Bone marrow-derived cells are implicated as a source of lymphatic endothelial progenitors in human breast cancer
- PMID: 25101222
- PMCID: PMC4121340
- DOI: 10.4161/onci.29080
Bone marrow-derived cells are implicated as a source of lymphatic endothelial progenitors in human breast cancer
Abstract
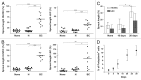
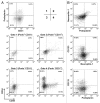
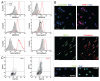
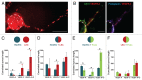
Bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) infiltrate into sites of neovascularization in adult tissues and mature into functional blood endothelial cells (BECs) during a process called vasculogenesis. Human marrow-derived EPCs have recently been reported to display a mixed myeloid and lymphatic endothelial cell (LEC) phenotype during inflammation-induced angiogenesis; however, their role in cancer remains poorly understood. We report the in vitro differentiation of human cord blood CD133+CD34+ progenitors into podoplanin+ cells expressing both myeloid markers (CD11b, CD14) and the canonical LEC markers vascular endothelium growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR-3), lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1 (LYVE-1), and prospero homeobox 1 (PROX-1). These podoplanin+ cells displayed sprouting behavior comparable to that of LECs in vitro and a dual hemangiogenic and lymphangiogenic activity in vivo in an endothelial cell sprouting assay and corneal vascularization assay, respectively. Furthermore, these cells expressed vascular endothelium growth factor (VEGF) family members A, -C, and -D. Thus, bone-marrow derived EPCs stimulate hemangiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis through their ability to differentiate into LECs and to produce angiogenic factors. Importantly, plasma from patients with breast cancer induced differentiation of CD34+ cord blood progenitors into hemangiogenic and lymphangiogenic CD11b+ myeloid cells, whereas plasma from healthy women did not have this effect. Consistent with these findings, circulating CD11b+ cells from breast cancer patients, but not from healthy women, displayed a similar dual angiogenic activity. Taken together, our results show that marrow-derived EPCs become hemangiogenic and lymphangiogenic upon exposure to cancer plasma. These newly identified functions of bone-marrow derived EPCs are expected to influence the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer.
Keywords: angiogenesis; bone-marrow derived cells; breast cancer; lymphangiogenesis; lymphatic endothelial cells; podoplanin; vasculogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD34+ VEGFR-3+ progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Mar;18(3):422-33. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12233. Epub 2014 Jan 22. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24450475 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphatic endothelial progenitors originate from plastic myeloid cells activated by toll-like receptor-4.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 9;12(6):e0179257. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179257. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28598999 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased Lymphangiogenic Activities and Genes Expression of Cord Blood Lymphatic Endothelial Progenitor Cells (VEGFR3+/Pod+/CD11b+ Cells) in Patient with Preeclampsia.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 19;22(8):4237. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084237. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921847 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphangiogenic growth factors, receptors and therapies.Thromb Haemost. 2003 Aug;90(2):167-84. doi: 10.1160/TH03-04-0200. Thromb Haemost. 2003. PMID: 12888864 Review.
-
[Characterization of markers and growth factors for lymphatic endothelium].Postepy Biochem. 2005;51(2):209-14. Postepy Biochem. 2005. PMID: 16209358 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
High Mobility Group Box-1 Promotes Inflammation-Induced Lymphangiogenesis via Toll-Like Receptor 4-Dependent Signalling Pathway.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 21;11(4):e0154187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154187. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27100831 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphatic Endothelial Cell Progenitors in the Tumor Microenvironment.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1234:87-105. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-37184-5_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32040857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Vasculogenic Factors in the Developing Embryo at Weeks Five and Seven With a Special Focus on CD133 and TIE2 Markers.Cureus. 2024 May 15;16(5):e60353. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60353. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38756714 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages: An Inflammatory Link Between Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis.Microcirculation. 2016 Feb;23(2):95-121. doi: 10.1111/micc.12259. Microcirculation. 2016. PMID: 26614117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of tumor neogenesis pipelines in tumor progression and their therapeutic potential.Cancer Med. 2023 Jan;12(2):1558-1571. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4979. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 35832030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
