The 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 3 enzyme potently synthesizes the 2'-5'-oligoadenylates required for RNase L activation
- PMID: 25275129
- PMCID: PMC4249133
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01763-14
The 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 3 enzyme potently synthesizes the 2'-5'-oligoadenylates required for RNase L activation
Abstract
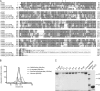
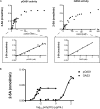
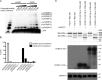
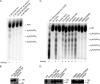
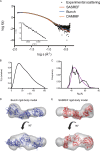
The members of the oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS) family of proteins are antiviral restriction factors that target a wide range of RNA and DNA viruses. They function as intracellular double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) sensors that, upon binding to dsRNA, undergo a conformational change and are activated to synthesize 2'-5'-linked oligoadenylates (2-5As). 2-5As of sufficient length act as second messengers to activate RNase L and thereby restrict viral replication. We expressed human OAS3 using the baculovirus system and purified it to homogeneity. We show that recombinant OAS3 is activated at a substantially lower concentration of dsRNA than OAS1, making it a potent in vivo sensor of dsRNA. Moreover, we find that OAS3 synthesizes considerably longer 2-5As than previously reported, and that OAS3 can activate RNase L intracellularly. The combined high affinity for dsRNA and the capability to produce 2-5As of sufficient length to activate RNase L suggests that OAS3 is a potent activator of RNase L. In addition, we provide experimental evidence to support one active site of OAS3 located in the C-terminal OAS domain and generate a low-resolution structure of OAS3 using SAXS.
Importance: We are the first to purify the OAS3 enzyme to homogeneity, which allowed us to characterize the mechanism utilized by OAS3 and identify the active site. We provide compelling evidence that OAS3 can produce 2'-5'-oligoadenylates of sufficient length to activate RNase L. This is contrary to what is described in the current literature but agrees with recent in vivo data showing that OAS3 harbors an antiviral activity requiring RNase L. Thus, our work redefines our understanding of the biological role of OAS3. Furthermore, we used a combination of mutagenesis and small-angle X-ray scattering to describe the active site and low-resolution structure of OAS3.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of RNase L in Egyptian Rousette Bat-Derived RoNi/7 Cells Is Dependent Primarily on OAS3 and Independent of MAVS Signaling.mBio. 2019 Nov 12;10(6):e02414-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02414-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31719180 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of RNase L is dependent on OAS3 expression during infection with diverse human viruses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 23;113(8):2241-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1519657113. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26858407 Free PMC article.
-
RNase L Antiviral Activity Is Not a Critical Component of the Oas1b-Mediated Flavivirus Resistance Phenotype.J Virol. 2019 Oct 29;93(22):e00946-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00946-19. Print 2019 Nov 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31462564 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct domain organization and diversity of 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetases.Biochem Cell Biol. 2024 Aug 1;102(4):305-318. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2023-0369. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Biochem Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38603810 Review.
-
Photolabeling of the enzymes of the 2-5A synthetase/RNase L/p68 kinase antiviral systems with azido probes.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1994;14:260-75. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78549-8_15. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1994. PMID: 7520331 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Functional evolution of the OAS1 viral sensor: Insights from old world primates.Infect Genet Evol. 2016 Oct;44:341-350. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Infect Genet Evol. 2016. PMID: 27393659 Free PMC article.
-
OAS1 and OAS3 negatively regulate the expression of chemokines and interferon-responsive genes in human macrophages.BMB Rep. 2019 Feb;52(2):133-138. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.2.129. BMB Rep. 2019. PMID: 30078389 Free PMC article.
-
Double-Stranded RNA Sensors and Modulators in Innate Immunity.Annu Rev Immunol. 2019 Apr 26;37:349-375. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-042718-041356. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Annu Rev Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30673536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of novel interferon responsive protein partners of human leukocyte antigen A (HLA-A) using cross-linking mass spectrometry (CLMS) approach.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 12;12(1):19422. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21393-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36371414 Free PMC article.
-
Oligoadenylate synthase-like (OASL) proteins: dual functions and associations with diseases.Exp Mol Med. 2015 Mar 6;47(3):e144. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.110. Exp Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25744296 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

