In vivo RNAi screening identifies a mechanism of sorafenib resistance in liver cancer
- PMID: 25216638
- PMCID: PMC4587571
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3679
In vivo RNAi screening identifies a mechanism of sorafenib resistance in liver cancer
Abstract
In solid tumors, resistance to therapy inevitably develops upon treatment with cytotoxic drugs or molecularly targeted therapies. Here, we describe a system that enables pooled shRNA screening directly in mouse hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC) in vivo to identify genes likely to be involved in therapy resistance. Using a focused shRNA library targeting genes located within focal genomic amplifications of human HCC, we screened for genes whose inhibition increased the therapeutic efficacy of the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib. Both shRNA-mediated and pharmacological silencing of Mapk14 (p38α) were found to sensitize mouse HCC to sorafenib therapy and prolong survival by abrogating Mapk14-dependent activation of Mek-Erk and Atf2 signaling. Elevated Mapk14-Atf2 signaling predicted poor response to sorafenib therapy in human HCC, and sorafenib resistance of p-Mapk14-expressing HCC cells could be reverted by silencing Mapk14. Our results suggest that a combination of sorafenib and Mapk14 blockade is a promising approach to overcoming therapy resistance of human HCC.
Figures
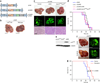

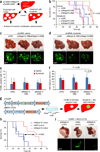


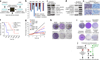
Comment in
-
Liver cancer: sorafenib resistance uncovered by novel RNAi screen.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014 Nov;11(11):622. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.166. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25286973 No abstract available.
-
Making sorafenib irresistible: In vivo screening for mechanisms of therapy resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma hits on Mapk14.Hepatology. 2015 May;61(5):1755-7. doi: 10.1002/hep.27739. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25677471 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Making sorafenib irresistible: In vivo screening for mechanisms of therapy resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma hits on Mapk14.Hepatology. 2015 May;61(5):1755-7. doi: 10.1002/hep.27739. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25677471 No abstract available.
-
BCRP/ABCG2 inhibition sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 31;8(12):e83627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083627. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24391798 Free PMC article.
-
Down-Regulation of TGF-β Expression Sensitizes the Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Sorafenib.Yonsei Med J. 2017 Sep;58(5):899-909. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.5.899. Yonsei Med J. 2017. PMID: 28792132 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of signaling pathways involved in sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma.Klin Lab Diagn. 2013 Oct;(10):66-8, 34-7. Klin Lab Diagn. 2013. PMID: 24640100 Review. English, Russian.
-
Molecular Mechanism and Prediction of Sorafenib Chemoresistance in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Dig Dis. 2015 Oct;33(6):771-9. doi: 10.1159/000439102. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Dig Dis. 2015. PMID: 26488287 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional repression of IFNβ1 by ATF2 confers melanoma resistance to therapy.Oncogene. 2015 Nov 12;34(46):5739-48. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.22. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25728676 Free PMC article.
-
Proline isomerisation as a novel regulatory mechanism for p38MAPK activation and functions.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Oct;23(10):1592-601. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.45. Epub 2016 May 27. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 27233083 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression: From Classic to Novel Clinicopathogenetic Implications.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 27;15(21):5178. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215178. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined De-Repression of Chemoresistance Associated Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 14 and Activating Transcription Factor 2 by Loss of microRNA-622 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 9;13(5):1183. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051183. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803354 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities and challenges provided by crosstalk between signalling pathways in cancer.Oncogene. 2016 Mar 3;35(9):1073-9. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.151. Epub 2015 May 18. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25982281 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

