Transcriptome-wide characterization of the eIF4A signature highlights plasticity in translation regulation
- PMID: 25273840
- PMCID: PMC4203936
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-014-0476-1
Transcriptome-wide characterization of the eIF4A signature highlights plasticity in translation regulation
Abstract
Background: Protein synthesis is tightly regulated and alterations to translation are characteristic of many cancers.Translation regulation is largely exerted at initiation through the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 F (eIF4F). eIF4F is pivotal for oncogenic signaling as it integrates mitogenic signals to amplify production of pro-growth and pro-survival factors. Convergence of these signals on eIF4F positions this factor as a gatekeeper of malignant fate. While the oncogenic properties of eIF4F have been characterized, genome-wide evaluation of eIF4F translational output is incomplete yet critical for developing novel translation-targeted therapies.
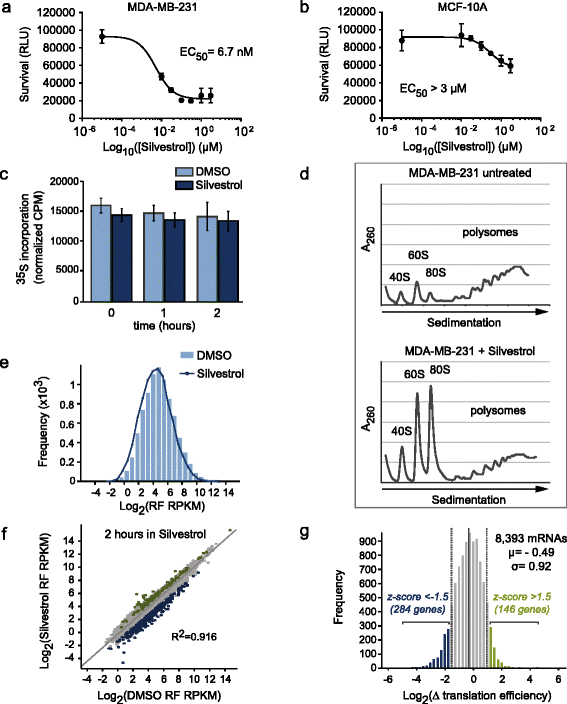
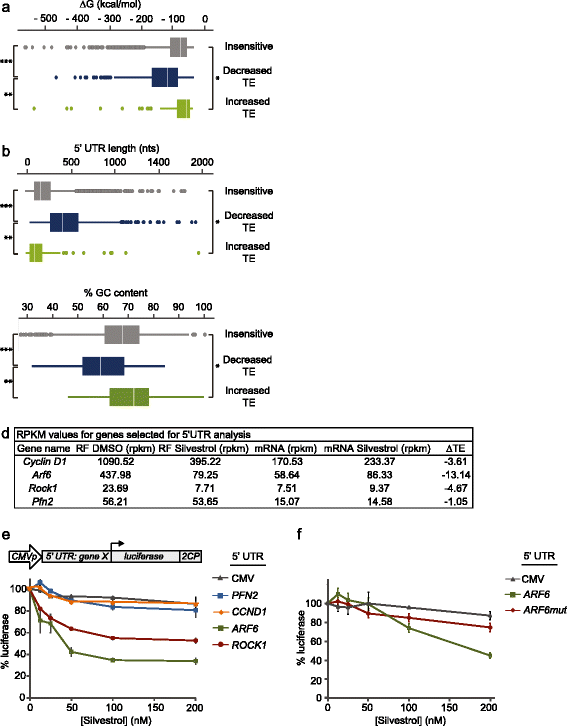
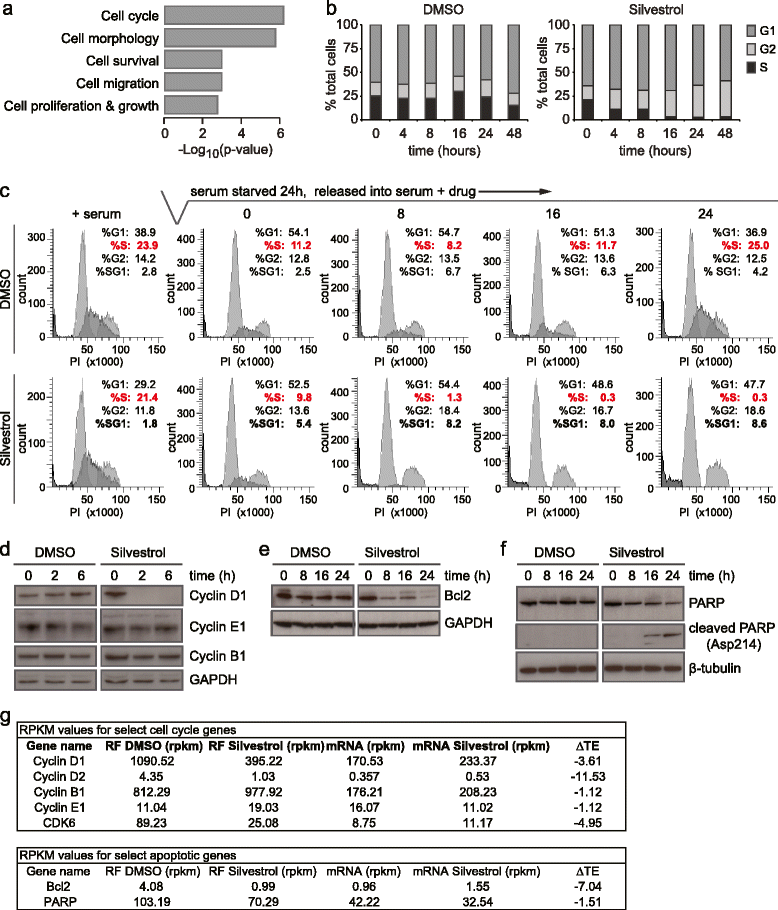
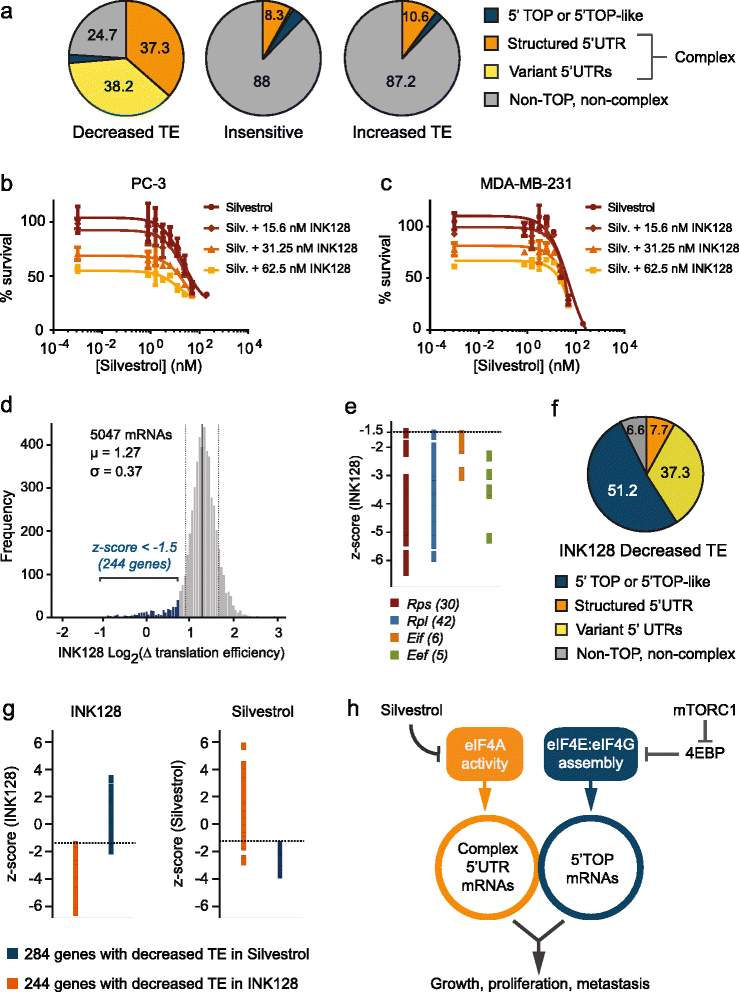
Results: To understand the impact of eIF4F on malignancy, we utilized a genome-wide ribosome profiling approach to identify eIF4F-driven mRNAs in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Using Silvestrol, a selective eIF4A inhibitor, we identify 284 genes that rely on eIF4A for efficient translation. Our screen confirmed several known eIF4F-dependent genes and identified many unrecognized targets of translation regulation. We show that 5′UTR complexity determines Silvestrol-sensitivity and altering 5′UTR structure modifies translational output. We highlight physiological implications of eIF4A inhibition, providing mechanistic insight into eIF4F pro-oncogenic activity.
Conclusions: Here we describe the transcriptome-wide consequence of eIF4A inhibition in malignant cells, define mRNA features that confer eIF4A dependence, and provide genetic support for Silvestrol’s anti-oncogenic properties. Importantly, our results show that eIF4A inhibition alters translation of an mRNA subset distinct from those affected by mTOR-mediated eIF4E inhibition. These results have significant implications for therapeutically targeting translation and underscore a dynamic role for eIF4F in remodeling the proteome toward malignancy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibiting CARD11 translation during BCR activation by targeting the eIF4A RNA helicase.Blood. 2014 Dec 11;124(25):3758-67. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-07-589689. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25320244 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA structural elements immediately upstream of the start codon dictate dependence upon eIF4A helicase activity.Genome Biol. 2019 Dec 30;20(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1901-2. Genome Biol. 2019. PMID: 31888698 Free PMC article.
-
eIF4B stimulates translation of long mRNAs with structured 5' UTRs and low closed-loop potential but weak dependence on eIF4G.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Sep 20;113(38):10464-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1612398113. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27601676 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting RNA helicases in cancer: The translation trap.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017 Dec;1868(2):510-520. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.09.006. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28965870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the eIF4A RNA helicase as an anti-neoplastic approach.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jul;1849(7):781-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.09.006. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25234619 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Helicases as Shadow Modulators of Cell Cycle Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 15;22(6):2984. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062984. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the eIF4F translation initiation complex: a critical nexus for cancer development.Cancer Res. 2015 Jan 15;75(2):250-63. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2789. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25593033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aven recognition of RNA G-quadruplexes regulates translation of the mixed lineage leukemia protooncogenes.Elife. 2015 Aug 12;4:e06234. doi: 10.7554/eLife.06234. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26267306 Free PMC article.
-
An mRNA-binding channel in the ES6S region of the translation 48S-PIC promotes RNA unwinding and scanning.Elife. 2019 Dec 2;8:e48246. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48246. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31789591 Free PMC article.
-
A parasitic fungus employs mutated eIF4A to survive on rocaglate-synthesizing Aglaia plants.Elife. 2023 Feb 28;12:e81302. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81302. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36852480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Larsson O, Li S, Issaenko OA, Avdulov S, Peterson M, Smith K, Bitterman PB, Polunovsky VA. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E induced progression of primary human mammary epithelial cells along the cancer pathway is associated with targeted translational deregulation of oncogenic drivers and inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2007;67:6814–6824. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0752. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Heys SD, Park KG, McNurlan MA, Calder AG, Buchan V, Blessing K, Eremin O, Garlick PJ. Measurement of tumour protein synthesis in vivo in human colorectal and breast cancer and its variability in separate biopsies from the same tumour. Clin Sci (Lond) 1991;80:587–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

