miR-15a/16 regulates macrophage phagocytosis after bacterial infection
- PMID: 25261473
- PMCID: PMC4216178
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401372
miR-15a/16 regulates macrophage phagocytosis after bacterial infection
Abstract
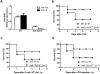
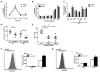
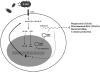
Bacterial infection and its associated sepsis are devastating clinical entities that lead to high mortality and morbidity in critically ill patients. Phagocytosis, along with other innate immune responses, exerts crucial impacts on the outcomes of these patients. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a novel class of regulatory noncoding RNAs that target specific mRNAs for modulation of translation and expression of a targeted protein. The roles of miRNAs in host defense against bacterial sepsis remain unclear. We found that bacterial infections and/or bacterial-derived LPS enhanced the level of miR-15a/16 in bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). Deletion of miR-15a/16 (miR-15a/16(-/-)) in myeloid cells significantly decreased the bacterial infection-associated mortality in sepsis mouse models. Moreover, miR-15a/16 deficiency (miR-15a/16(-/-)) resulted in augmented phagocytosis and generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in BMDMs. Supportively, overexpression of miR-15a/16 using miRNA mimics led to decreased phagocytosis and decreased generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Mechanistically, deletion of miR-15a/16 upregulated the expression of TLR4 via targeting the principle transcriptional regulator PU.1 locating on the promoter region of TLR4, and further modulated the downstream signaling molecules of TLR4, including Rho GTPase Cdc 42 and TRAF6. In addition, deficiency of miR-15a/16 also facilitated TLR4-mediated proinflammatory cytokine/chemokine release from BMDMs at the initial phase of infections. Taken together, miR-15a/16 altered phagocytosis and bacterial clearance by targeting, at least partially, on the TLR4-associated pathways, subsequently affecting the survival of septic mice.
Copyright © 2014 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
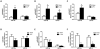
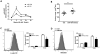

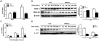
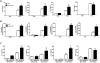
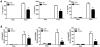
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-21 Limits Uptake of Listeria monocytogenes by Macrophages to Reduce the Intracellular Niche and Control Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 May 23;7:201. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00201. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28589100 Free PMC article.
-
miR-718 represses proinflammatory cytokine production through targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN).J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 7;292(14):5634-5644. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.749325. Epub 2017 Feb 16. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28209713 Free PMC article.
-
The miR-15a-5p-XIST-CUL3 regulatory axis is important for sepsis-induced acute kidney injury.Ren Fail. 2019 Nov;41(1):955-966. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1669460. Ren Fail. 2019. PMID: 31658856 Free PMC article.
-
Early innate immune responses to bacterial LPS.Curr Opin Immunol. 2017 Feb;44:14-19. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.10.005. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Curr Opin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27842237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Host miRNAs by Intracellular Bacterial Pathogens.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Aug 3;6:79. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00079. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27536558 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression and 7-day time course of circulating microRNAs in septic patients treated with nephrotoxic antibiotic agents.BMC Nephrol. 2022 Mar 19;23(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-02726-6. BMC Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35305556 Free PMC article.
-
miR-15a-5p regulates expression of multiple proteins in the megakaryocyte GPVI signaling pathway.J Thromb Haemost. 2019 Mar;17(3):511-524. doi: 10.1111/jth.14382. Epub 2019 Feb 25. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 30632265 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs reshape immunity and inflammatory responses in bacterial infection.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2018 May 25;3:14. doi: 10.1038/s41392-018-0006-9. eCollection 2018. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2018. PMID: 29844933 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of MicroRNA Expression Profiles in Weaned Pig Skeletal Muscle after Lipopolysaccharide Challenge.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Sep 16;16(9):22438-55. doi: 10.3390/ijms160922438. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26389897 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as Regulators of Phagocytosis.Cells. 2022 Apr 19;11(9):1380. doi: 10.3390/cells11091380. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563685 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deutschman CS, Tracey KJ. Sepsis: Current Dogma and New Perspectives. Immunity. 2014;40:463–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

