Structural modulation of gut microbiota during alleviation of type 2 diabetes with a Chinese herbal formula
- PMID: 25279787
- PMCID: PMC4331591
- DOI: 10.1038/ismej.2014.177
Structural modulation of gut microbiota during alleviation of type 2 diabetes with a Chinese herbal formula
Abstract
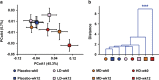
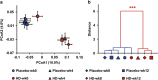
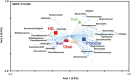
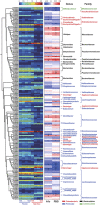
The gut microbiota is hypothesized to have a critical role in metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes (T2D). A traditional Chinese herbal formula, Gegen Qinlian Decoction (GQD), can alleviate T2D. To find out whether GQD modulates the composition of the gut microbiota during T2D treatment, 187 T2D patients were randomly allocated to receive high (HD, n=44), moderate (MD, n=52), low dose GQD (LD, n=50) or the placebo (n=41) for 12 weeks in a double-blinded trial. Patients who received the HD or MD demonstrated significant reductions in adjusted mean changes from baseline of fasting blood glucose (FBG) and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) compared with the placebo and LD groups. Pyrosequencing of the V3 regions of 16S rRNA genes revealed a dose-dependent deviation of gut microbiota in response to GQD treatment. This deviation occurred before significant improvement of T2D symptoms was observed. Redundancy analysis identified 47 GQD-enriched species level phylotypes, 17 of which were negatively correlated with FBG and 9 with HbA1c. Real-time quantitative PCR confirmed that GQD significantly enriched Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, which was negatively correlated with FBG, HbA1c and 2-h postprandial blood glucose levels and positively correlated with homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function. Therefore, these data indicate that structural changes of gut microbiota are induced by Chinese herbal formula GQD. Specifically, GQD treatment may enrich the amounts of beneficial bacteria, such as Faecalibacterium spp. In conclusion, changes in the gut microbiota are associated with the anti-diabetic effects of GQD.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural Alteration of Gut Microbiota during the Amelioration of Human Type 2 Diabetes with Hyperlipidemia by Metformin and a Traditional Chinese Herbal Formula: a Multicenter, Randomized, Open Label Clinical Trial.mBio. 2018 May 22;9(3):e02392-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02392-17. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29789365 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Alleviation Effects of GQD, a Traditional Chinese Medicine Formula, on Diabetes Rats Linked to Modulation of the Gut Microbiome.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Oct 8;11:740236. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.740236. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34692563 Free PMC article.
-
Double-blinded, randomized clinical trial of Gegen Qinlian decoction pinpoints Faecalibacterium as key gut bacteria in alleviating hyperglycemia.Precis Clin Med. 2024 Feb 14;7(1):pbae003. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbae003. eCollection 2024 Mar. Precis Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38495337 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of Gegen Qinlian decoction for normalizing hyperglycemia in diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Complement Ther Med. 2017 Aug;33:6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 26. Complement Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28735827 Review.
-
The role of gut microbiota in the development of type 1, type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2015 Mar;16(1):55-65. doi: 10.1007/s11154-015-9309-0. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2015. PMID: 25619480 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Herbal Formula-3 ameliorates OVA-induced food allergy in mice may via modulating the gut microbiota.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Sep 15;11(9):5812-5823. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31632550 Free PMC article.
-
Variability in the Response of Bacterial Community Assembly to Environmental Selection and Biotic Factors Depends on the Immigrated Bacteria, as Revealed by a Soil Microcosm Experiment.mSystems. 2019 Dec 3;4(6):e00496-19. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00496-19. mSystems. 2019. PMID: 31796565 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiota: The Potential Key Target of TCM's Therapeutic Effect of Treating Different Diseases Using the Same Method-UC and T2DM as Examples.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Mar 30;12:855075. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.855075. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35433500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interrelations between Gut Microbiota Composition, Nutrient Intake and Diabetes Status in an Adult Japanese Population.J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 5;11(11):3216. doi: 10.3390/jcm11113216. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35683603 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiota and Antidiabetic Drugs: Perspectives of Personalized Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 May 31;12:853771. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.853771. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35711668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. 1998;15:539–553. - PubMed
-
- Balamurugan R, Janardhan HP, George S, Chittaranjan SP, Ramakrishna BS. Bacterial succession in the colon during childhood and adolescence: molecular studies in a southern Indian village. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;88:1643–1647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

