.Cancer Sci. 2016 Jul;107(7):899-907. doi: 10.1111/cas.12946. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27088547 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MALAT1 mediates doxorubicin resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating miR-3129-5p/Nova1 axis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Jan;476(1):279-292. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03904-6. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 32965597
-
NOVA1 acts as an oncogene in melanoma via regulating FOXO3a expression.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 May;22(5):2622-2630. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13527. Epub 2018 Mar 2. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29498217 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA‑181 serves an oncogenic role in breast cancer via the inhibition of SPRY4.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Dec;18(6):5603-5613. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9572. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Mol Med Rep. 2018. Retraction in: Mol Med Rep. 2022 May;25(5):157. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12673. PMID: 30365052 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Luteolin suppresses tumor proliferation through inducing apoptosis and autophagy via MAPK activation in glioma.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Mar 28;12:2383-2396. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S191158. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 30992674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359: 492–507. - PubMed
-
- Gabayan AJ, Green SB, Sanan A, Jenrette J, Schultz C, et al. (2006) GliaSite brachytherapy for treatment of recurrent malignant gliomas: a retrospective multi-institutional analysis. Neurosurgery 58: 701–709 discussion – - PubMed
-
- Esteller M (2011) Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet 12: 861–874. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

