SAR405838: an optimized inhibitor of MDM2-p53 interaction that induces complete and durable tumor regression
- PMID: 25145672
- PMCID: PMC4247201
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0799
SAR405838: an optimized inhibitor of MDM2-p53 interaction that induces complete and durable tumor regression
Abstract
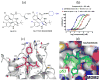
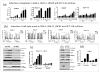
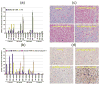
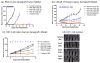
Blocking the oncoprotein murine double minute 2 (MDM2)-p53 protein-protein interaction has long been considered to offer a broad cancer therapeutic strategy, despite the potential risks of selecting tumors harboring p53 mutations that escape MDM2 control. In this study, we report a novel small-molecule inhibitor of the MDM2-p53 interaction, SAR405838 (MI-77301), that has been advanced into phase I clinical trials. SAR405838 binds to MDM2 with K(i) = 0.88 nmol/L and has high specificity over other proteins. A cocrystal structure of the SAR405838:MDM2 complex shows that, in addition to mimicking three key p53 amino acid residues, the inhibitor captures additional interactions not observed in the p53-MDM2 complex and induces refolding of the short, unstructured MDM2 N-terminal region to achieve its high affinity. SAR405838 effectively activates wild-type p53 in vitro and in xenograft tumor tissue of leukemia and solid tumors, leading to p53-dependent cell-cycle arrest and/or apoptosis. At well-tolerated dose schedules, SAR405838 achieves either durable tumor regression or complete tumor growth inhibition in mouse xenograft models of SJSA-1 osteosarcoma, RS4;11 acute leukemia, LNCaP prostate cancer, and HCT-116 colon cancer. Remarkably, a single oral dose of SAR405838 is sufficient to achieve complete tumor regression in the SJSA-1 model. Mechanistically, robust transcriptional upregulation of PUMA induced by SAR405838 results in strong apoptosis in tumor tissue, leading to complete tumor regression. Our findings provide a preclinical basis upon which to evaluate SAR405838 as a therapeutic agent in patients whose tumors retain wild-type p53.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Significant Differences in the Development of Acquired Resistance to the MDM2 Inhibitor SAR405838 between In Vitro and In Vivo Drug Treatment.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 12;10(6):e0128807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128807. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26070072 Free PMC article.
-
Novel MDM2 inhibitor SAR405838 (MI-773) induces p53-mediated apoptosis in neuroblastoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):82757-82769. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12634. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27764791 Free PMC article.
-
SAR405838: A Novel and Potent Inhibitor of the MDM2:p53 Axis for the Treatment of Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Mar 1;22(5):1150-60. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1522. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26475335 Free PMC article.
-
MDM2/X inhibitors under clinical evaluation: perspectives for the management of hematological malignancies and pediatric cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2017 Jul 3;10(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0500-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28673313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mouse models of Mdm2 and Mdm4 and their clinical implications.Chin J Cancer. 2013 Jul;32(7):371-5. doi: 10.5732/cjc.012.10286. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Chin J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23327795 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficient Synthesis of Fully Substituted Pyrrolidine-Fused 3-Spirooxindoles via 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of Aziridine and 3-Ylideneoxindole.Molecules. 2016 Aug 24;21(9):1113. doi: 10.3390/molecules21091113. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27563867 Free PMC article.
-
Rational drug design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel chiral tetrahydronaphthalene-fused spirooxindole as MDM2-CDK4 dual inhibitor against glioblastoma.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Aug;10(8):1492-1510. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.12.013. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 32963945 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous measurement of p53:Mdm2 and p53:Mdm4 protein-protein interactions in whole cells using fluorescence labelled foci.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 29;9(1):17933. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54123-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31784573 Free PMC article.
-
The R882H substitution in the human de novo DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A disrupts allosteric regulation by the tumor supressor p53.J Biol Chem. 2019 Nov 29;294(48):18207-18219. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010827. Epub 2019 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31640986 Free PMC article.
-
MDM2 Derived from Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma Extracellular Vesicles Induces MMP2 Production from Preadipocytes.Cancer Res. 2019 Oct 1;79(19):4911-4922. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0203. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31387924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hainaut P, Hollstein M. p53 and human cancer: the first ten thousand mutations. Advances in cancer research. 2000;77:81–137. - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Bayle JH, Olson D, Levine AJ. The p53-mdm2 autoregulatory feedback loop. Genes Dev. 1993;7:1126–32. - PubMed
-
- Momand J, Wu HH, Dasgupta G. MDM2--master regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Gene. 2000;242:15–29. - PubMed
-
- Bond GL, Hu W, Levine AJ. MDM2 is a central node in the p53 pathway: 12 years and counting. Current cancer drug targets. 2005;5:3–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

