New insights in (inter)cellular mechanisms by heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- PMID: 25189801
- PMCID: PMC4221658
- DOI: 10.1007/s11897-014-0219-3
New insights in (inter)cellular mechanisms by heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
Abstract
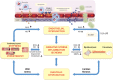
Recently, a new paradigm for the development of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) has been proposed, which identifies a systemic pro-inflammatory state induced by comorbidities as the origin of microvascular endothelial cell inflammation and subsequent concentric cardiac remodeling and dysfunction. This review further discusses the pivotal role of the inflamed endothelium in the pathogenesis of HFpEF-specific cardiac remodeling. The potential importance of reciprocal interactions of the endothelium with cardiac fibroblasts and cardiomyocytes and with the cardiac neurohumoral response in this cardiac remodeling process is outlined.
Conflict of interest statement
Carsten Tschöpe and Sophie Van Linthout declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel paradigm for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: comorbidities drive myocardial dysfunction and remodeling through coronary microvascular endothelial inflammation.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Jul 23;62(4):263-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.02.092. Epub 2013 May 15. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23684677 Review.
-
Connecting heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and renal dysfunction: the role of endothelial dysfunction and inflammation.Eur J Heart Fail. 2016 Jun;18(6):588-98. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.497. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016. PMID: 26861140 Review.
-
Inflammatory Mechanisms in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction.Physiology (Bethesda). 2023 Sep 1;38(5):0. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00004.2023. Epub 2023 Apr 4. Physiology (Bethesda). 2023. PMID: 37013947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and Molecular Differences between HFpEF and HFrEF: A Step Ahead in an Improved Pathological Understanding.Cells. 2020 Jan 18;9(1):242. doi: 10.3390/cells9010242. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31963679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiomyocyte Functional Etiology in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction Is Distinctive-A New Preclinical Model.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Jun 1;7(11):e007451. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007451. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29858360 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Options.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 14;10(9):2274. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092274. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac contractility modulation: mechanisms of action in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and beyond.Eur J Heart Fail. 2019 Jan;21(1):14-22. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1349. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019. PMID: 30485591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex-Specific Effects of Plastic Caging in Murine Viral Myocarditis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 17;22(16):8834. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168834. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445539 Free PMC article.
-
Similarities and Differences Between HFmrEF and HFpEF.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Sep 20;8:678614. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.678614. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34616777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Syndecan-2-Selected Mesenchymal Stromal Cells on the Early Onset of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy in Diabetic db/db Mice.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 May 21;8:632728. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.632728. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34095245 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

