Chromatin insulator factors involved in long-range DNA interactions and their role in the folding of the Drosophila genome
- PMID: 25165871
- PMCID: PMC4148193
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004544
Chromatin insulator factors involved in long-range DNA interactions and their role in the folding of the Drosophila genome
Abstract
Chromatin insulators are genetic elements implicated in the organization of chromatin and the regulation of transcription. In Drosophila, different insulator types were characterized by their locus-specific composition of insulator proteins and co-factors. Insulators mediate specific long-range DNA contacts required for the three dimensional organization of the interphase nucleus and for transcription regulation, but the mechanisms underlying the formation of these contacts is currently unknown. Here, we investigate the molecular associations between different components of insulator complexes (BEAF32, CP190 and Chromator) by biochemical and biophysical means, and develop a novel single-molecule assay to determine what factors are necessary and essential for the formation of long-range DNA interactions. We show that BEAF32 is able to bind DNA specifically and with high affinity, but not to bridge long-range interactions (LRI). In contrast, we show that CP190 and Chromator are able to mediate LRI between specifically-bound BEAF32 nucleoprotein complexes in vitro. This ability of CP190 and Chromator to establish LRI requires specific contacts between BEAF32 and their C-terminal domains, and dimerization through their N-terminal domains. In particular, the BTB/POZ domains of CP190 form a strict homodimer, and its C-terminal domain interacts with several insulator binding proteins. We propose a general model for insulator function in which BEAF32/dCTCF/Su(HW) provide DNA specificity (first layer proteins) whereas CP190/Chromator are responsible for the physical interactions required for long-range contacts (second layer). This network of organized, multi-layer interactions could explain the different activities of insulators as chromatin barriers, enhancer blockers, and transcriptional regulators, and suggest a general mechanism for how insulators may shape the organization of higher-order chromatin during cell division.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
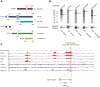
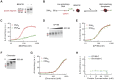
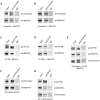

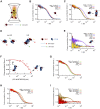
Similar articles
-
The chromosomal association/dissociation of the chromatin insulator protein Cp190 of Drosophila melanogaster is mediated by the BTB/POZ domain and two acidic regions.BMC Cell Biol. 2010 Dec 31;11:101. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-11-101. BMC Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 21194420 Free PMC article.
-
Functional sub-division of the Drosophila genome via chromatin looping: the emerging importance of CP190.Nucleus. 2013 Mar-Apr;4(2):115-22. doi: 10.4161/nucl.23389. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Nucleus. 2013. PMID: 23333867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coordinated control of dCTCF and gypsy chromatin insulators in Drosophila.Mol Cell. 2007 Dec 14;28(5):761-72. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.09.024. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 18082602 Free PMC article.
-
EAST Organizes Drosophila Insulator Proteins in the Interchromosomal Nuclear Compartment and Modulates CP190 Binding to Chromatin.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 21;10(10):e0140991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140991. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26489095 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin insulators: regulatory mechanisms and epigenetic inheritance.Mol Cell. 2008 Oct 10;32(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.017. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18851828 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Architectural proteins, transcription, and the three-dimensional organization of the genome.FEBS Lett. 2015 Oct 7;589(20 Pt A):2923-30. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.05.025. Epub 2015 May 22. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 26008126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The N-Terminal Part of Drosophila CP190 Is a Platform for Interaction with Multiple Architectural Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 2;24(21):15917. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115917. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958900 Free PMC article.
-
New Drosophila promoter-associated architectural protein Mzfp1 interacts with CP190 and is required for housekeeping gene expression and insulator activity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jul 8;52(12):6886-6905. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae393. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38769058 Free PMC article.
-
Su(Hw) interacts with Combgap to establish long-range chromatin contacts.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2024 May 21;17(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13072-024-00541-x. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2024. PMID: 38773468 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin Remodelers in the 3D Nuclear Compartment.Front Genet. 2020 Nov 3;11:600615. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.600615. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33329746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Elgin SC, Grewal SI (2003) Heterochromatin: silence is golden. Curr Biol 13: R895–R898. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

