Crosstalk between muscularis macrophages and enteric neurons regulates gastrointestinal motility
- PMID: 25036630
- PMCID: PMC4149228
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.050
Crosstalk between muscularis macrophages and enteric neurons regulates gastrointestinal motility
Erratum in
- Cell. 2014 Aug 28;158(5):1210. Dosage error in article text
Abstract
Intestinal peristalsis is a dynamic physiologic process influenced by dietary and microbial changes. It is tightly regulated by complex cellular interactions; however, our understanding of these controls is incomplete. A distinct population of macrophages is distributed in the intestinal muscularis externa. We demonstrate that, in the steady state, muscularis macrophages regulate peristaltic activity of the colon. They change the pattern of smooth muscle contractions by secreting bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2), which activates BMP receptor (BMPR) expressed by enteric neurons. Enteric neurons, in turn, secrete colony stimulatory factor 1 (CSF1), a growth factor required for macrophage development. Finally, stimuli from microbial commensals regulate BMP2 expression by macrophages and CSF1 expression by enteric neurons. Our findings identify a plastic, microbiota-driven crosstalk between muscularis macrophages and enteric neurons that controls gastrointestinal motility. PAPERFLICK:
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
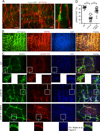
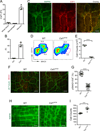
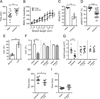
Comment in
-
Macrophages have a grip on the gut.Immunity. 2014 Jul 17;41(1):11-3. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.07.002. Immunity. 2014. PMID: 25035949
-
GI motility: microbiota and macrophages join forces.Cell. 2014 Jul 17;158(2):239-240. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.040. Cell. 2014. PMID: 25036623
Similar articles
-
Chronic Electroacupuncture With High-Frequency at ST-36 Promotes Gastrointestinal Motility by Regulating Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 Secretion of Muscularis Macrophages.Neuromodulation. 2024 Feb;27(2):321-332. doi: 10.1016/j.neurom.2023.03.013. Epub 2023 May 26. Neuromodulation. 2024. PMID: 37245142
-
Macrophages regulate gastrointestinal motility through complement component 1q.Elife. 2023 Apr 26;12:e78558. doi: 10.7554/eLife.78558. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37159507 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of gut microbiota in the association between gastrointestinal motility and 5‑HT expression/M2 macrophage abundance in the gastrointestinal tract.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Sep;16(3):3482-3488. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6955. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28714029
-
Muscularis macrophages: Key players in intestinal homeostasis and disease.Cell Immunol. 2018 Aug;330:142-150. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.12.009. Epub 2017 Dec 26. Cell Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29291892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mentation on the immunological modulation of gastrointestinal motility.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2008 May;20 Suppl 1:81-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2008.01105.x. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2008. PMID: 18402645 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Macrophages in the Development and Treatment of Gut Inflammation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 2;9:625423. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.625423. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33738283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Microbiota and the Immune System on the Development and Organization of the Enteric Nervous System.Gastroenterology. 2016 Nov;151(5):836-844. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.07.044. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 27521479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic sclerosis gastrointestinal dysmotility: risk factors, pathophysiology, diagnosis and management.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023 Mar;19(3):166-181. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00900-6. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36747090 Review.
-
Neuroimmune Communication in Health and Disease.Physiol Rev. 2018 Oct 1;98(4):2287-2316. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00035.2017. Physiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 30109819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-Like Receptor 7 Agonist-Induced Dermatitis Causes Severe Dextran Sulfate Sodium Colitis by Altering the Gut Microbiome and Immune Cells.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Sep 25;7(1):135-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.09.010. eCollection 2019. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30510995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aberle H, Haghighi AP, Fetter RD, McCabe BD, Magalhaes TR, Goodman CS. wishful thinking encodes a BMP type II receptor that regulates synaptic growth in Drosophila. Neuron. 2002;33:545–558. - PubMed
-
- Abrams GD, Bishop JE. Effect of the normal microbial flora on gastrointestinal motility. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967;126:301–304. - PubMed
-
- Boeckxstaens GE, de Jonge WJ. Neuroimmune mechanisms in postoperative ileus. Gut. 2009;58:1300–1311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21-AI105047/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI104848/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS015547/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK093786/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA32551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI09561/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI095611/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013330/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA173861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI105047/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI104848/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA173861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA032551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

