MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China
- PMID: 25084400
- PMCID: PMC4118890
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103698
MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China
Abstract
Background: In South China (Gejiu City, Yunnan Province), lung cancer incidence and associated mortality rate is the most prevalent and observed forms of cancer. Lung cancer in this area is called Gejiu squamous cell lung carcinoma (GSQCLC). Research has demonstrated that overexpression of miR-21 occurs in many cancers. However, the unique relationship between miR-21 and its target genes in GSQCLC has never been investigated. The molecular mechanism involved in GSQCLC must be compared to other non-small cell lung cancers in order to establish a relation and identify potential therapeutic targets.
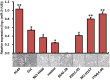
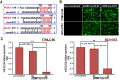
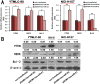
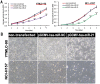
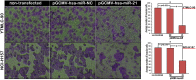
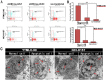
Methodology/principal findings: In the current study, we initially found overexpression of miR-21 occurring in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines when compared to the immortalized lung epithelial cell line BEAS-2B. We also demonstrated that high expression of miR-21 could increase tumor cell proliferation, invasion, viability, and migration in GSQCLC cell line (YTMLC-90) and NSCLC cell line (NCI-H157). Additionally, our results revealed that miR-21 could suppress YTMLC-90 and NCI-H157 cell apoptosis through arresting cell-cycle at G2/M phase. Furthermore, we demonstrated that PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2 are common target genes of miR-21 in NSCLC. Finally, our studies showed that down-regulation of miR-21 could lead to a significant increase in PTEN and RECK and decrease in Bcl-2 at the mRNA and protein level in YTMLC-90 and NCI-H157 cell lines. However, we have not observed any remarkable difference in the levels of miR-21 and its targets in YTMLC-90 cells when compared with NCI-H157 cells.
Conclusions/significance: miR-21 simultaneously regulates multiple programs that enhance cell proliferation, apoptosis and tumor invasiveness by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2 in GSQCLC. Our results demonstrated that miR-21 may play a vital role in tumorigenesis and progression of lung squamous cell carcinoma and suppression of miR-21 may be a novel approach for the treatment of lung squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
 nucleolus,
nucleolus,  mitochondria,
mitochondria,  karyotheca,
karyotheca,  high density chromatin,
high density chromatin,  apoptotic body,
apoptotic body,  cell vacuolation.
cell vacuolation.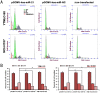
Similar articles
-
Effects and mechanism of microRNA‑218 against lung cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jan;23(1):28. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11666. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33179084 Free PMC article.
-
Icariin regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of human ovarian cancer cells through microRNA-21 by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2.Oncol Rep. 2015 Jun;33(6):2829-36. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3891. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25845681
-
MiR-590-5p regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting RECK.Histol Histopathol. 2021 Mar;36(3):355-365. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-306. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Histol Histopathol. 2021. PMID: 33447989
-
MiR-132 promotes the proliferation, invasion and migration of human pancreatic carcinoma by inhibition of the tumor suppressor gene PTEN.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019 Nov;148:65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.09.019. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 28941804 Review.
-
A Comprehensive Study on Signal Transduction and Therapeutic Role of miR-877 in Human Cancers.Adv Biomed Res. 2023 May 15;12:118. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_412_21. eCollection 2023. Adv Biomed Res. 2023. PMID: 37434921 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Direct repression of the oncogene CDK4 by the tumor suppressor miR-486-5p in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 7;7(23):34011-21. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8514. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27049724 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNAs in Tumor Radioresistance.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 28;12(11):1586. doi: 10.3390/biom12111586. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic Circular miR-21 Sponge as Tool for Lung Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 9;23(6):2963. doi: 10.3390/ijms23062963. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328383 Free PMC article.
-
Micro-RNA 205-5p is Involved in the Progression of Gastric Cancer and Targets Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN) in SGC-7901 Human Gastric Cancer Cells.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Aug 24;25:6367-6377. doi: 10.12659/MSM.915970. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31444971 Free PMC article.
-
R. nukuhivensis acts by reinforcing skin barrier function, boosting skin immunity and by inhibiting IL-22 induced keratinocyte hyperproliferation.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 11;9(1):4132. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39831-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30858525 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gompelmann D, Eberhardt R, Herth FJ (2011) Advanced malignant lung disease: what the specialist can offer. Respiration 2: 111–123. - PubMed
-
- Mark RK, Matthew AF, Scott AB, Karen EM, Albert BJ, et al. (2011) ProvenCare Lung Cancer: A Multi-Institutional Improvement Collaborative. CA Cancer J Clin 61: 382–396. - PubMed
-
- Duan JJ, Chen WQ, Zhang SW (2009) International Comparison of Malignant Tumor Mortality. Chin J Social Medicine 26: 377–378.
-
- Ruan YH (2005) Detection of related Genetic Alterations in Lung Cancer among Yunnan Tin Miners and study on an Animal Model of Lung Cancer with Yunnan Tin Miners Dust in F344 Rats. Kunming: Kunming Medical University, Yunnan, China 1–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

