Ginger compound [6]-shogaol and its cysteine-conjugated metabolite (M2) activate Nrf2 in colon epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 25148906
- PMCID: PMC4176387
- DOI: 10.1021/tx500211x
Ginger compound [6]-shogaol and its cysteine-conjugated metabolite (M2) activate Nrf2 in colon epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
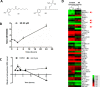
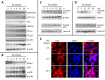
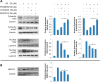
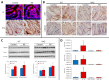
In this study, we identified Nrf2 as a molecular target of [6]-shogaol (6S), a bioactive compound isolated from ginger, in colon epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo. Following 6S treatment of HCT-116 cells, the intracellular GSH/GSSG ratio was initially diminished but was then elevated above the basal level. Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) correlated inversely with the GSH/GSSG ratio. Further analysis using gene microarray showed that 6S upregulated the expression of Nrf2 target genes (AKR1B10, FTL, GGTLA4, and HMOX1) in HCT-116 cells. Western blotting confirmed upregulation, phosphorylation, and nuclear translocation of Nrf2 protein followed by Keap1 decrease and upregulation of Nrf2 target genes (AKR1B10, FTL, GGTLA4, HMOX1, and MT1) and glutathione synthesis genes (GCLC and GCLM). Pretreatment of cells with a specific inhibitor of p38 (SB202190), PI3K (LY294002), or MEK1 (PD098059) attenuated these effects of 6S. Using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, we found that 6S modified multiple cysteine residues of Keap1 protein. In vivo 6S treatment induced Nrf2 nuclear translocation and significantly upregulated the expression of MT1, HMOX1, and GCLC in the colon of wild-type mice but not Nrf2(-/-) mice. Similar to 6S, a cysteine-conjugated metabolite of 6S (M2), which was previously found to be a carrier of 6S in vitro and in vivo, also activated Nrf2. Our data demonstrated that 6S and its cysteine-conjugated metabolite M2 activate Nrf2 in colon epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo through Keap1-dependent and -independent mechanisms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cysteine-conjugated metabolite of ginger component [6]-shogaol serves as a carrier of [6]-shogaol in cancer cells and in mice.Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):976-85. doi: 10.1021/tx4001286. Epub 2013 May 15. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23638641 Free PMC article.
-
6-shogaol-rich extract from ginger up-regulates the antioxidant defense systems in cells and mice.Molecules. 2012 Jul 4;17(7):8037-55. doi: 10.3390/molecules17078037. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 22763741 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 mediates 15-deoxy-Δ(12,14)-prostaglandin J2-induced expression of glutamate cysteine ligase expression via Nrf2 signaling in human breast cancer cells.Chem Res Toxicol. 2011 Aug 15;24(8):1231-41. doi: 10.1021/tx200090n. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Chem Res Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21728338
-
Synthesis, evaluation, and metabolism of novel [6]-shogaol derivatives as potent Nrf2 activators.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Jun;95:243-54. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.03.026. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27021962
-
A novel shogaol analog suppresses cancer cell invasion and inflammation, and displays cytoprotective effects through modulation of NF-κB and Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathways.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013 Nov 1;272(3):852-62. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.07.011. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23899529
Cited by
-
Influence of Diet on the Bioavailability of Active Components from Zingiber officinale Using an In Vitro Digestion Model.Foods. 2023 Oct 24;12(21):3897. doi: 10.3390/foods12213897. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37959015 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review on soft rot disease management in ginger (Zingiber officinale) for enhancing its pharmaceutical and industrial values.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 14;9(7):e18337. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18337. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37539157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immature ginger reduces triglyceride accumulation by downregulating Acyl CoA carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase-1 genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Food Nutr Res. 2023 Mar 2;67. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v67.9126. eCollection 2023. Food Nutr Res. 2023. PMID: 37050926 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of New Shogaol Analogues as NRF2 Activators and Evaluation of Their Anti-Inflammatory Activity, Modes of Action and Metabolic Stability.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Feb 13;12(2):475. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020475. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830033 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphenol-Rich Ginger (Zingiber officinale) for Iron Deficiency Anaemia and Other Clinical Entities Associated with Altered Iron Metabolism.Molecules. 2022 Sep 28;27(19):6417. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196417. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234956 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leung A. Y., and Foster S. (1996) Encyclopedia of Common Natural Ingredients Used in Food, Drugs, and Cosmetics, 2nd ed., pp 271–274, Wiley, New York.
-
- Jiang H.; Solyom A. M.; Timmermann B. N.; Gang D. R. (2005) Characterization of gingerol-related compounds in ginger rhizome (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) by high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 19, 2957–2964. - PubMed
-
- Jiang H.; Timmermann B. N.; Gang D. R. (2007) Characterization and identification of diarylheptanoids in ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) using high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 21, 509–518. - PubMed
-
- Jiang H.; Xie Z.; Koo H. J.; McLaughlin S. P.; Timmermann B. N.; Gang D. R. (2006) Metabolic profiling and phylogenetic analysis of medicinal Zingiber species: Tools for authentication of ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc). Phytochemistry 67, 1673–1685. - PubMed
-
- Yu Y.; Huang T.; Yang B.; Liu X.; Duan G. (2007) Development of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry with microwave distillation and simultaneous solid-phase microextraction for rapid determination of volatile constituents in ginger. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 43, 24–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

