Acute neuroinflammation impairs context discrimination memory and disrupts pattern separation processes in hippocampus
- PMID: 25209285
- PMCID: PMC4160778
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0542-14.2014
Acute neuroinflammation impairs context discrimination memory and disrupts pattern separation processes in hippocampus
Abstract
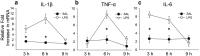
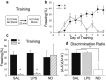
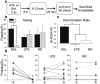
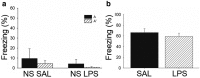
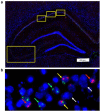
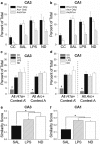
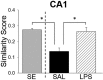
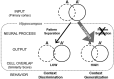
Although it is known that immune system activation can impair cognition, no study to date has linked cognitive deficits during acute neuroinflammation to dysregulation of task-relevant neuronal ensemble activity. Here, we assessed both neural circuit activity and context discrimination memory retrieval, in a within-subjects design, of male rats given systemic administration of saline or lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Rats were exposed over several days to two similar contexts: one of which was paired with weak foot shock and the other was not. After reaching criteria for discriminative freezing, rats were given systemic LPS or saline injection and tested for retrieval of context discrimination 6 h later. Importantly, LPS administration produced an acute neuroinflammatory response in dorsal hippocampus at this time (as assessed by elevation of proinflammatory cytokine mRNA levels) and abolished retrieval of the previously acquired discrimination. The impact of neuroinflammation on hippocampal CA3 and CA1 neural circuit activity was assessed using the Arc/Homer1a cellular analysis of temporal activity by fluorescence in situ hybridization imaging method. Whereas the saline-treated subjects discriminated and had low overlap of hippocampal ensembles activated in the two contexts, LPS-treated subjects did not discriminate and had greater ensemble overlap (i.e., reduced orthogonalization). Additionally, retrieval of standard contextual fear conditioning, which does not require context discrimination, was not affected by pretesting LPS administration. Together, the behavioral and circuit analyses data provide compelling evidence that LPS administration impairs context discrimination memory by disrupting cellular pattern separation processes within the hippocampus, thus linking acute neuroinflammation to disruption of specific neural circuit functions and cognitive impairment.
Keywords: computation; discrimination; hippocampus; imaging; memory; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/3412470-11$15.00/0.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic lipopolysaccharide administration impairs retrieval of context-object discrimination, but not spatial, memory: Evidence for selective disruption of specific hippocampus-dependent memory functions during acute neuroinflammation.Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Feb;44:159-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.09.014. Epub 2014 Oct 19. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 25451612 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation alters the hippocampal pattern of behaviorally induced Arc expression.J Neurosci. 2005 Jan 19;25(3):723-31. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4469-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15659610 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid-beta (1-42) lesion of CA1 rat dorsal hippocampus reduces contextual fear memory and increases expression of microglial genes regulating neuroinflammation.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Sep 1;393:112795. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112795. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 32619564
-
Deoxyelephantopin ameliorates lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced memory impairments in rats: Evidence for its anti-neuroinflammatory properties.Life Sci. 2018 Aug 1;206:45-60. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.05.035. Epub 2018 May 21. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29792878
-
Neuronal Ensembles Organize Activity to Generate Contextual Memory.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Mar 15;16:805132. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.805132. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35368306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
BAP31 regulates IRAK1-dependent neuroinflammation in microglia.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Dec 28;16(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1661-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31883536 Free PMC article.
-
Histological Architecture Underlying Brain-Immune Cell-Cell Interactions and the Cerebral Response to Systemic Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2017 Jan 19;8:17. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00017. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28154566 Free PMC article.
-
Acetyl-L-Carnitine via Upegulating Dopamine D1 Receptor and Attenuating Microglial Activation Prevents Neuronal Loss and Improves Memory Functions in Parkinsonian Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jan;55(1):583-602. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0293-5. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 27975173
-
Sex differences and similarities in the neuroimmune response to central administration of poly I:C.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Sep 6;18(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02235-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34488804 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal inflammation by gut microbiota disturbance induces memory impairment in mice.Mucosal Immunol. 2018 Mar;11(2):369-379. doi: 10.1038/mi.2017.49. Epub 2017 Jun 14. Mucosal Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28612842
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
